CS601_Topic100
Summary
TLDRThis video script explores two key spread spectrum techniques used in wireless communications: Frequency Hopping Spread Spectrum (FHSS) and Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum (DSSS). FHSS spreads the signal across multiple frequencies, hopping between them based on a pseudo-random pattern, providing resistance to interference. DSSS, on the other hand, expands the signal's bandwidth by replacing each data bit with a sequence of chips, offering security and improved resistance to narrowband interference. Both methods allow multiple users to share the same frequency band, with distinct mechanisms for bandwidth utilization and interference avoidance.
Takeaways
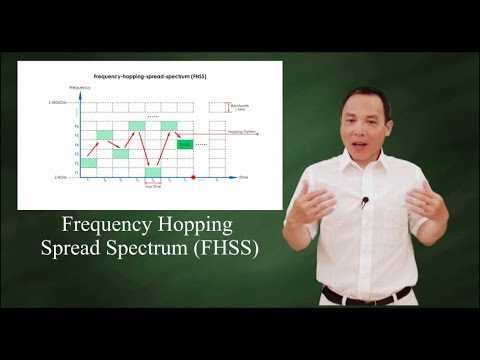
- 😀 FHSS (Frequency Hopping Spread Spectrum) involves modulating a source signal across different carrier frequencies at different time intervals, expanding its bandwidth.
- 😀 A pseudo-random code generator creates K-bit patterns that dictate which frequency is used in each hopping period for FHSS.
- 😀 In FHSS, multiple stations can share the same bandwidth by hopping to different frequencies at different times, making it similar to Frequency Division Multiplexing (FDM).
- 😀 The hopping frequency sequence in FHSS repeats after a set number of periods (e.g., after 8 hops), ensuring a periodic but pseudo-random frequency usage.
- 😀 The bandwidth used in FHSS is significantly larger than the original signal bandwidth, providing resilience against interference.
- 😀 DSSS (Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum) replaces each data bit with a series of *n* bits (called chips), spreading the signal over a wider bandwidth.
- 😀 The chip generator in DSSS creates a spreading code (chips), and each data bit is replaced by this code, increasing the chip rate to *n* times the data rate.
- 😀 DSSS enhances the signal's integrity and security by spreading it over a broader frequency range, making it less vulnerable to interference.
- 😀 Unlike FHSS, where frequencies are dynamically allocated based on hopping patterns, DSSS uses a fixed spreading code to expand bandwidth per station.
- 😀 Both FHSS and DSSS are techniques that improve signal resilience and security, but FHSS is more suited to dynamic environments with potential interference, while DSSS is better for environments requiring higher signal integrity.
Q & A
What is Frequency Hopping Spread Spectrum (FHSS)?
-Frequency Hopping Spread Spectrum (FHSS) is a spread spectrum technique where a signal hops between multiple frequencies in a pseudo-random manner, spreading the signal over a wider bandwidth than its original source.
How does FHSS generate carrier frequencies during hopping periods?
-In FHSS, a pseudo-random code generator creates a K-bit pattern for each hopping period. This pattern is then mapped to a frequency table, which determines the carrier frequency to be used during each hopping period.
What is the role of the frequency synthesizer in FHSS?
-The frequency synthesizer takes the frequency selected by the frequency table and generates the corresponding carrier signal at that frequency, which is then modulated by the source signal.
How are the hopping frequencies selected in FHSS?
-The hopping frequencies in FHSS are selected using a pseudo-random code pattern generated by the pseudo-random noise (PN) generator. The pattern is mapped to specific frequencies, and after a defined number of hops, the pattern repeats.
What is meant by a 'pseudo-random code' in FHSS?
-A pseudo-random code in FHSS refers to a sequence of bits generated in a random-like pattern, which is repeated after a certain number of hops. It is used to determine the carrier frequencies during each hopping period.
What is the advantage of FHSS in terms of bandwidth sharing?
-FHSS allows multiple stations to share the same bandwidth by using different frequencies during different hopping periods. Each station uses one frequency per hop, but all stations can occupy the same bandwidth by hopping between frequencies.
What is Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum (DSSS)?
-Direct Sequence Spread Spectrum (DSSS) is a spread spectrum technique in which each data bit is replaced by a sequence of n bits, called chips, which increases the bandwidth of the original signal.
How does DSSS differ from FHSS in terms of spreading the signal?
-In DSSS, the original signal is spread by replacing each data bit with a sequence of chips, while in FHSS, the signal is spread by hopping between different carrier frequencies in a pseudo-random manner.
What is the role of the chip generator in DSSS?
-The chip generator in DSSS produces a spreading code of n bits for each data bit. These chips are then used to modulate the original signal, expanding its bandwidth.
How does DSSS improve resistance to interference compared to FHSS?
-DSSS improves resistance to interference by spreading each data bit over multiple chips, which makes the signal less vulnerable to narrowband interference. FHSS, on the other hand, changes frequencies periodically, avoiding interference but not necessarily spreading each bit in the same way.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тариф5.0 / 5 (0 votes)