Defisiensi Enzim Sphingomyelinase
Summary
TLDRThis video explores the concept of enzymes and their crucial role in human metabolism, explaining their structure, function, and factors that influence their activity. The discussion then shifts to Niemann-Pick disease, a rare genetic disorder affecting lipid metabolism, specifically the inability to break down sphingomyelin due to enzyme deficiencies. The video compares the severity of Niemann-Pick types A and B, highlighting their symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment approaches. With a focus on the importance of enzymes in biological processes and their connection to inherited diseases, the content offers valuable insights into both enzyme biology and rare metabolic disorders.
Takeaways
- 😀 Enzymes are proteins that catalyze biochemical reactions, speeding up processes by lowering activation energy.
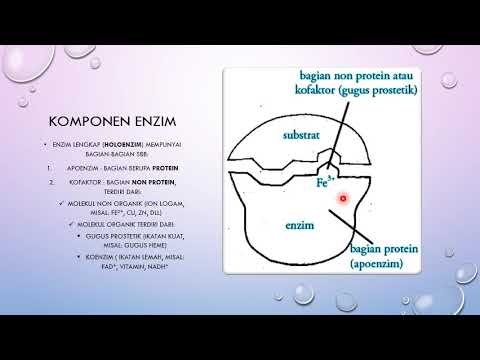
- 😀 Holoenzymes are made up of two components: apoenzymes (protein) and cofactors (non-protein).
- 😀 Enzymes can be affected by temperature, pH, and the concentration of substrates and enzymes.
- 😀 Enzymes are specific to certain substrates and have active sites where reactions take place.
- 😀 The Lock and Key Theory explains enzyme-substrate interaction as a rigid, precise fit.
- 😀 The Induced Fit Theory suggests that enzymes adapt their shape to fit the substrate during the reaction.
- 😀 Enzymes can work in a reversible manner, either synthesizing or breaking down substrates.
- 😀 Inhibitors can block enzyme activity, with types including competitive, non-competitive, and feedback inhibitors.
- 😀 Niemann-Pick Disease is a genetic disorder caused by a deficiency of sphingomyelinase, affecting the breakdown of sphingomyelin.
- 😀 NPD Type A presents early in life with severe symptoms and is often fatal by age 3, while NPD Type B has milder symptoms that can develop at any age.
- 😀 Diagnosis of Niemann-Pick Disease involves clinical exams, genetic tests, and blood tests, while treatment is mostly supportive to manage symptoms.
Q & A
What are enzymes, and why are they important in human metabolism?
-Enzymes are proteins that act as biocatalysts, speeding up chemical reactions in the body. They are essential for human metabolism because they facilitate biochemical reactions, including breaking down substances and speeding up processes that would otherwise take much longer.
What is the role of the apoenzyme and cofactor in enzyme function?
-The apoenzyme is the protein part of an enzyme, while the cofactor is a non-protein component that is required for the enzyme’s activity. Together, they form the holoenzyme, which is the complete, functional enzyme capable of catalyzing reactions.
What is the active site of an enzyme, and how does it contribute to enzyme function?
-The active site of an enzyme is the specific region where the enzyme binds to a substrate, enabling the reaction to take place. This binding is crucial for the enzyme to function as it allows the conversion of the substrate into the product.
What is the difference between the Lock and Key Theory and the Induced Fit Theory?
-The Lock and Key Theory suggests that the enzyme’s active site is rigid and only fits a specific substrate like a key fits a lock. In contrast, the Induced Fit Theory proposes that the active site is flexible and adjusts its shape to fit the substrate, ensuring the reaction can still proceed.
How do factors like temperature, pH, and concentration influence enzyme activity?
-Enzyme activity is influenced by temperature, as they are thermolabile (affected by heat). The optimal temperature for most human enzymes is between 35-40°C. pH affects enzyme activity because enzymes work best within a certain pH range, usually between 6 and 8. Additionally, enzyme and substrate concentration also impact reaction rates; more enzymes with fewer substrates speed up reactions, while an abundance of substrates with fewer enzymes slows it down.
What are enzyme inhibitors, and how do they affect enzyme function?
-Enzyme inhibitors are substances that interfere with enzyme activity. They can be competitive, non-competitive, or feedback inhibitors. Competitive inhibitors block the active site, preventing the substrate from binding. Non-competitive inhibitors bind to the enzyme elsewhere, changing its shape and affecting substrate binding. Feedback inhibitors are produced by the end product of a reaction and prevent further enzyme activity when enough product has been made.
What causes Niemann-Pick disease, and how does it affect the body?
-Niemann-Pick disease is caused by a genetic mutation that results in a deficiency of the enzyme acid sphingomyelinase. This leads to the accumulation of sphingomyelin in cells, especially in macrophages, and causes damage to organs like the liver, spleen, and brain.
What are the key differences between Niemann-Pick type A and type B?
-Niemann-Pick type A is a severe form, typically fatal by age 3, characterized by a complete lack of acid sphingomyelinase activity. Type B is less severe, with partial enzyme activity, and can present later in life with milder symptoms. Both types involve sphingomyelin accumulation.
How is Niemann-Pick disease diagnosed?
-Niemann-Pick disease is diagnosed through clinical examination, genetic testing to identify mutations in the SMPD1 gene, and blood tests to measure enzyme activity, particularly in white blood cells.
What are the treatments available for Niemann-Pick disease?
-There is no cure for Niemann-Pick disease. Treatment focuses on supportive care to manage symptoms, such as nutritional support, medication to improve quality of life, and regular monitoring of symptoms. Type B may also involve regular laboratory tests to monitor disease progression.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тариф5.0 / 5 (0 votes)