LEYES de los GASES 🎈 TRUCO FÁCIL para Aprender las Fórmulas
Summary
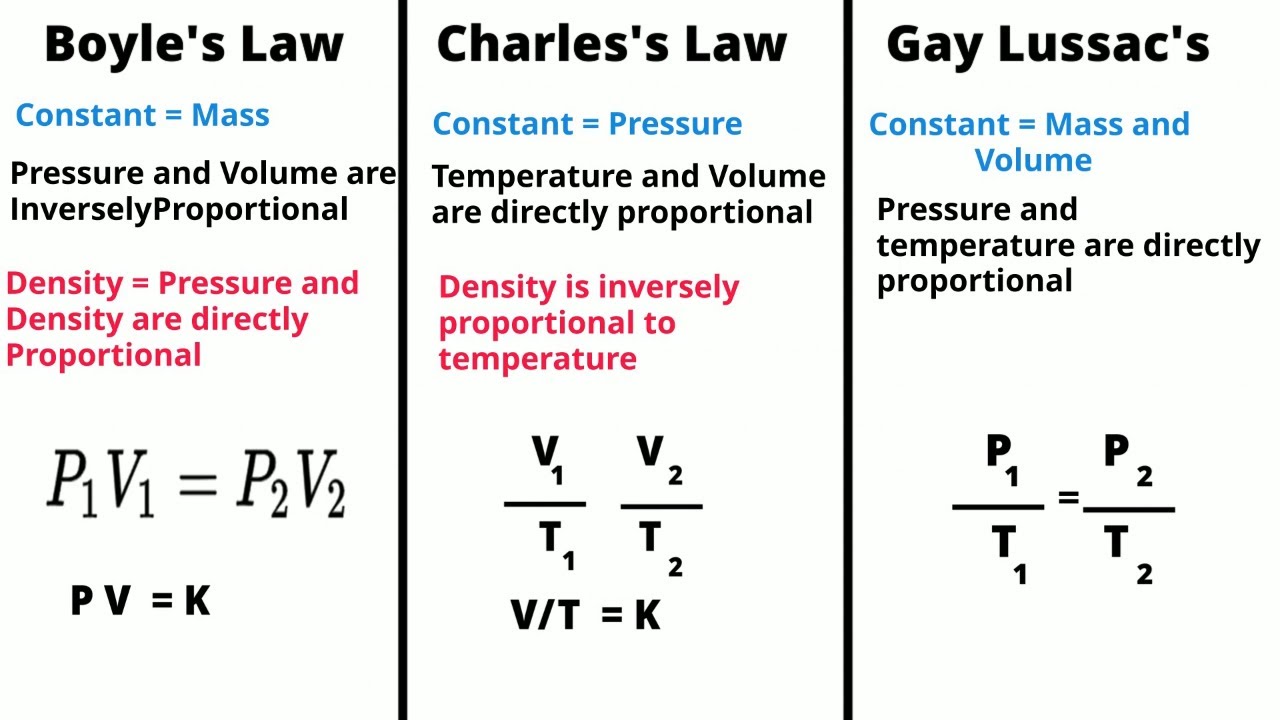
TLDRIn this video, Susi simplifies the laws of gases, focusing on Boyle’s, Charles’s, and Gay-Lussac’s laws. She introduces the general gas law equation and explains how each law can be derived by removing a specific constant (temperature, pressure, or volume). Using real-life examples—like a syringe (Boyle’s), a balloon in the sun (Charles’s), and a pressure cooker (Gay-Lussac’s)—Susi illustrates how these laws relate to everyday experiences, making complex concepts easier to grasp. Her approach offers a clear and memorable method for understanding and memorizing these gas laws.
Takeaways
- 😀 The video explains the laws of gases and provides tricks to memorize them easily.
- 😀 The general equation for gases is introduced as a foundation for understanding Boyle's, Charles's, and Gay-Lussac's laws.
- 😀 The general equation of gases can be used to derive the formulas for Boyle's, Charles's, and Gay-Lussac's laws by identifying which constant to remove.
- 😀 Boyle's Law relates pressure and volume in an inversely proportional relationship, meaning higher pressure leads to lower volume.
- 😀 An everyday example for Boyle's Law is a syringe: applying pressure results in reduced volume.
- 😀 Charles's Law shows that volume and temperature are directly proportional: higher temperature leads to higher volume.
- 😀 A real-life example of Charles's Law is a balloon that expands when left under the sun, as the temperature increases the volume.
- 😀 Gay-Lussac's Law explains that pressure and temperature are directly proportional: higher temperature results in higher pressure.
- 😀 A real-world example of Gay-Lussac's Law is an express pot, where higher temperature leads to increased pressure.
- 😀 Understanding these laws is simplified by associating them with everyday examples, making it easier to remember the formulas and relationships.
- 😀 The combined law of gases, which merges all these relationships, can be memorized by learning the general equation and focusing on constants.
Q & A
What is the general gas law mentioned in the video?
-The general gas law is the equation: P1 * V1 / T1 = P2 * V2 / T2, which relates pressure (P), volume (V), and temperature (T) of a gas in its initial and final states.
How can you derive the Boyle's law from the general gas law?
-To derive Boyle’s law, we need to keep temperature constant. This means the temperature terms will cancel out, leaving the equation as P1 * V1 = P2 * V2, which shows the inverse relationship between pressure and volume.
What real-world example is used to explain Boyle’s law?
-The real-world example used for Boyle’s law is a syringe. When you push the plunger, the pressure inside increases while the volume decreases, illustrating the inverse relationship between pressure and volume.
How is Charles’s law derived from the general gas law?
-In Charles’s law, we keep pressure constant. This allows us to simplify the equation to V1 / T1 = V2 / T2, which shows the directly proportional relationship between volume and temperature.
What example illustrates Charles’s law in the video?
-The example of a balloon left in the sun is used to explain Charles’s law. As the temperature rises, the volume of the gas inside the balloon increases, demonstrating the direct relationship between temperature and volume.
How does Gay-Lussac’s law relate to pressure and temperature?
-Gay-Lussac’s law shows that pressure and temperature are directly proportional when the volume is kept constant. The equation simplifies to P1 / T1 = P2 / T2, meaning that as temperature increases, pressure also increases.
What everyday example is used to explain Gay-Lussac’s law?
-An express pot is used as an example of Gay-Lussac’s law. As the temperature in the pot increases, the pressure inside also increases, demonstrating the direct relationship between pressure and temperature.
How can remembering real-world examples help with understanding gas laws?
-Remembering real-world examples like the syringe, balloon, and express pot makes it easier to visualize the behavior of gases and understand the relationships in Boyle’s, Charles’s, and Gay-Lussac’s laws.
Why is the general gas law also called the combined law of gases?
-The general gas law is called the combined law of gases because it combines all three gas laws (Boyle’s, Charles’s, and Gay-Lussac’s) into one equation, showing how pressure, volume, and temperature are interconnected.
How can the trick of learning the general gas law help in memorizing the specific gas laws?
-By understanding the general gas law and knowing which variable remains constant for each specific law, you can easily derive the formulas for Boyle’s, Charles’s, and Gay-Lussac’s laws without having to memorize each one individually.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифПосмотреть больше похожих видео
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)