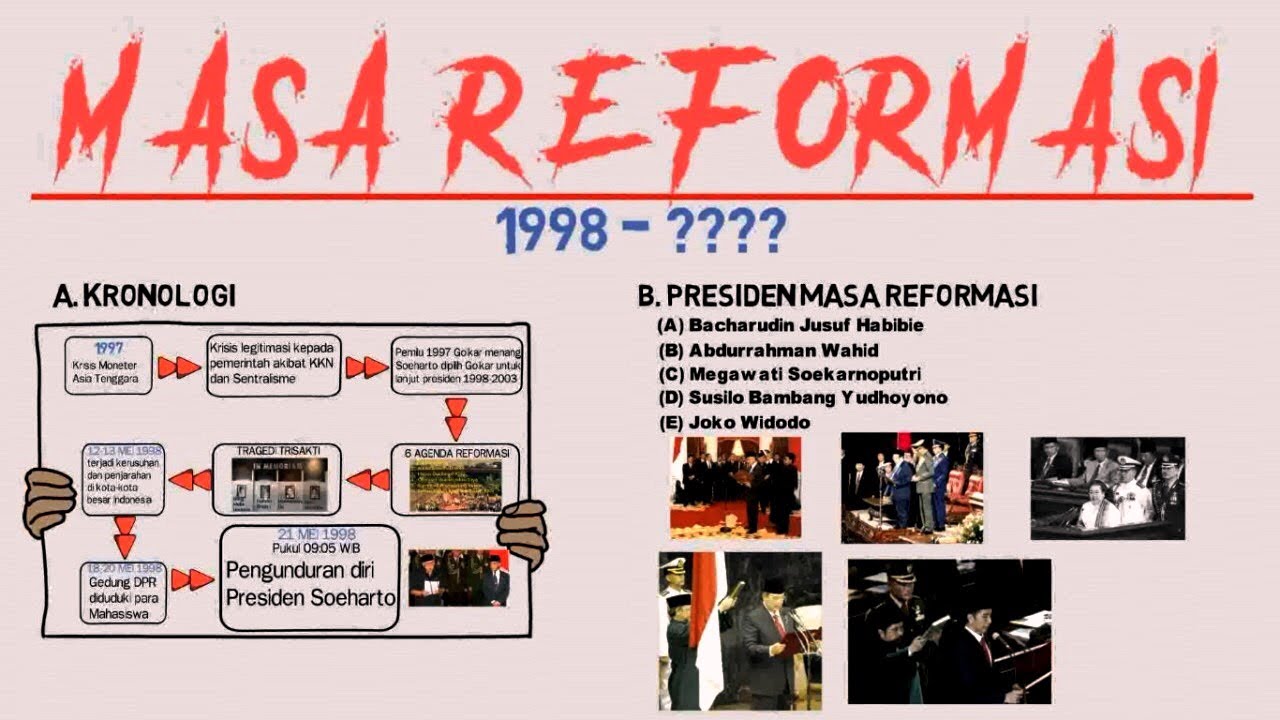
Masa Orde Reformasi: Masa Pemerintahan B.J. Habibie | Part 1
Summary
TLDRThis video provides an insightful overview of Indonesia's Reform Order era, which began in 1998 following President Soeharto's resignation and the rise of BJ Habibie. It covers key political and economic policies during Habibie's leadership, such as political reforms, the liberation of political prisoners, the acceleration of the 1999 elections, and the elimination of the dual-function of the Indonesian military. The video also discusses the economic crisis and the steps taken to stabilize the country. Finally, it highlights the end of Habibie's presidency and the election of Abdurrahman Wahid as the 4th President of Indonesia.
Takeaways
- 😀 The Reform Era in Indonesia began in 1998 with the appointment of President BJ Habibie after President Soeharto resigned, marking a significant shift from the New Order government.
- 😀 One of the key characteristics of the Reform Era was the political and economic reforms that aimed to address the issues of the New Order, including the multidimensional crisis Indonesia faced.
