DNA | Ácidos Nucleicos - Brasil Escola
Summary
TLDRIn this engaging biology lesson, Professor Fred explains the structure and significance of DNA, the molecule that carries genetic information. He discusses how DNA is composed of nucleotides made up of phosphate groups, deoxyribose sugar, and nitrogenous bases (adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine). The professor also covers the bonding of bases, forming a double helix structure, and provides interesting facts, like how human DNA shares 95% similarity with chimpanzees and 65% with bananas. He emphasizes that only 1% of the DNA varies between individuals, highlighting the uniqueness of each person. The video ends with fun facts and invites viewers to subscribe.
Takeaways
- 😀 DNA is the most important genetic material in our bodies, carrying the information for our traits through genes.
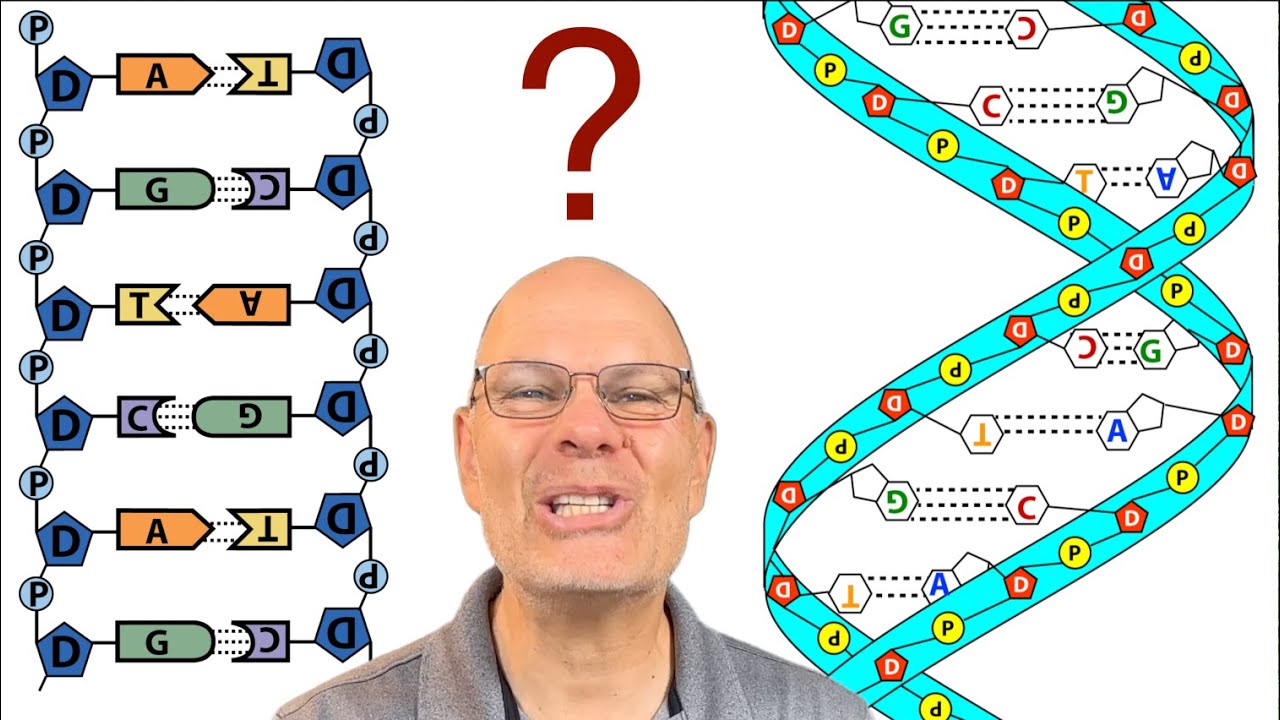
- 😀 DNA consists of nucleotides made up of three components: phosphate group, sugar (deoxyribose), and nitrogenous bases.
- 😀 There are four main nitrogenous bases in DNA: adenine (A), thymine (T), cytosine (C), and guanine (G).
- 😀 Adenine pairs with thymine, and cytosine pairs with guanine, forming hydrogen bonds between complementary bases.
- 😀 DNA forms a double helix structure due to the hydrogen bonds between its nucleotide pairs.
- 😀 The acronym DNA stands for 'Deoxyribonucleic Acid' (Acido Desoxirribonucleico in Portuguese).
- 😀 DNA can be classified into purines (adenine, guanine) and pyrimidines (cytosine, thymine).
- 😀 1 gram of DNA can store up to 215 million gigabytes of information, making it an incredibly efficient data storage system.
- 😀 Human DNA shares approximately 65% of its sequence with banana DNA and 95% with chimpanzee DNA.
- 😀 99% of human DNA is compatible with that of any other person, with unique genetic differences accounting for less than 1%.
- 😀 The total genetic material in a 65kg person weighs about 200 grams, despite every cell containing DNA.
Q & A
What is the main focus of the video?
-The video primarily focuses on explaining the structure of DNA and its role as the genetic material in organisms.
What are genes and how are they related to DNA?
-Genes are sections of DNA that carry the information for specific characteristics or traits of an organism. DNA is composed of many genes, which ultimately express those traits.
What are nucleotides and what components make them up?
-Nucleotides are the building blocks of DNA. Each nucleotide is made up of three components: a phosphate group, a sugar (deoxyribose in DNA), and a nitrogenous base.
What is the significance of the nitrogenous bases in DNA?
-The nitrogenous bases in DNA (adenine, thymine, cytosine, and guanine) pair in a specific way: adenine pairs with thymine, and cytosine pairs with guanine, forming the rungs of the DNA helix.
What are the two categories of nitrogenous bases in DNA?
-The two categories are purines (adenine and guanine) and pyrimidines (cytosine and thymine).
How does the structure of DNA contribute to its function?
-The structure of DNA is a double helix, with two strands held together by hydrogen bonds between complementary bases. This structure allows for the storage of genetic information and its transmission during cell division.
What is the role of hydrogen bonds in DNA structure?
-Hydrogen bonds between complementary nitrogenous bases (two bonds between adenine and thymine, three bonds between cytosine and guanine) stabilize the double helix structure of DNA.
What is the molecular size of DNA and its potential for data storage?
-1 gram of DNA can store up to 215 million gigabytes (GB) of information, making it an incredibly dense form of data storage.
How similar is human DNA to other species?
-Human DNA shares about 65% similarity with banana DNA, and about 95% with chimpanzee DNA. This highlights the commonality of genetic material across different organisms.
What percentage of human DNA is identical to another person's DNA?
-99% of human DNA is identical to that of any other person, which shows the remarkable genetic similarity between individuals, with less than 1% accounting for individual differences.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тариф5.0 / 5 (0 votes)