Synthesis of ATP (2018) Drew Berry and Franc Tétaz
Summary
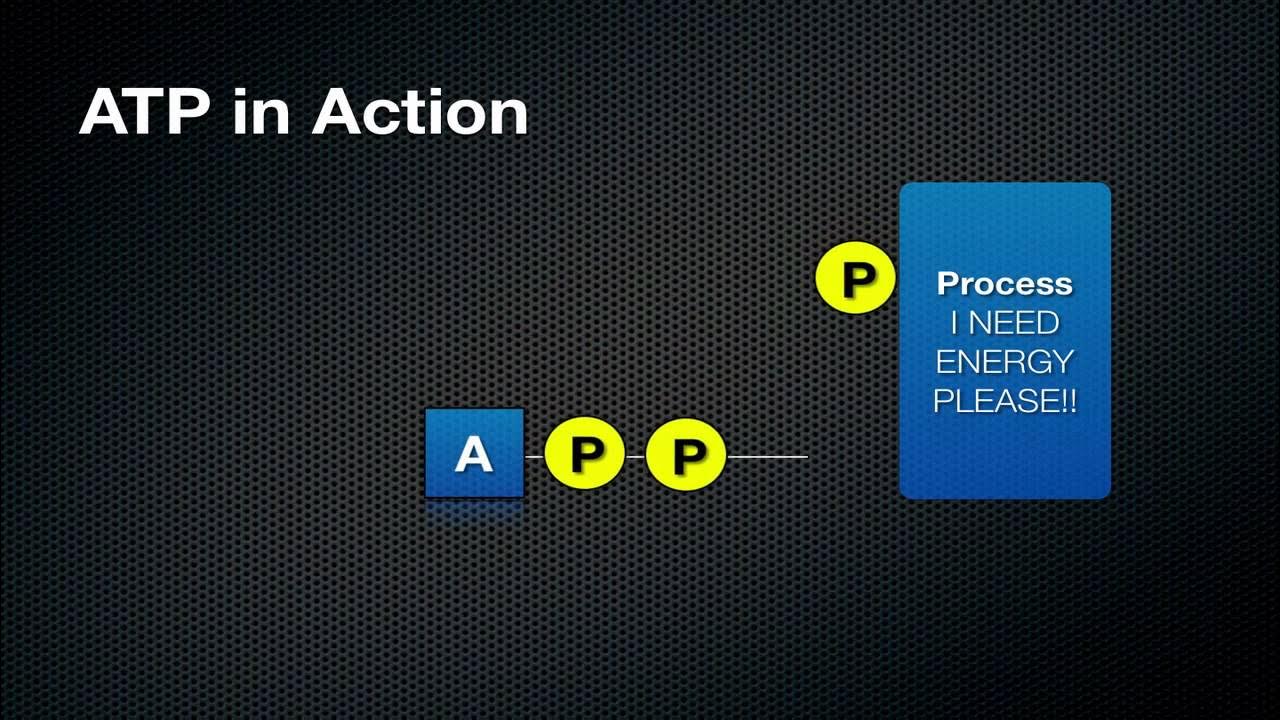
TLDRATP, or adenosine triphosphate, is a vital molecule for all life on Earth, powering biochemical reactions within cells and being a key component of DNA and RNA. Mitochondria act as cellular energy converters, transforming nutrients and oxygen into ATP. Inside, molecular motors with enzymes create ATP by converting mechanical energy into chemical energy. A rotating axle, driven by a proton gradient, powers the ATP synthesis process, essential for life.
Takeaways
- 🌐 ATP is a crucial molecule for all life on Earth.
- ⚡ ATP powers biochemical activities within living cells.
- 🧬 ATP is a key component of DNA and RNA.
- 🔋 Mitochondria are the cellular structures that generate ATP.
- 🍽️ ATP production is fueled by food and oxygen.
- 🔄 ATP is created through a process involving molecular motors.
- 🔬 Enzymes facilitate the formation of ATP by converting mechanical energy into chemical energy.
- 🔄 A ring of enzymes works in unison to create ATP.
- 🔄 The process involves a rotating axle powered by a molecular motor.
- ⚙️ The molecular motor is driven by a proton gradient across a membrane.
- 🔋 The ATP synthesis process is essential for life.
Q & A
What is ATP and why is it important for life on Earth?
-ATP, or adenosine triphosphate, is a tiny energetic molecule that drives biochemical activity inside living cells and is a key building block of DNA and RNA. It is essential for all life on Earth as it provides the energy needed for cellular functions.
Where is ATP generated within a cell?
-ATP is generated within the mitochondria of a cell, which are often referred to as the cell's 'powerhouses'.
How does the process of ATP generation relate to the food we eat and the air we breathe?
-Mitochondria convert energy from the food we eat and oxygen from the air we breathe into ATP. This conversion process involves the breakdown of food molecules and the intake of oxygen to produce ATP.
What are the molecular motors inside mitochondria and what is their role?
-The molecular motors inside mitochondria are rows of enzymes that work together to generate ATP. They bring together reactants to form chemical bonds, converting mechanical energy into chemical energy.
How many molecules of ATP are created with each cycle of the molecular motor?
-A ring of enzymes within the molecular motor creates three molecules of ATP with each cycle.
What powers the sequence of the molecular motor?
-The sequence of the molecular motor is powered by a rotating axle, which is attached to a rotary molecular motor.
What moves the rotary molecular motor?
-The rotary molecular motor is moved by the force of protons pushing from the other side of the membrane.
What causes the protons to push from one side of the membrane to the other?
-A difference in proton concentration across the membrane propels the protons, creating a molecular mechanism that drives ATP synthesis.
How is the biochemical activity inside living cells related to ATP?
-ATP drives biochemical activity inside living cells by providing the necessary energy for various cellular processes, including growth, repair, and maintenance.
Why is ATP considered a key building block of DNA and RNA?
-ATP is considered a key building block of DNA and RNA because it provides the energy required for the synthesis and replication of these nucleic acids, which are essential for the storage and transmission of genetic information.
What role do enzymes play in the ATP synthesis process?
-Enzymes in the ATP synthesis process facilitate the bringing together of reactants to form chemical bonds, thus converting mechanical energy into chemical energy that is stored in the form of ATP.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тариф5.0 / 5 (0 votes)