Dasar-Dasar EKG (Prinsip EKG) : #1 ELEKTROKARDIOGRAM
Summary
TLDRThis video provides an insightful introduction to electrocardiograms (EKG), explaining its role in recording the heart's electrical activity. Key concepts covered include the conduction pathway from the sinoatrial (SA) node to the ventricles, and the different components of an EKG, such as the P wave, QRS complex, and T wave. The script also covers electrode placement for both extremity and precordial leads and offers a detailed explanation of the EKG reading speed and interpretation. With practical demonstrations, it provides a comprehensive understanding of EKG's fundamentals and its clinical relevance in diagnosing heart conditions.
Takeaways
- 😀 The script discusses the basics of Electrocardiogram (ECG), an essential tool for recording the electrical activity of the heart.
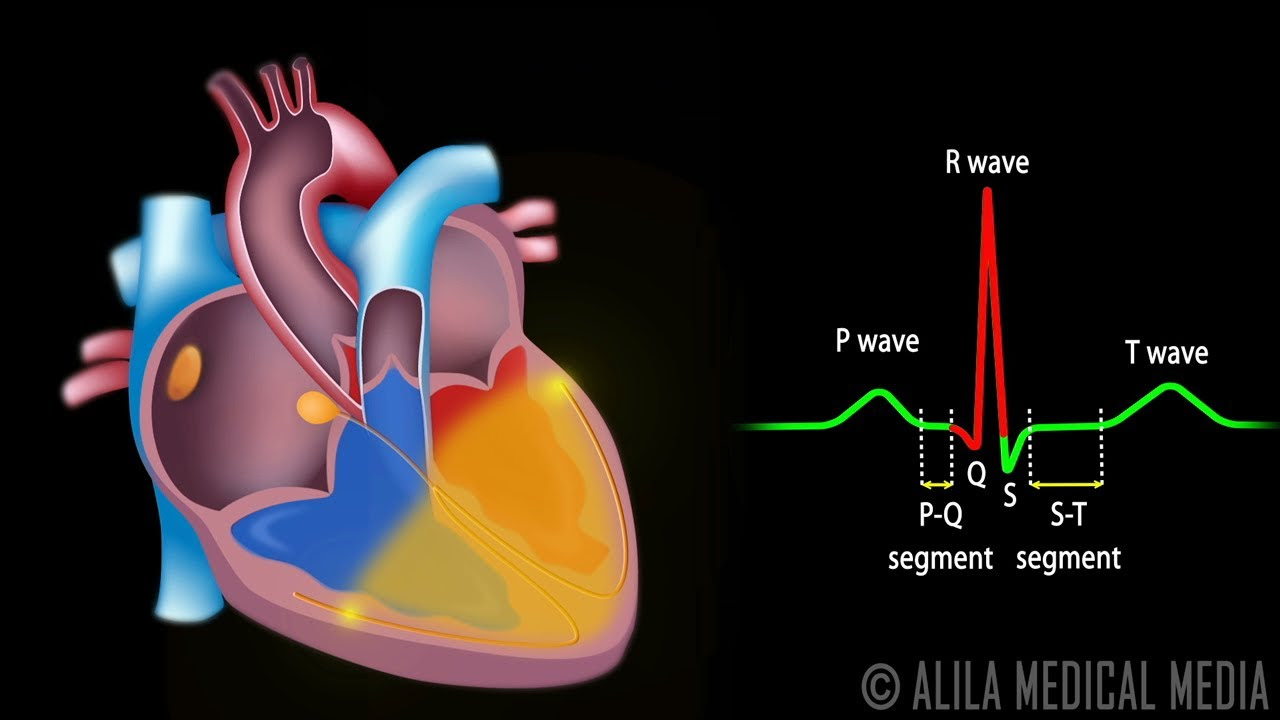
- 😀 The heart's electrical conduction system begins with the Sinoatrial (SA) node, which triggers atrial depolarization, represented by the P-wave on the ECG.
- 😀 The impulse from the SA node travels to the Atrioventricular (AV) node, causing an isoelectric phase on the ECG.
- 😀 After passing through the AV node, the electrical impulse travels through the Bundle of His and branches into the right and left bundles, leading to ventricular depolarization, shown as the QRS complex.
