Newton’s Universal Gravitation vs Coulomb’s Law
Summary
TLDRIn this video, the presenter explores the similarities and differences between Newton's Law of Universal Gravitation and Coulomb's Law. Both laws follow an inverse square law, with forces proportional to the product of masses or charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them. The key difference lies in the nature of the forces: gravitational force is always attractive, while electrostatic force can be either attractive or repulsive. The video also highlights the significantly stronger electric force compared to gravitational force, as demonstrated through practical examples involving the Earth and Moon, as well as two electrons.
Takeaways
- 😀 Newton's Law of Universal Gravitation and Coulomb's Law are both inverse square laws, meaning the force is proportional to the product of two quantities and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
- 😀 Both laws describe conservative forces, meaning no energy is lost when these forces act, unlike friction.
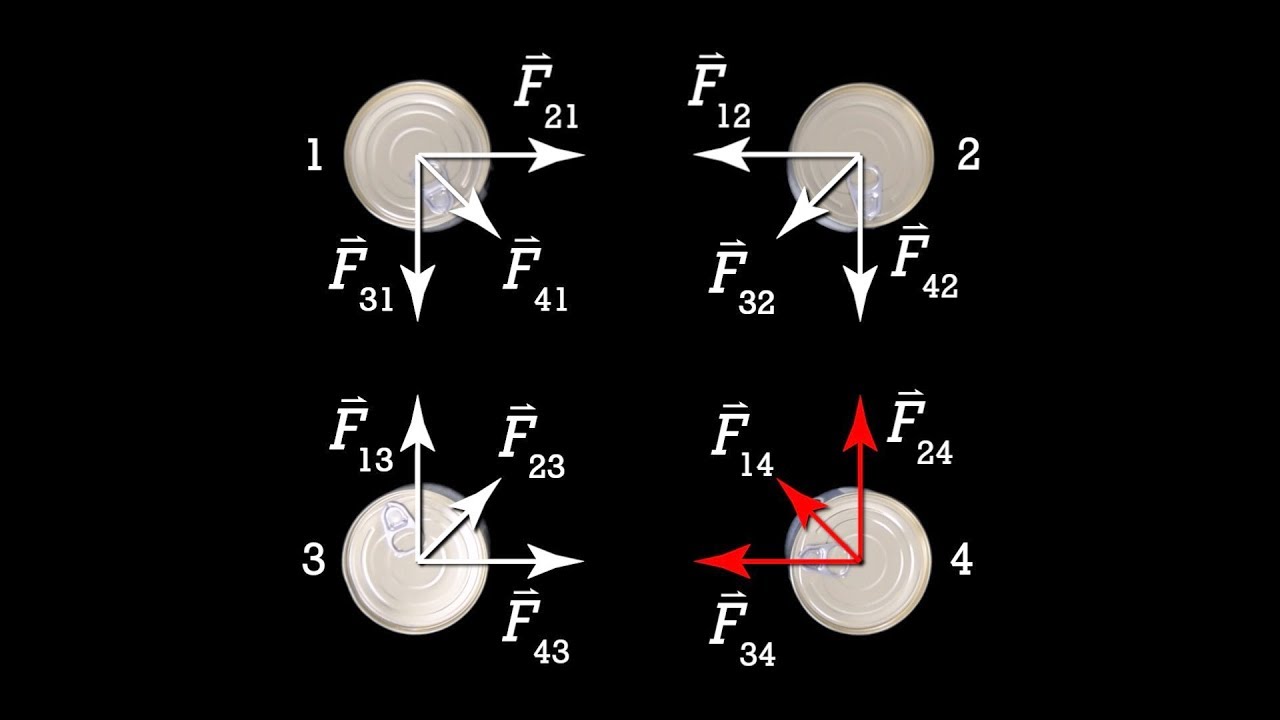
- 😀 The force in both Newton's Law and Coulomb's Law is equal in magnitude but opposite in direction for two interacting objects.
- 😀 Gravitational force is always attractive, while Coulomb's force can be either attractive or repulsive depending on the charges involved.
- 😀 The gravitational constant (G) is extremely small, making the gravitational force much weaker compared to the electrostatic force described by Coulomb's constant (k), which is very large.
- 😀 Gravitational force depends on the masses of the objects, while Coulomb's force depends on the charges of the objects.
- 😀 An example of gravitational force: The force between the Earth and the Moon is calculated using their masses and the distance between them.
- 😀 An example of Coulomb's force: The force between two electrons is calculated using their charges and the distance separating them.
- 😀 The electric force is 1.3 × 10²⁰ times stronger than the gravitational force, as shown by comparing forces for masses and charges of similar magnitude.
- 😀 Both laws require precise calculations involving constants (G for gravity, k for Coulomb's law) and distance measurements, with the distance being squared in both formulas.
Q & A
What is the primary focus of the video?
-The video aims to compare the similarities and differences between Newton's law of universal gravitation and Coulomb's law, highlighting how both equations describe forces between objects, with a focus on their similarities.
How does Newton's law of universal gravitation describe the force between masses?
-Newton's law of universal gravitation states that every mass attracts every other mass with a force directly proportional to the product of their masses and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them.
What is Coulomb's law and how does it differ from Newton's law?
-Coulomb's law describes the force between two charges, where like charges repel and opposite charges attract. The force is directly proportional to the product of the charges and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between them. The key difference from Newton's law is that Coulomb's law can involve both attractive and repulsive forces, while gravity is always attractive.
What are the key similarities between Newton's law and Coulomb's law?
-Both laws are inverse square laws, meaning the force is inversely proportional to the square of the distance between the objects. They also both have constants, and the force is directly proportional to the product of the respective properties—masses in gravity and charges in Coulomb's law.
What does 'inverse square law' mean in the context of these two forces?
-The 'inverse square law' means that the force decreases with the square of the distance between the objects. As the distance between them increases, the force decreases rapidly, specifically by the square of the distance.
What does the term 'conservative forces' refer to in this context?
-Both gravitational and electrostatic forces are considered conservative forces, meaning no energy is lost through friction or other dissipation mechanisms. The work done by these forces only depends on the initial and final positions of the objects, not the path taken.
How does the gravitational constant (G) compare to Coulomb's constant (k)?
-The gravitational constant (G) is very small, making gravitational forces much weaker compared to electrostatic forces. In contrast, Coulomb's constant (k) is very large, making the electrostatic force significantly stronger than the gravitational force.
Why is the electric force much stronger than the gravitational force?
-The electric force is much stronger than the gravitational force because Coulomb's constant is much larger than the gravitational constant. For example, when comparing forces between 1 kg masses and 1 coulomb charges, the electric force is 1.3 × 10^20 times greater.
What happens when two objects have like charges versus opposite charges in Coulomb's law?
-When two objects have like charges (both positive or both negative), they repel each other. When they have opposite charges (one positive, one negative), they attract each other.
What example did the video use to demonstrate the calculation of gravitational and electrostatic forces?
-The video used the example of two objects, one with a mass of 1 kg and the other with 1 coulomb charge, each separated by a distance of 1 meter, to calculate both gravitational and electrostatic forces. It compared the two forces to show how much stronger the electric force is than gravity.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифПосмотреть больше похожих видео
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)