Física - Ondas e luz: reflexão da luz
Summary
TLDRThis lesson on light reflection explains how light behaves when it encounters a surface, with no change in frequency, wavelength, or speed. The two main laws of reflection are discussed: the incident and reflected rays always lie in the same plane, and the angle of incidence equals the angle of reflection. The lesson also introduces two types of reflection: specular, where light reflects off smooth surfaces like mirrors, and diffuse, where light scatters off rough surfaces. The lesson emphasizes that both types obey the same fundamental laws, despite the difference in reflection behavior.
Takeaways
- 😀 Reflection is a phenomenon that occurs when a wave encounters an obstacle and returns to its original medium.
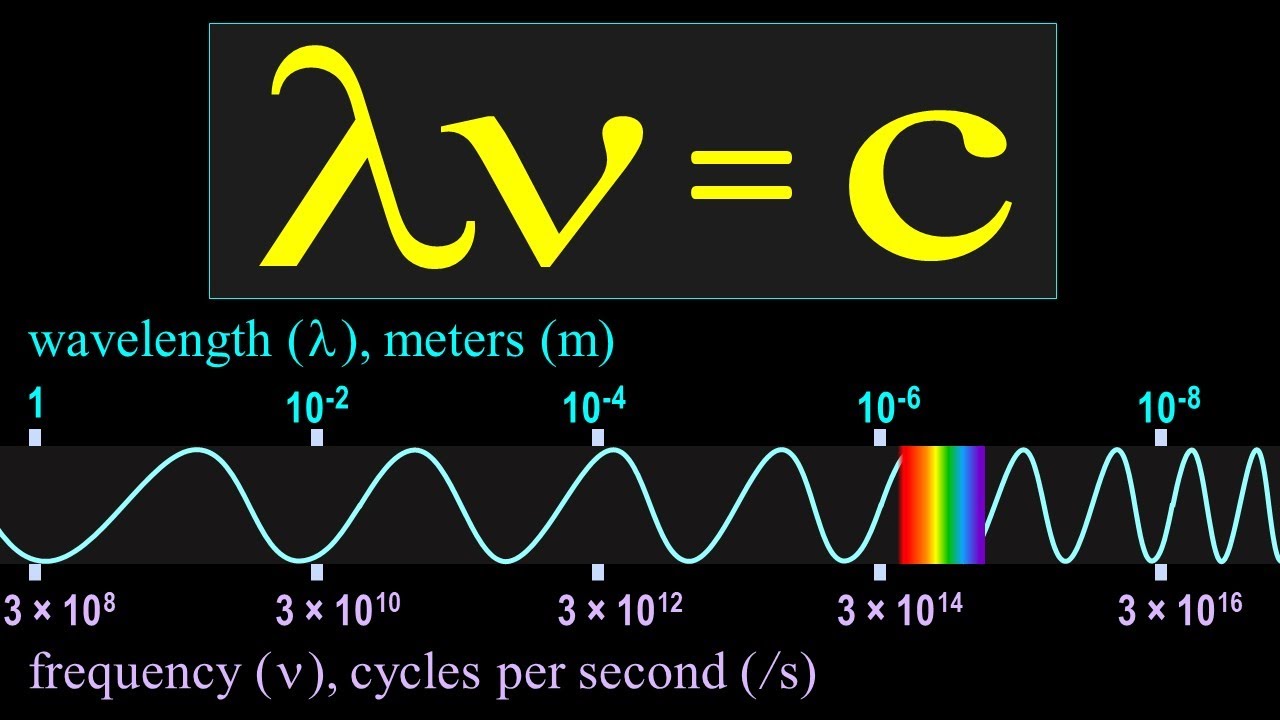
- 😀 Reflection doesn't alter the frequency, wavelength, or speed of a wave because it stays within the same propagation medium.
- 😀 The first law of reflection states that the incident ray and the reflected ray are always in the same plane.
- 😀 The second law of reflection states that the angle of incidence is always equal to the angle of reflection, both measured relative to the normal line.
- 😀 No exceptions exist to the laws of reflection; the rays will always adhere to these principles, regardless of surface irregularities.
- 😀 Specular reflection occurs when light reflects off a smooth surface, maintaining parallelism among the reflected rays.
- 😀 Examples of specular reflection include reflections in mirrors or a calm lake surface.
- 😀 Diffuse reflection happens when light reflects off a rough or irregular surface, causing rays to scatter in different directions.
- 😀 A common example of diffuse reflection is the pattern seen on a CD, where light interacts with the surface's microscopic grooves, creating a color pattern.
- 😀 Both specular and diffuse reflections obey the laws of reflection, but in diffuse reflection, the normals vary across the surface, causing different reflection angles for each ray.
- 😀 Understanding reflection is essential for studying image formation in mirrors and understanding color formation, especially in optical phenomena like interference.
Q & A
What is the main topic discussed in the video?
-The main topic discussed is the reflection of light, focusing on its principles and types, including specular and diffuse reflection.
What is reflection in the context of waves?
-Reflection is a phenomenon that occurs when a wave encounters an obstacle and returns to the medium of origin. The wave’s properties, like frequency, wavelength, and speed, remain unchanged during reflection.
What is the significance of the normal line in the study of light reflection?
-The normal line is a reference line used to measure the angles of incidence and reflection. These angles are measured in relation to this normal line, not the surface.
What does the first law of reflection state?
-The first law of reflection states that the incident ray and the reflected ray always lie in the same plane. This means both rays must be in the same plane of reflection without any deviation.
What does the second law of reflection state?
-The second law of reflection states that the angle of incidence is always equal to the angle of reflection. This means the angle between the incident ray and the normal is equal to the angle between the reflected ray and the normal.
Are there any exceptions to the laws of reflection?
-No, there are no exceptions to the laws of reflection. The two rays will always lie in the same plane, and the angles of incidence and reflection will always be equal.
What is the difference between specular and diffuse reflection?
-In specular reflection, light rays that are parallel before hitting a smooth surface remain parallel after reflection, as seen in mirrors. In diffuse reflection, light rays scatter in different directions after striking an irregular or rough surface.
Can you give an example of specular reflection?
-An example of specular reflection is the reflection of light on a mirror. In this case, parallel rays of light reflect off the smooth surface and remain parallel.
What is the role of surface irregularities in diffuse reflection?
-Surface irregularities cause light rays to scatter in multiple directions. Each point on the surface has its own orientation, and thus the incident rays form different angles with the surface, leading to the scattered reflection.
How does a CD exhibit diffuse reflection?
-A CD has microscopic grooves that act as surface irregularities. When light strikes the CD, it reflects in various directions due to these irregularities, causing interference and creating a visible pattern of colors on the surface.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

GCSE Physics - Refraction of waves #63

ABC Zoom - Refraction: why glass prisms bend and separate light

Refraction and Snell's law | Geometric optics | Physics | Khan Academy

REFLEXÃO TOTAL DA LUZ - ÓPTICA - Aula 9 - Prof. Boaro
Frequency, Wavelength, and the Speed of Light

O QUE É RADIAÇÃO ELETROMAGNÉTICA
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)