Early Embryonic Development part 1
Summary
TLDRThe transcript discusses the rapid cell division in early-stage embryo development, particularly in species like frogs and drosophila. It compares the speed and nature of mitosis in these embryos to normal eukaryotic cells, explaining that early embryos lack the G1 and G2 phases, allowing faster cell division. Key proteins like cyclins and their role in regulating the cell cycle are explored, highlighting how their availability affects mitosis. The process slows as embryos mature, transitioning to a more typical cell cycle with all phases involved. This acceleration and transition process are critical for embryonic development.
Takeaways
- 😀 The process of cell division during early embryo development is rapid, as evidenced by the rapid division of frog and Drosophila embryos.
- 😀 The early embryonic cell cycle lacks the G1 and G2 phases, which are typically present in normal eukaryotic cells, leading to faster division without prior growth.
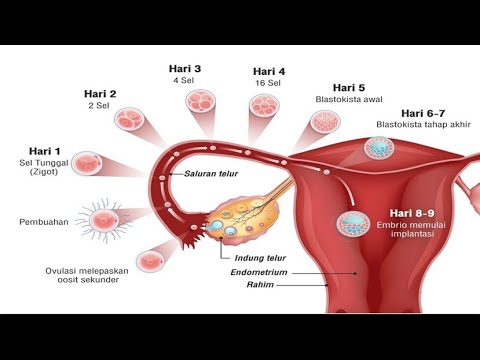
- 😀 In the early stages of embryonic development, cells undergo rapid division, forming thousands of cells in a short time (e.g., 37,000 cells in 43 hours in frogs).
- 😀 The cell cycle in normal eukaryotic cells consists of four phases: G1 (growth), S (DNA synthesis), G2 (preparation for mitosis), and M (mitosis).
- 😀 The presence of cyclins, especially Cyclin B, and CDK1 proteins regulates the cell cycle, activating M-phase promoting factor (MPF) to trigger mitosis.
- 😀 In early-stage embryos, resources like proteins, ribosomes, and RNA are already present in the egg cell, allowing for rapid cell division without requiring growth before mitosis.
- 😀 The differences between normal eukaryotic cell cycles and early-stage embryo cycles are the absence of growth phases (G1 and G2) in embryos, speeding up the process.
- 😀 Cyclin levels rise and fall during the cell cycle; high cyclin concentrations promote the activation of MPF, leading to mitosis, while low cyclin levels signal the end of mitosis and the entry into the interphase.
- 😀 In Drosophila embryos, a gene called 'gstring' is involved in activating MPF, which plays a critical role in regulating the rapid division of cells during early development.
- 😀 The transition from a rapid cell division phase to a slower, more typical cycle occurs after several rounds of mitosis, with the reintroduction of G1 and G2 phases, called the 'amit-blastula transition'.
Q & A
What happens when the male and female pronuclei fuse in embryonic development?
-When the male and female pronuclei fuse, they form a zygote, which marks the beginning of the embryo's development and initiates rapid cell division.
How does the rate of cell division in early embryonic development compare to normal eukaryotic cells?
-In early embryonic development, cell division occurs at a much faster rate. For example, a frog embryo can produce 37,000 cells in 43 hours, while a typical eukaryotic cell takes about 24 hours for one cell division.
What are the main phases of the cell cycle in typical eukaryotic cells?
-In typical eukaryotic cells, the cell cycle consists of four phases: G1 (growth), S (DNA synthesis), G2 (growth), and M (mitosis).
Why do early embryonic cells divide more rapidly than normal eukaryotic cells?
-Early embryonic cells divide more rapidly because they lack the G1 and G2 phases, meaning they skip the growth stages and go straight from DNA replication (S-phase) to mitosis (M-phase). This allows for faster division.
What molecules regulate the cell cycle in eukaryotic cells?
-The cell cycle is regulated by cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases (CDK1). Cyclins bind to CDK1, activating it and promoting progression through the cell cycle.
How does the presence of cyclins affect the cell cycle in embryos?
-In early embryonic development, cyclins are present in sufficient amounts, which allows for rapid progression through the cell cycle, particularly the transition from S-phase to mitosis, without the need for growth phases.
What is the role of cyclin B in regulating the cell cycle during mitosis?
-Cyclin B binds to CDK1 to activate it, which allows the cell to proceed into mitosis. After mitosis, cyclin B is degraded, inactivating CDK1 and signaling the cell to enter the next phase.
What is the significance of the 'mitotic blastula transition' (MBT) in embryonic development?
-The MBT is a key point in embryonic development when the cell cycle transitions from rapid mitotic divisions (which lack G1 and G2 phases) to a more typical cycle that includes growth phases, marking the slowdown of cell division.
What role does the availability of resources play in early embryo development?
-In early embryo development, resources like proteins, ribosomes, and mRNA are already present in the egg in sufficient amounts, allowing rapid division. In contrast, typical eukaryotic cells must first synthesize these resources before dividing.
How does the embryo cell cycle change after the 13th cell division in Drosophila embryos?
-After the 13th cell cycle in Drosophila embryos, the amount of cyclin starts to decrease, leading to slower cell division. This is part of the transition from rapid mitotic divisions to a more typical cell cycle with G1 and G2 phases reintroduced.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тариф5.0 / 5 (0 votes)