- 😀 BJ Habibie’s government implemented major political reforms, such as the release of political prisoners (Tapol and Napol) and the establishment of a more democratic political system.
- 😀 A significant political reform was the formation of the 'Reformation Development Cabinet' under BJ Habibie, contrasting with the previous cabinets of the New Order era.
- 😀 The 1999 general elections were a milestone as they were accelerated to just two years after the last elections of the New Order, and allowed a multi-party system, involving 48 political parties.
- 😀 The 1999 elections saw the rise of five major political parties, including the Indonesian Democratic Party of Struggle (PDI-P), Golkar, and the United Development Party (PPP), which had the most significant support.
- 😀 BJ Habibie’s presidency was marked by various MPR Decrees, including the amendments to the 1945 Constitution, which introduced term limits for the president and vice president, limiting their time in office to two terms or 10 years.
- 😀 BJ Habibie also initiated a referendum for East Timor in 1999, offering the people the choice of autonomy or independence. The majority (79%) voted for independence, leading to East Timor’s eventual secession from Indonesia.
- 😀 BJ Habibie’s economic policies included the liquidation of troubled banks caused by the 1997-1998 monetary crisis, conducting market operations to reduce inflation, and attempting to stabilize the Indonesian Rupiah’s value against the US Dollar.
- 😀 The end of BJ Habibie’s presidency came when the MPR rejected his accountability report in September 1999. This led to his decision not to run for re-election, and ultimately, Abdurrahman Wahid became the fourth president of Indonesia in October 1999.
Q & A
What marks the beginning of the Reform Order in Indonesia?
-The Reform Order in Indonesia began in 1998, following the resignation of President Soeharto on May 21st and the appointment of BJ Habibie as his successor.
What were the main political policies implemented by President BJ Habibie?
-BJ Habibie’s political policies included the release of political prisoners (TAPOL and NAPOL), the formation of the Reform Development Cabinet, the acceleration of the 1999 elections, and the establishment of MPR decrees that amended the Constitution, limited presidential terms, and eliminated Pancasila as the sole political ideology.
How did President BJ Habibie address the political crisis during the transition from the New Order regime?
-President BJ Habibie aimed to foster democratic reforms by holding a multi-party election in 1999, releasing political prisoners, and issuing various MPR decrees, such as limiting the presidential term to two terms and opening up the political space by eliminating the requirement for Pancasila as the sole political ideology.
How did the 1999 elections differ from previous elections under the New Order?
-The 1999 elections were the first to use a multi-party system, with 48 political parties participating, in contrast to the controlled party system of the New Order era.
What was the result of the 1999 referendum on East Timor?
-In the 1999 referendum on East Timor, 79% of the population voted for independence, while only 21% voted for special autonomy under Indonesia.
What were some key economic policies during BJ Habibie's presidency?
-BJ Habibie’s key economic policies included liquidating problematic banks, implementing market operations to reduce inflation, and working to improve the value of the Indonesian Rupiah.
What was the impact of BJ Habibie’s policies on the role of the military in politics?
-BJ Habibie took steps to reduce the military's political role by limiting the number of seats held by the military in the Indonesian Parliament, reflecting the desire to eliminate the military's dual function (Dwifungsi ABRI).
How did BJ Habibie address the demands for press freedom?
-BJ Habibie abolished the SIUPP (Press Publishing Permit), a tool previously used by the New Order regime to control media, in order to foster a more open and democratic press environment.
What were some of the critical MPR decrees passed during BJ Habibie’s administration?
-Important MPR decrees during BJ Habibie’s administration included TAP MPR No. 8/1998 (which amended the 1945 Constitution), TAP MPR No. 13/1998 (limiting presidential terms to two periods), and TAP MPR No. 18/1998 (allowing the use of multiple political ideologies).
What led to the end of BJ Habibie's presidency?
-BJ Habibie’s presidency ended when the MPR rejected his accountability report in September 1999. Following this, he chose not to run for re-election, and in October 1999, Abdurrahman Wahid was elected as the new President of Indonesia.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифПосмотреть больше похожих видео
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)