PRINSIP KELISTRIKAN DAN SISTEM INSTALASI LISTRIK ~ MATERI PRAKARYA KELAS 9 BAB 2
Summary
TLDRIn this educational video, the topic of electrical principles and electrical installation systems for 9th-grade students is covered. The video explains the basic concepts of electricity, including the nature of electric charge, current, and voltage. It further explores different types of electrical current, such as direct current (DC) and alternating current (AC), as well as their practical uses. The video also discusses various power plants like hydropower, nuclear, geothermal, solar, and wind energy, explaining how each generates electricity. The importance of electricity in daily life is emphasized, highlighting its role in powering devices and improving efficiency in activities.
Takeaways
- 😀 Electricity is the technology that has revolutionized human life by overcoming distance and time, making daily activities easier and more efficient.
- 😀 Despite widespread use of electricity, some remote areas in Indonesia remain without access, often due to cultural beliefs and traditional lifestyles.
- 😀 Electricity is the result of the movement of charged particles, with two types of charges: negative (excess electrons) and positive (deficit of electrons).
- 😀 The direction of electric current is traditionally from positive to negative, although electrons (negative charge) actually move in conductors.
- 😀 There are two main types of electric current: DC (Direct Current) which flows in one direction, and AC (Alternating Current) which changes direction continuously.
- 😀 DC is used in devices like batteries, handphones, and power banks, while AC powers most household appliances like refrigerators, washing machines, and fans.
- 😀 Electric current plays a crucial role in powering devices for daily activities such as lighting, cooking, and communication.
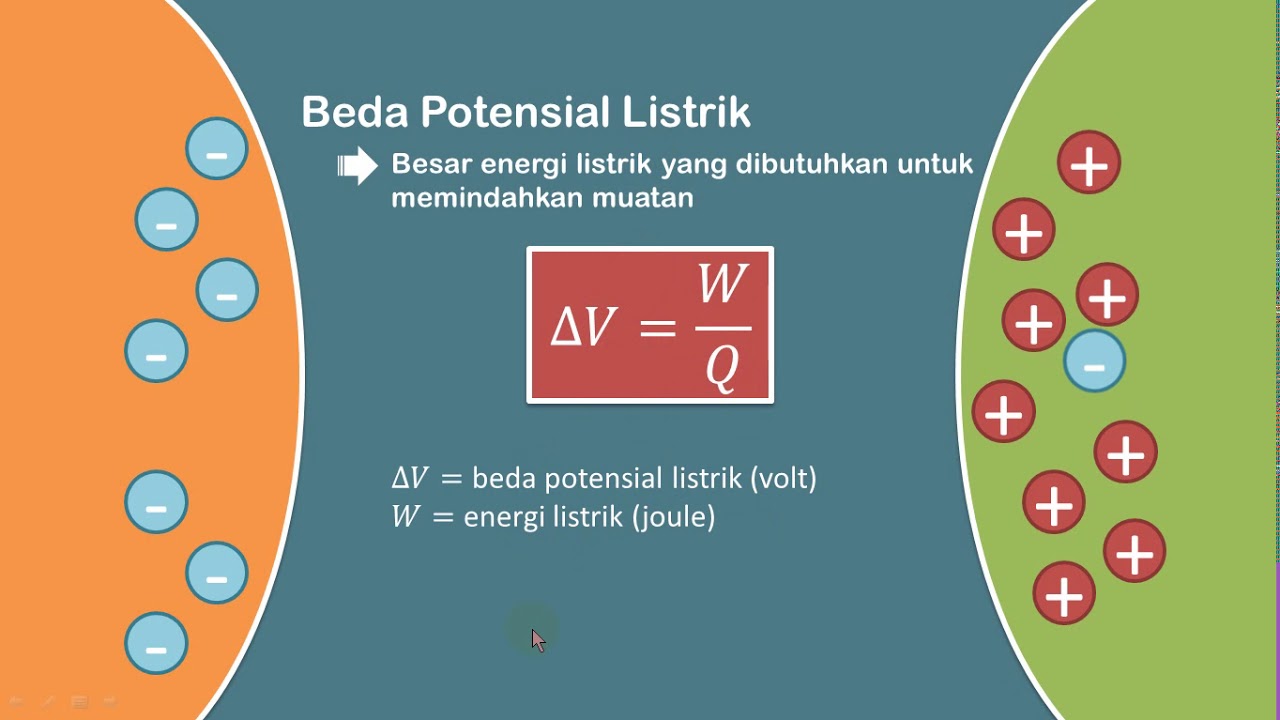
- 😀 Key concepts of electricity include charge (muatan listrik), electric field (medan listrik), electric potential (potensial listrik), electric current (arus listrik), and electromagnetism (elektromagnet).
- 😀 Electricity can be generated in various ways, with power plants that convert other forms of energy into electricity, such as gas, wind, water, solar, geothermal, and nuclear energy.
- 😀 Different types of power plants have their own strengths and limitations, and they include gas, hydropower, coal, nuclear, geothermal, solar, and wind energy plants.
Q & A
What is the main focus of the video discussed in the transcript?
-The main focus of the video is to explain the principles of electricity and electrical installation systems, specifically in relation to a craft and technology class for 9th-grade students.
What is the definition of electricity provided in the video?
-Electricity is defined as the property of materials that arises from the presence of electric charges, which can be either negative or positive.
What are the two types of electrical charges mentioned?
-The two types of electrical charges mentioned are negative charge (excess electrons) and positive charge (lack of electrons).
What is the difference between Direct Current (DC) and Alternating Current (AC)?
-Direct Current (DC) is an electrical current that flows in one direction, while Alternating Current (AC) is a current where the flow of electrons changes direction periodically.
Can you give examples of devices that use DC and AC electricity?
-Examples of devices that use DC electricity include phones, remote controls, and power banks. Devices that use AC electricity include televisions, refrigerators, and air conditioners.
What is the significance of electricity in daily life, according to the video?
-Electricity is crucial for modern living as it powers devices and systems that make daily activities more efficient and convenient, such as lighting, electronics, and energy sources.
What is the function of an electromagnet?
-An electromagnet is a device that generates a magnetic field by moving electric charge, often used in various electrical devices to generate and interact with magnetic fields.
What are the different types of power plants mentioned in the video?
-The types of power plants mentioned are gas power plants (PLTG), hydroelectric power plants (PLTB), steam power plants (PLTU), nuclear power plants (PLTN), geothermal power plants (PLTP), solar power plants (PLTS), and wind power plants (PLTA).
What is the principle behind a hydroelectric power plant (PLTB)?
-A hydroelectric power plant generates electricity by converting the potential and kinetic energy of water into electrical energy, typically using a turbine connected to a generator.
Why is solar energy considered renewable and how is it harnessed?
-Solar energy is considered renewable because it is derived from sunlight, a natural resource that is abundant and not depleted by use. It is harnessed through solar panels that convert sunlight into electricity.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифПосмотреть больше похожих видео

Prinsip Kelistrikan dan Sistem Instalasi Listrik || Prakarya Kelas IX Semester 1
IPA Kelas 9 : Listrik Statis IV (Potensial Listrik dan Energi Listrik)

RAF Modul5 ILB

BAB 4 LISTRIK, MAGNET DAN SUMBER ENERGI ALTERNATIF - PART 2 (IPA Kelas 9 Kurikulum Merdeka)

KELISTRIKAN PART 1: LISTRIK STATIS (IPA KELAS 9 SMP)

SOAL LATIHAN BAB 4 LISTRIK MAGNET DAN SUMBER ENERGI ALTERNATIF (IPA Kelas 9 Kurikulum Merdeka)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
