Jenis dan Komponen Peta
Summary
TLDRThis video provides an insightful exploration of maps, covering various types and components. It introduces map presentation methods, including line maps and photo or satellite image maps, explaining the difference between vector and raster data. The video then delves into map classifications, including general maps and thematic maps, and outlines the essential components such as title, scale, legend, inset, and grid. The role of UTM coordinates and indexing in digital maps is also highlighted, alongside the importance of projections. Overall, the content offers a comprehensive guide for understanding map creation and interpretation.
Takeaways
- 😀 Different types of maps include line maps (vector) and photo maps (raster), each using different methods to represent Earth's objects.
- 😀 Line maps display Earth’s features as points and lines, while photo maps use pixels to represent objects based on brightness values.
- 😀 Maps can be categorized by content: general maps provide broad information, and thematic maps focus on specific data like the distribution of flora, fauna, or mineral resources.
- 😀 Maps come in two formats: hardcopy (physical printed maps) and digital (stored as spatial data files with different layers).
- 😀 Digital maps can have separate layers for various features, like health facilities or educational institutions, stored in different file formats (e.g., SHP for ArcGIS).
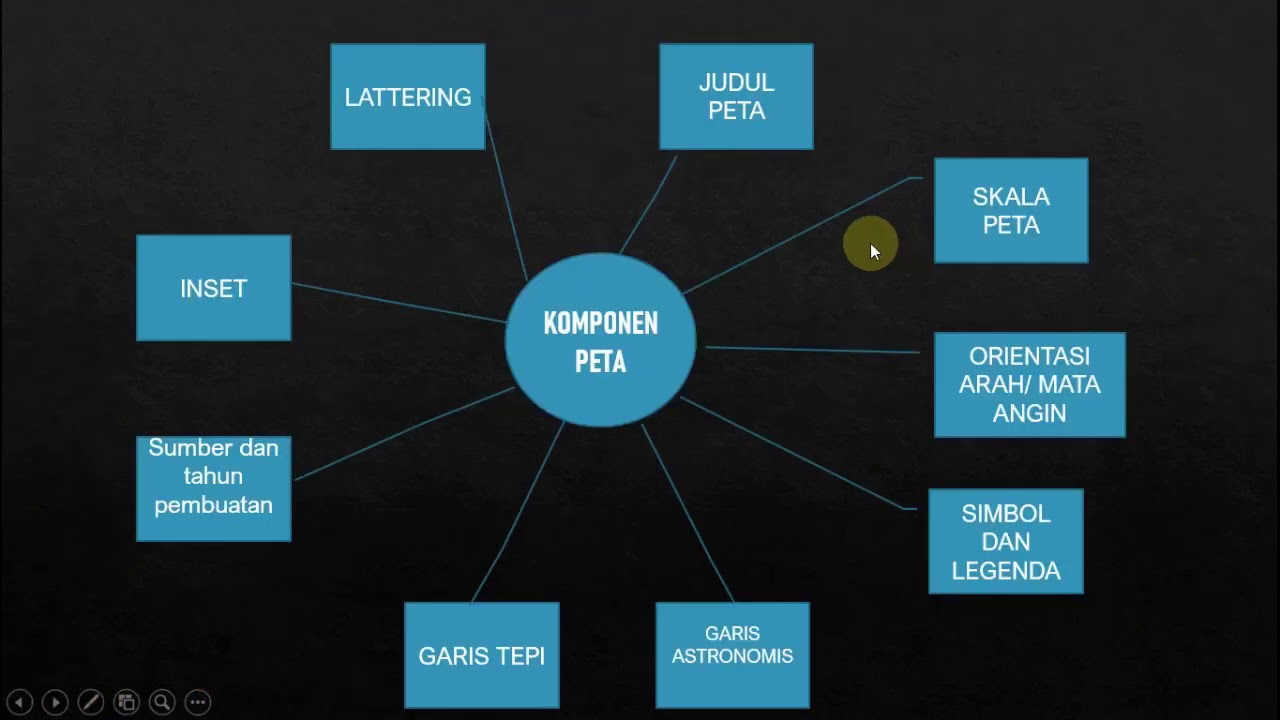
- 😀 Map components include a title, scale, legend, inset, coordinate system, and grid, which help interpret the map’s information.
- 😀 The scale of a map can be verbal (e.g., '1 inch = 1 mile'), numerical (e.g., '1:63,500'), or graphical (a scale bar).
- 😀 The legend explains symbols and colors used on the map, helping readers understand what each representation means (e.g., roads, rivers).
- 😀 An inset map shows the relative location of the mapped area within a larger region, such as a province within a country.
- 😀 A coordinate system (e.g., UTM) helps accurately position features on the Earth’s surface using grids of latitude and longitude.
- 😀 Indexing divides maps into grid sections, making it easier to find specific areas, and allows for detailed breakdowns with smaller-scale maps.
Q & A
What is the difference between line maps and photo maps?
-Line maps represent geographical features using lines and points, while photo maps (also known as satellite maps) display actual images of the area, with features represented as pixels with specific brightness values.
What are the two main types of maps based on content?
-Maps can be classified into two types based on content: general maps, which provide a broad overview of geographical areas, and thematic maps, which focus on specific phenomena, such as the distribution of flora, fauna, or resources.
How do general maps differ from thematic maps?
-General maps display basic geographic information about a region, like boundaries and landscapes, without focusing on specific data. In contrast, thematic maps highlight particular subjects or phenomena, such as resource distribution or population density.
What are the different types of map scales, and how do they work?
-The three main types of map scales are verbal scale (e.g., '1 inch = 1 mile'), numerical scale (e.g., '1:50,000'), and graphical scale (a visual bar scale showing distances directly). These scales show the relationship between distances on the map and actual distances on the ground.
What role does the legend play in a map?
-The legend explains the meaning of symbols and colors used on the map. It helps the reader interpret the map correctly by defining what each symbol represents, such as roads, rivers, or buildings.
What is an inset on a map, and what is its purpose?
-An inset is a smaller map within a larger map, showing a specific area in greater detail or within a broader context. It helps provide additional information about the location relative to a larger geographical area.
How is digital map data structured?
-Digital maps are stored as spatial database files, which are divided into layers. Each layer represents a different type of geographic information, such as health facilities or educational institutions. These layers are stored as separate files and can be managed with specialized software like ArcGIS.
What is the importance of the grid and coordinates on a map?
-The grid system, formed by horizontal and vertical lines, helps locate specific points on a map by referencing geographic coordinates. Coordinates are used to determine exact locations on the Earth’s surface, typically represented as latitude and longitude or other systems like UTM.
What is indexing in map reading, and why is it important?
-Indexing refers to the system of assigning unique codes to sections of a map. This helps in organizing and referencing maps, making it easier to locate specific regions. Indexing is especially useful when maps are divided into multiple sections for more detailed study.
What is the difference between a grid and a graticule on a map?
-A grid is a network of lines that helps locate points on a map, while a graticule specifically refers to the network of latitude and longitude lines used for geospatial referencing. Graticules are projections that represent global coordinates on the map.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифПосмотреть больше похожих видео
Peta (Jenis, Komponen & Proyeksi).
Geografi - PETA

Mastering Kubernetes: Volumes (Persistent Volumes and Claims, ConfigMaps, Secrets, etc)

Pengelolaan Rapat / Pertemuan || Manajemen Perkantoran - Fase F

(Inet) 4.3 - Konsep Dasar Dynamic Routing

Galaksi : Pengertian, Ciri dan Jenisnya #galaxy #bendalangit
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
