RING OF FIRE | Fakta Fenomena Ring Of Fire Di Indonesia
Summary
TLDRThe video explores the fascinating Ring of Fire, a vast area surrounding the Pacific Ocean known for its frequent earthquakes and volcanic eruptions. Viewers learn how tectonic plates interact to form this geological phenomenon, with specific attention to Indonesia's position on the Ring of Fire. The script delves into the science of plate tectonics, the formation of earthquakes, and the potential of volcanic eruptions. Despite its dangers, the region's fertile soil and geothermal energy offer significant benefits, making it a unique and dynamic part of the world.
Takeaways
- 😀 The Pacific Ring of Fire is a region around the Pacific Ocean known for frequent earthquakes and volcanic eruptions.
- 🌍 The Ring of Fire stretches over 40,000 kilometers and is often referred to as the 'Pacific Belt' due to its significant seismic activity.
- 💥 81% of the world's largest earthquakes occur along the Ring of Fire, making it one of the most seismically active regions on Earth.
- 🌋 The formation of the Ring of Fire is tied to tectonic plate movements, where one plate is pushed beneath another in a process known as subduction.
- 🌎 Indonesia, located in the Pacific Ring of Fire, is highly prone to natural disasters like earthquakes, tsunamis, and volcanic eruptions.
- 🔬 Tectonic plates move just a few centimeters each year, but when these movements suddenly shift, they can cause catastrophic events like earthquakes.
- 🔥 Volcanoes within the Ring of Fire are fueled by energy that has accumulated over millions of years, causing explosive eruptions.
- 🌿 The fertile volcanic soil created by eruptions contributes to the rich biodiversity in countries like Indonesia, where many people live near volcanoes.
- ⚡ Geothermal energy, generated by the heat from tectonic activities in the Ring of Fire, is a valuable and sustainable source of power for regions like Indonesia.
- 🌊 The Ring of Fire also poses a risk of tsunamis, especially in regions like Japan and the west coast of the Americas, due to underwater earthquakes.
Q & A
What is the Ring of Fire, and why is it significant?
-The Ring of Fire is a vast geological region surrounding the Pacific Ocean, known for its frequent earthquakes and volcanic eruptions. It is significant because it accounts for 75% of the world's earthquakes and 81% of the largest volcanic eruptions, making it one of the most geologically active areas on Earth.
How long is the Ring of Fire?
-The Ring of Fire stretches for approximately 40,000 kilometers, forming a horseshoe-shaped belt around the Pacific Ocean.
What geological processes lead to the formation of the Ring of Fire?
-The Ring of Fire is formed due to tectonic plate movements, specifically the subduction process, where one tectonic plate is pushed under another. This leads to volcanic activity and earthquakes, shaping the regions surrounding the Pacific Ocean.
What are tectonic plates, and how do they relate to the Ring of Fire?
-Tectonic plates are large pieces of Earth's crust that float on the molten layer beneath them. The movements and interactions of these plates, such as subduction, are responsible for the volcanic and seismic activity found in the Ring of Fire.
Why is Indonesia particularly vulnerable to natural disasters from the Ring of Fire?
-Indonesia is located on the convergence of several tectonic plates, including the Indo-Australian, Eurasian, and Pacific plates. This makes the country prone to earthquakes, volcanic eruptions, and tsunamis due to the frequent subduction and plate movements in the region.
What is subduction, and how does it contribute to volcanic eruptions and earthquakes?
-Subduction is the process in which one tectonic plate is forced beneath another. This movement generates intense friction and pressure, which can lead to volcanic eruptions and earthquakes when the built-up energy is released.
How did the Ring of Fire form historically?
-The Ring of Fire began forming over 200 million years ago due to the movement of tectonic plates. Over time, interactions such as subduction resulted in volcanic activity and seismic disturbances, creating the belt of activity around the Pacific Ocean.
What are the benefits of living in regions affected by the Ring of Fire?
-Despite the risks of natural disasters, regions around the Ring of Fire benefit from fertile soil due to volcanic ash, which makes the land highly productive for agriculture. Additionally, these regions have potential geothermal energy resources that can be harnessed for alternative power.
How do volcanic eruptions contribute to soil fertility?
-Volcanic eruptions release ash and minerals that enrich the soil, making it more fertile and conducive to agriculture. This is why many populations in volcanic regions, like Indonesia, continue to live in areas prone to eruptions.
Why is the Ring of Fire also known as a source of geothermal energy?
-The intense volcanic activity in the Ring of Fire generates heat from beneath Earth's surface, creating potential geothermal energy sources. These areas, rich in geothermal potential, can be harnessed for clean, renewable energy.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифПосмотреть больше похожих видео

