Kultur Jaringan, Apa Faedahnya?
Summary
TLDRThis video explores the fascinating process of plant tissue culture, also known as micropropagation, a modern biotechnological method of plant cloning. The process involves manipulating plant tissues in aseptic conditions to create genetically identical plants, using techniques like sterilization, initiation, multiplication, and acclimatization. Unlike traditional farming, tissue culture allows rapid, large-scale plant propagation without requiring large land areas. It ensures high-quality, uniform plants, ideal for creating superior plant varieties. While humans and animals cannot be cloned this way, plant tissue culture offers significant advantages in agriculture and biotechnology.
Takeaways
- 😀 Plant tissue culture, also known as micropropagation, is a method of asexual plant reproduction in a sterile environment.
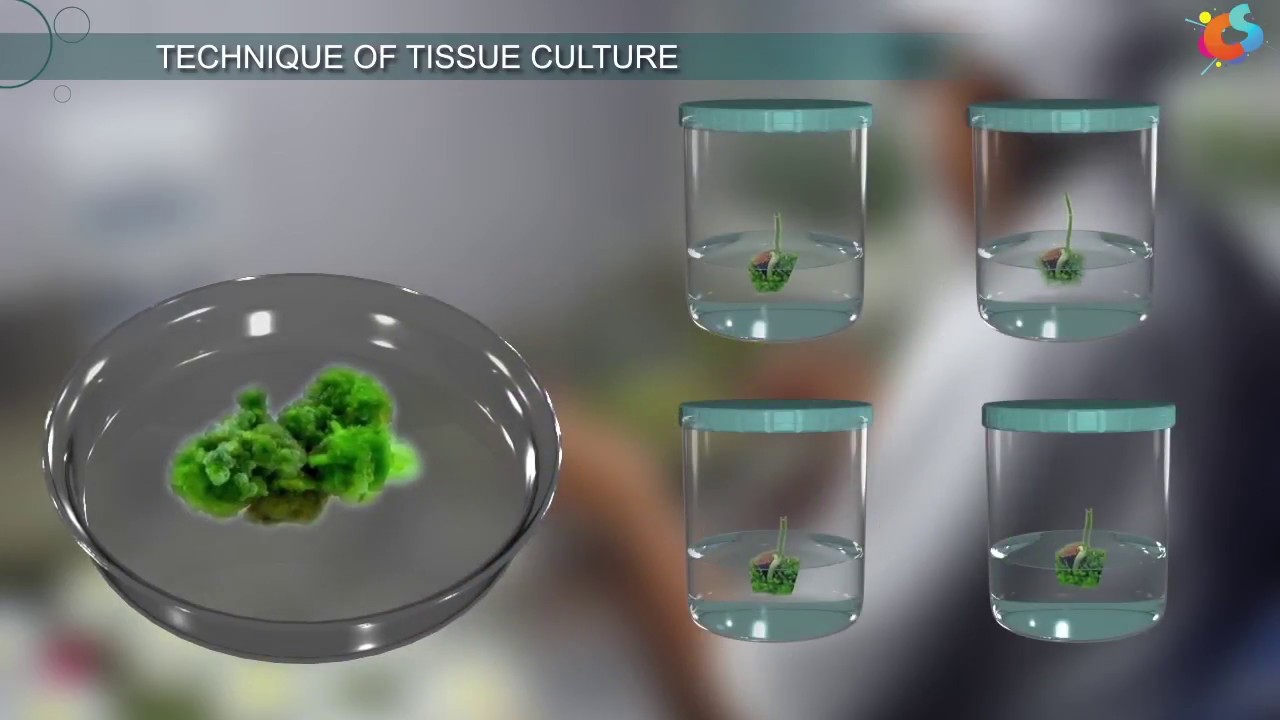
- 🌱 It involves manipulating parts of a plant to create genetically identical plants through a process that begins with selecting and sterilizing explants (small parts of the plant).
- 🔬 Tissue culture is an example of modern biotechnology, which differs from conventional biotechnology that relies on microorganisms.
- 🥡 An example of traditional biotechnology is tempeh, a food product made with fungi, which utilizes microbial fermentation.
- 🧬 The difference between conventional and modern biotechnology lies in the methods used; conventional biotechnology uses simple methods with microorganisms, while modern biotechnology uses more complex methods like genetic engineering.
- 🌿 Tissue culture has several stages, including media preparation, explant collection, callus formation, and acclimatization to environmental conditions.
- 🧫 Media for plant tissue culture includes agar, minerals, amino acids, vitamins, and plant growth hormones, and must be sterile to avoid contamination.
- 🌍 The explants used in tissue culture must come from parts of the plant with totipotency, such as root tips or stem tips, allowing them to develop into new plants.
- 🚀 Tissue culture is advantageous because it doesn't require large land areas, and it produces many genetically identical plants in a short period of time.
- 🌟 The plants created through tissue culture are genetically identical to their parent plants, ensuring uniform quality, especially if the parent plant is of a superior variety.
- 🐾 While human and animal cells also possess totipotency, they cannot regenerate into whole new individuals like plant cells, which limits tissue culture applications to plants.
Q & A
What is micropropagation in plant biotechnology?
-Micropropagation, also known as tissue culture, is a method of vegetative plant reproduction that involves manipulating plant tissue in aseptic conditions to produce new plants that are genetically identical to the parent plant.
What is totipotency in plants?
-Totipotency is the ability of plant cells to develop into a complete, mature plant. This characteristic is crucial in tissue culture because it allows specific plant cells, such as from roots or stems, to regenerate into new plants.
Why is aseptic technique important in tissue culture?
-Aseptic technique is essential in tissue culture to prevent contamination by microorganisms, which could hinder plant growth or result in failed propagation. Sterilizing both the plant tissue and the growth medium is necessary for success.
How does tissue culture differ from traditional plant propagation methods?
-Unlike traditional plant propagation, which involves planting seeds or cuttings, tissue culture uses a small piece of plant tissue (explant) and grows it in a controlled, sterile environment. This allows for rapid propagation and the creation of genetically identical plants.
What role does the growth medium play in tissue culture?
-The growth medium in tissue culture contains a mix of nutrients, vitamins, and growth regulators that are vital for the development and multiplication of plant cells. The medium provides the necessary conditions for plant tissue to grow and regenerate.
What is the purpose of the 'multiplication' stage in tissue culture?
-The multiplication stage involves growing and developing the plant tissue (explant) into a mass of undifferentiated cells called callus, which eventually differentiates into small plantlets. This process ensures the rapid production of many new plants from a single explant.
Why is it important to control environmental conditions in tissue culture?
-Environmental factors such as temperature, humidity, and light need to be carefully controlled to promote the optimal growth of the plant tissue and avoid stress or contamination. These conditions ensure that the plantlets develop correctly and quickly.
What happens during the 'acclimatization' phase of tissue culture?
-During the acclimatization phase, the plantlets are gradually adapted to outdoor conditions by being moved from the sterile laboratory environment to a greenhouse. This helps them adjust to natural sunlight, humidity, and air quality before being planted outside.
What are some benefits of using tissue culture for plant propagation?
-Tissue culture allows for the rapid production of large numbers of plants in a small space, ensures the plants are genetically identical to the parent, and is particularly useful for propagating superior or disease-free varieties.
Can tissue culture be applied to humans or animals?
-While human and animal cells also possess totipotency, they cannot be used in the same way as plant cells for cloning or regeneration of new individuals. Human and animal cells typically only form the tissues of the original body and cannot develop into whole organisms like plant cells can.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тариф5.0 / 5 (0 votes)