- 😀 The ECG waveform consists of several key components: P-wave (atrial depolarization), PR interval (time from atrial to ventricular depolarization), QRS complex (ventricular depolarization), QT interval (total depolarization and repolarization of ventricles), and T-wave (ventricular repolarization).
- 😀 The script emphasizes the importance of proper electrode placement for accurate ECG readings, such as using red for the right arm, yellow for the left arm, green for the left leg, and black for the right leg.
- 😀 Correct placement of precordial leads (V1-V6) is also crucial for accurate ECG interpretation, with V1 placed at the 4th intercostal space along the parasternal line and V2-V6 following specific positions.
- 😀 ECG paper speed is typically 25 mm per second, with each small square on the paper representing 0.04 seconds, and each millimeter of vertical height representing 0.1 millivolts.
- 😀 The script explains the use of different leads (e.g., I, II, III for extremity leads, and V1-V6 for precordial leads) to assess various parts of the heart, such as the septal, anterior, and lateral regions.
- 😀 It also highlights that the optimal view of the heart's electrical activity is often provided by lead II, which gives the clearest representation of the heart's rhythm.
- 😀 The session concludes with a brief overview of ECG components and their significance in diagnosing heart conditions, with a call to support the channel for more educational content.
Q & A
What is an electrocardiogram (ECG) and its main purpose?
-An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a medical tool used to record the electrical activity of the heart. Its main purpose is to measure the heart's electrical signals and help detect any abnormal heart rhythms or other cardiac issues.
What are the key principles behind reading an EKG?
-The key principles behind reading an EKG include understanding the conduction pathway of the heart's electrical signals, such as the role of the sinoatrial (SA) node, atrioventricular (AV) node, His bundle, and Purkinje fibers. These components contribute to the different phases seen on the EKG, including the P wave, QRS complex, and T wave.
What is the significance of the P wave in an EKG?
-The P wave in an EKG represents atrial depolarization. It occurs when the electrical impulse from the sinoatrial (SA) node travels through the atria, causing them to contract.
What does the PR interval indicate in an EKG reading?
-The PR interval reflects the period between the start of atrial depolarization (indicated by the P wave) and the beginning of ventricular depolarization. It shows how long it takes for the electrical signal to travel through the AV node and reach the ventricles.
How is ventricular depolarization represented in an EKG?
-Ventricular depolarization is represented by the QRS complex in an EKG. This complex shows the electrical activity as the impulse moves through the His bundle and into the ventricles, causing them to contract.
What is the QT interval, and why is it important?
-The QT interval represents the total time it takes for both depolarization and repolarization of the ventricles to occur. It is important because abnormal QT intervals can indicate issues such as arrhythmias or other heart problems.
What are the different leads used in EKG and their functions?
-In an EKG, there are two types of leads: extremity leads (I, II, III, aVR, aVL, and aVF) and precordial (chest) leads (V1-V6). Extremity leads monitor the heart's electrical activity from different angles, while precordial leads focus on specific areas of the heart, such as the septal, anterior, lateral, and inferior regions.
Where should the EKG electrodes be placed on the body?
-For extremity leads, electrodes should be placed on the right arm (red), left arm (yellow), right leg (black), and left leg (green). For precordial leads, electrodes should be placed on the chest at specific locations: V1 at the 4th intercostal space along the parasternal line, V2 at the 4th intercostal space along the parasternal line, V3 between V2 and V4, V4 at the 5th intercostal space along the midclavicular line, V5 at the 5th intercostal space along the anterior axillary line, and V6 at the 5th intercostal space along the midaxillary line.
What does the 'isoelectric' segment on an EKG indicate?
-An isoelectric segment on an EKG refers to a flat line, typically seen between the end of the P wave and the beginning of the QRS complex. This segment represents the period when no electrical activity is detected, such as the time between atrial and ventricular depolarization.
How is the heart's electrical conduction pathway described in an EKG?
-The heart's electrical conduction pathway begins with the sinoatrial (SA) node, which initiates the electrical impulse. This impulse travels to the atrioventricular (AV) node, then through the His bundle, and finally into the left and right bundle branches and Purkinje fibers, resulting in ventricular depolarization and contraction. This pathway creates the distinct waveforms seen on the EKG.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тариф5.0 / 5 (0 votes)