IMAGE FORMED IN PLANE MIRROR | RAY DIAGRAM IN PLANE MIRRORS | MELC BASED
Summary
TLDRIn this lesson, students explore the reflection of light in plane mirrors, learning key concepts such as the angle of incidence, angle of reflection, and the laws governing reflection. The video explains two types of reflection: regular (specular) and diffuse, illustrating how images are formed in mirrors. A ray diagram demonstrates how to locate and describe images, highlighting characteristics such as virtual image formation, lateral inversion, and equal distance from the mirror. The lesson concludes by explaining the significance of the word 'ambulance' being written in reverse for visibility in rear-view mirrors, emphasizing the practical application of these principles.
Takeaways
- 😀 Reflection of light is the process of light bouncing back when it strikes a surface.
- 🪞 A plane mirror is a flat reflective surface that produces clear images through reflection.
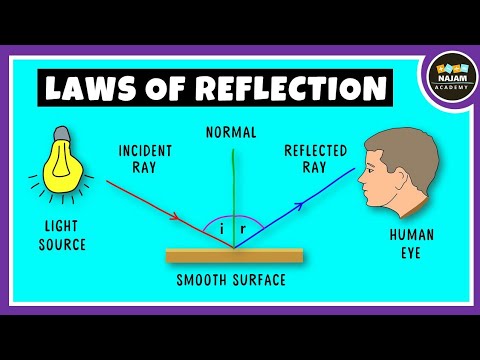
- 📏 The normal line is drawn perpendicular to the mirror's surface at the point of incidence.
- ➡️ The incident ray is the ray of light approaching the mirror, while the reflected ray is the ray leaving it.
- 🔄 The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection, as per the laws of reflection.
- ✨ There are two types of reflection: regular (specular) reflection on smooth surfaces and diffuse reflection on rough surfaces.
- 👀 Regular reflection produces clear images, while diffuse reflection scatters light, allowing us to see objects around us.
- 🔍 Images formed by plane mirrors are virtual, meaning they cannot be projected onto a screen.
- 📏 The size and orientation of the image in a plane mirror are the same as the object it reflects.
- 🔄 Lateral inversion occurs in plane mirrors, reversing the left and right sides of the image.
Q & A
What is reflection in the context of light?
-Reflection is the bouncing or returning back of light when it hits a surface, such as a mirror.
What are the two types of reflection mentioned in the script?
-The two types of reflection are regular (specular) reflection, which occurs on smooth surfaces like mirrors, and diffuse (irregular) reflection, which occurs on rough surfaces like wood.
What is the normal line in the context of reflection?
-The normal line is an imaginary line drawn perpendicular to the surface of the mirror at the point where the incident ray strikes.
How is the angle of incidence defined?
-The angle of incidence is the angle between the normal line and the incident ray.
What does the law of reflection state?
-The law of reflection states that the incident ray, the reflected ray, and the normal line all lie in the same plane, and the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
What characteristics define an image formed by a plane mirror?
-The image formed by a plane mirror is virtual, upright, the same size as the object, and laterally inverted.
What is meant by lateral inversion?
-Lateral inversion refers to the reversal of the left and right sides of an object in its image; for example, the left part of an object becomes the right part of the image.
Why is the word 'ambulance' written in reverse on an ambulance car?
-The word 'ambulance' is written in reverse so that drivers in vehicles behind can read it correctly in their rearview mirrors, allowing them to yield to the ambulance.
What does it mean for an image to be virtual?
-A virtual image is formed by extending reflected rays that do not actually meet; the image appears to be behind the mirror.
How does the distance of the image from the mirror compare to the distance of the object from the mirror?
-The distance of the image from the mirror is equal to the distance of the object from the mirror.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тариф5.0 / 5 (0 votes)