Mengenal Penyebab Tsunami Pada Suatu Wilayah, Salah Satunya Indonesia

Seisme (Gempa Bumi) #kumer

Jalur cincin api Indonesia ( Ring Of Fire )

Pacific Ring Of Fire | Fact about Natural Ring Of Volcano
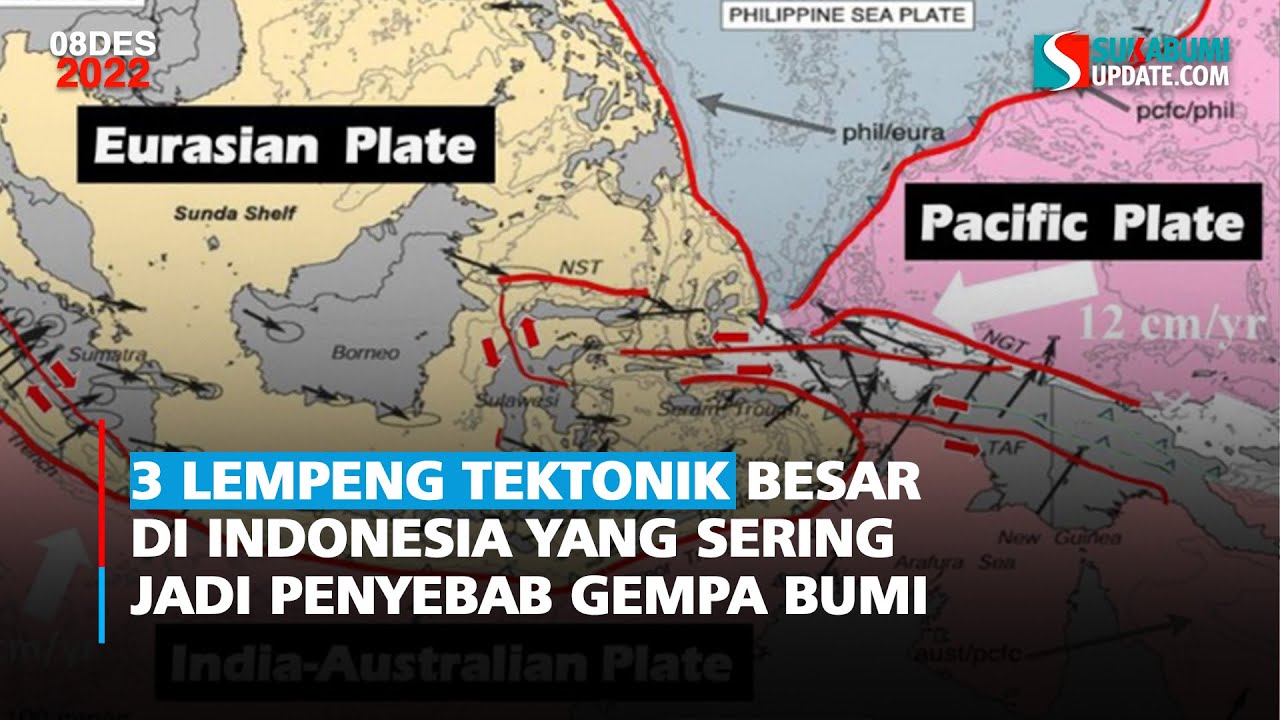
3 Lempeng Tektonik Besar di Indonesia yang Sering Jadi Penyebab Gempa Bumi

Conheça as PLACAS TECTÔNICAS e seus principais MOVIMENTOS
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
