Constant-pressure calorimetry | Thermodynamics | AP Chemistry | Khan Academy
Summary
TLDRThe video introduces calorimetry, the measurement of heat flow, and demonstrates how a simple coffee cup calorimeter can be used for constant-pressure calorimetry. It explores the transfer of heat between a heated copper block and water, calculating the heat gained by water and lost by copper. The video explains key thermodynamic concepts, including the system, surroundings, and the universe, before diving into the concepts of exothermic and endothermic reactions. The video concludes with the relationship between heat transfer at constant pressure and the change in enthalpy, distinguishing between exothermic and endothermic processes.
Takeaways
- 😀 Calorimetry is the process of measuring heat flow, and a calorimeter is a device used for this purpose.
- 😀 A simple calorimeter can be made using two coffee cups, with one acting as a loose-fitting lid, exposed to atmospheric pressure.
- 😀 The calorimeter can be used for constant-pressure calorimetry, where heat flow is measured at constant pressure.
- 😀 The heat gained by the water in the calorimeter can be calculated using the equation q = mcΔT, where m is mass, c is specific heat, and ΔT is the temperature change.
- 😀 Example calculation: 150 grams of water gains 3.1 × 10³ joules of energy, raising the temperature from 25°C to 30°C.
- 😀 The heat lost by the copper block in the calorimeter can also be calculated using the same equation. In this case, 120 grams of copper loses 3.3 × 10³ joules of energy.
- 😀 The energy transfer between copper and water isn't perfect; some heat may be lost to the environment, causing a discrepancy in the heat gained and lost.
- 😀 The system in thermodynamics refers to the part of the universe being studied, such as the reactants and products in a chemical reaction.
- 😀 The surroundings include everything else, such as the water in the calorimeter, the coffee cup, and the environment outside.
- 😀 For a chemical reaction, if heat is released, it flows from the system to the surroundings, causing an increase in the water's temperature (exothermic reaction).
- 😀 In an endothermic reaction, heat flows from the surroundings to the system, leading to a decrease in the water's temperature as energy is absorbed by the system.
Q & A
What is calorimetry?
-Calorimetry refers to the measurement of heat flow, typically to determine the heat transferred during physical or chemical processes.
How is a simple calorimeter made?
-A simple calorimeter can be made using two coffee cups, with one acting as a container and the other as a loose-fitting lid, allowing exposure to constant atmospheric pressure.
What is the purpose of the thermometer in the calorimeter?
-The thermometer is used to measure the temperature change of the water, allowing for the calculation of the heat gained or lost during the experiment.
What are the key components of the calorimeter in the script?
-The key components of the calorimeter are two coffee cups, water, a stir bar, and a thermometer.
What does a positive heat value for water indicate?
-A positive heat value for water indicates that the water has gained heat during the experiment.
How do you calculate the heat gained by the water in the calorimeter?
-The heat gained by the water is calculated using the equation q = mcΔT, where 'm' is the mass of the water, 'c' is the specific heat of water, and ΔT is the change in temperature.
Why does the temperature of the water increase when copper is added?
-The temperature of the water increases because the copper block is initially at a higher temperature, and heat flows from the copper to the water until thermal equilibrium is reached.
Why are the heat values for the water and copper not exactly the same in the experiment?
-The heat values are not exactly the same because some energy may have been lost to the surroundings, suggesting that the calorimeter is not a perfect insulator.
What does a negative heat value for copper signify?
-A negative heat value for copper indicates that the copper has lost energy during the process, transferring heat to the water.
What is the relationship between heat transfer and the enthalpy change (ΔH) in a constant-pressure calorimeter?
-In constant-pressure calorimetry, the heat transfer is equivalent to the change in enthalpy (ΔH). If heat is lost by the system, ΔH is negative (exothermic reaction), and if heat is absorbed by the system, ΔH is positive (endothermic reaction).
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифПосмотреть больше похожих видео

Heat Capacity, Specific Heat, and Calorimetry

PRAKTIKUM PENENTUAN PERUBAHAN ENTALPI REAKSI PENETRALAN

KALORIMETER : Menghitung Perubahan Entalpi dengan Kalorimetri - Kimia kelas XI
Calorimetry
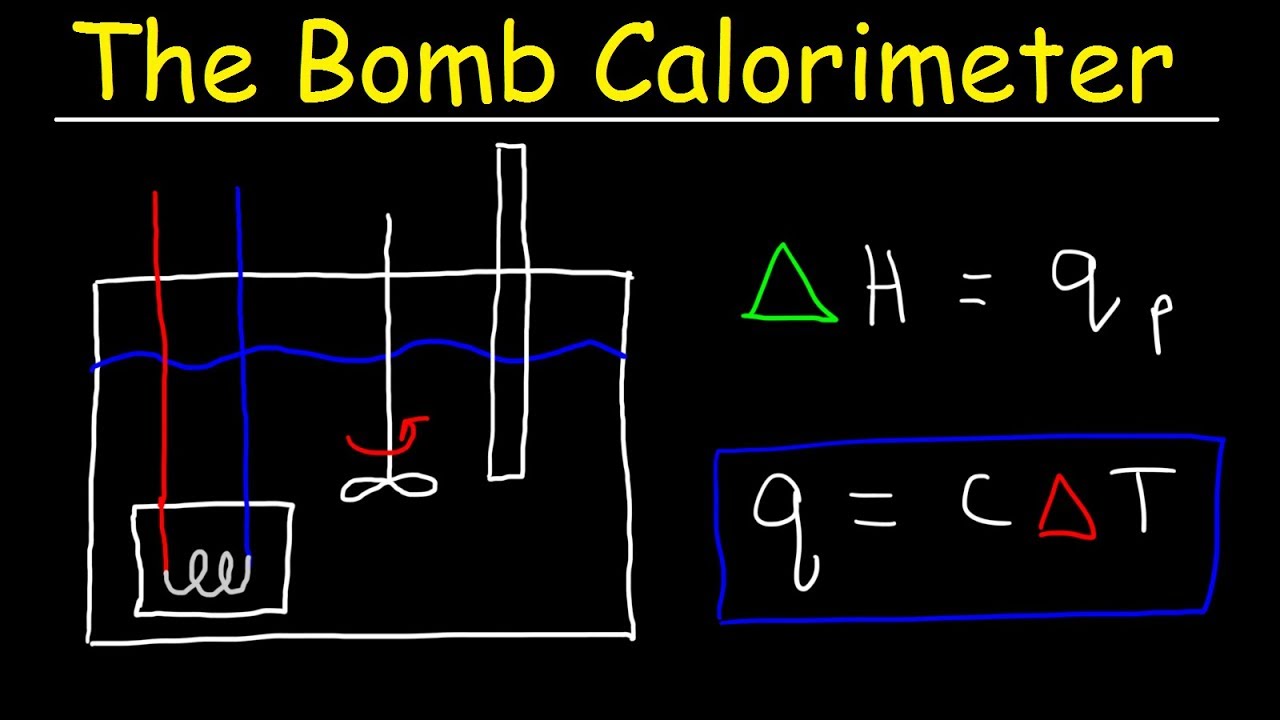
Bomb Calorimeter vs Coffee Cup Calorimeter Problem - Constant Pressure vs Constant Volume Calorimet

Termologia | Calorimetria - Parte II (RESUMÃO)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
