Trigeminal Nerve Anatomy - Cranial Nerve 5 Course and Distribution
Summary
TLDRThis video script delves into the anatomy of the trigeminal nerve, the largest cranial nerve, which arises from four nuclei and branches into three divisions: the ophthalmic, maxillary, and mandibular. The ophthalmic and maxillary branches are purely sensory, while the mandibular branch contains both sensory and motor components. The script describes the nerve's origin, course, and distribution across the face, providing a comprehensive overview of its function and structure.
Takeaways
- 🧠 The trigeminal nerve is the fifth cranial nerve and the largest one.
- 🌿 It originates from four nuclei: three sensory (mesencephalic, principal sensory, spinal) and one motor nucleus.
- 🌐 It divides into three main branches: V1 (Ophthalmic), V2 (Maxillary), and V3 (Mandibular).
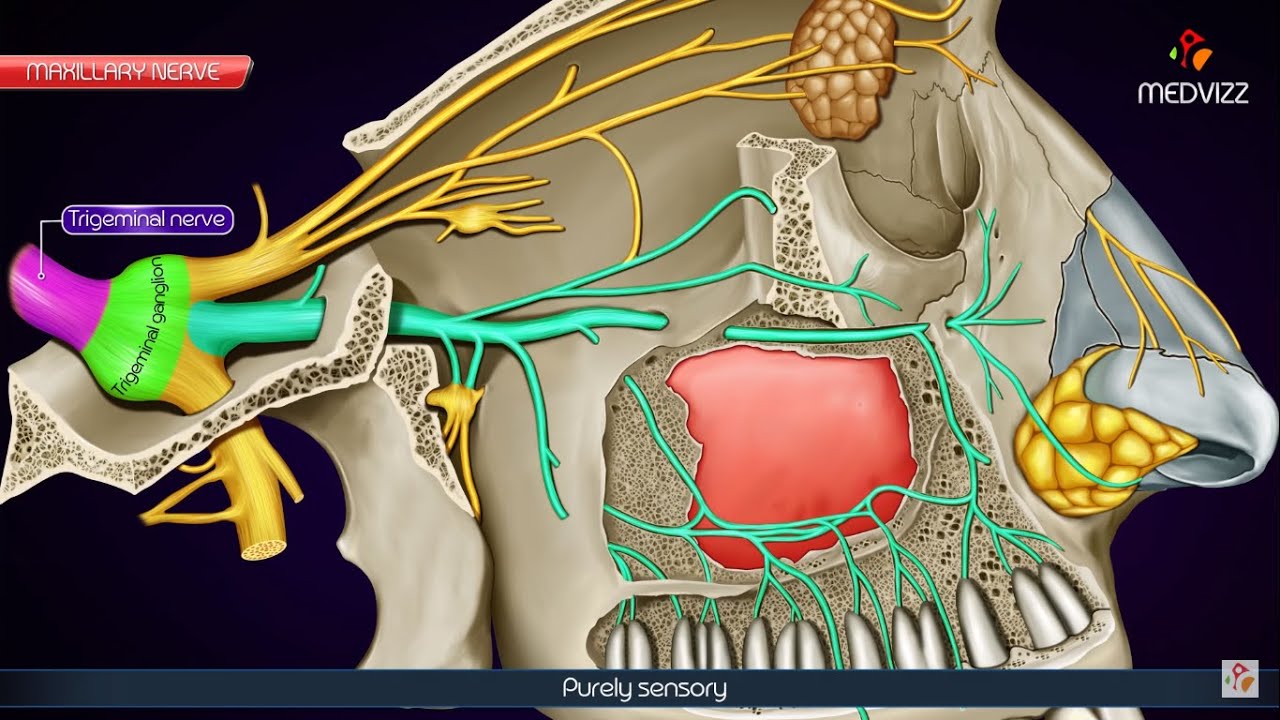
- 👁️ The Ophthalmic and Maxillary branches are purely sensory, while the Mandibular branch has both sensory and motor components.
- 📍 The trigeminal nerve arises in the midbrain, pons, medulla, and upper spinal cord.
- 🔍 The trigeminal ganglion is located in the middle cranial fossa, within the trigeminal cave of the temporal bone.
- 🚀 The Ophthalmic division exits the skull through the superior orbital fissure and supplies the forehead, scalp, and sinuses.
- 🦷 The Maxillary division exits through the foramen rotundum and supplies the middle part of the face, including the lower eyelid and cheek.
- 🦴 The Mandibular division exits through the foramen ovale and supplies the mouth, external ear, lower lip, and anterior 2/3 of the tongue, as well as motor functions to muscles of mastication.
- 💪 The motor component of the Mandibular branch supplies muscles of the first branchial arch, including muscles of mastication and certain ear and palate muscles.
- 👨🏫 The video provides a comprehensive overview of the trigeminal nerve's origin, course, and distribution.
Q & A
What is the trigeminal nerve?
-The trigeminal nerve is the fifth cranial nerve and the largest one, responsible for sensation in the face and motor functions of the muscles involved in mastication.
How many nuclei does the trigeminal nerve arise from?
-The trigeminal nerve arises from four nuclei: the mesencephalic nucleus, the principal sensory nucleus, the spinal nucleus, and the motor nucleus.
What are the three branches of the trigeminal nerve?
-The three branches of the trigeminal nerve are the V1 (Ophthalmic), V2 (Maxillary), and V3 (Mandibular).
Which branches of the trigeminal nerve are purely sensory?
-The Ophthalmic (V1) and Maxillary (V2) branches are purely sensory.
What is the function of the Mandibular branch (V3) of the trigeminal nerve?
-The Mandibular branch (V3) is mixed, having both sensory and motor components. It supplies sensation to parts of the face and motor function to the muscles of mastication.
Where does the trigeminal nerve originate?
-The trigeminal nerve originates in the brainstem, specifically from the midbrain, pons, and medulla.
What is the role of the trigeminal ganglion in the trigeminal nerve?
-The trigeminal ganglion is the site where the sensory fibers from the trigeminal nerve converge before entering the brainstem.
Where is the trigeminal ganglion located?
-The trigeminal ganglion is located in the middle cranial fossa, within a depression of the temporal bone called the trigeminal cave.
What are the three main branches of the Ophthalmic division of the trigeminal nerve?
-The three main branches of the Ophthalmic division are the frontal, nasociliary, and lacrimal branches.
Which areas of the face does the Maxillary branch of the trigeminal nerve supply?
-The Maxillary branch supplies the middle part of the face, including the lower eyelid, conjunctiva, skin of the cheek, maxillary sinus, nasal cavity, upper lip, molars, incisors, canines, and the superior part of the palate.
What are the four terminal branches of the Mandibular branch of the trigeminal nerve?
-The four terminal branches of the Mandibular branch are the buccal, inferior alveolar, auriculotemporal, and lingual branches.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифПосмотреть больше похожих видео
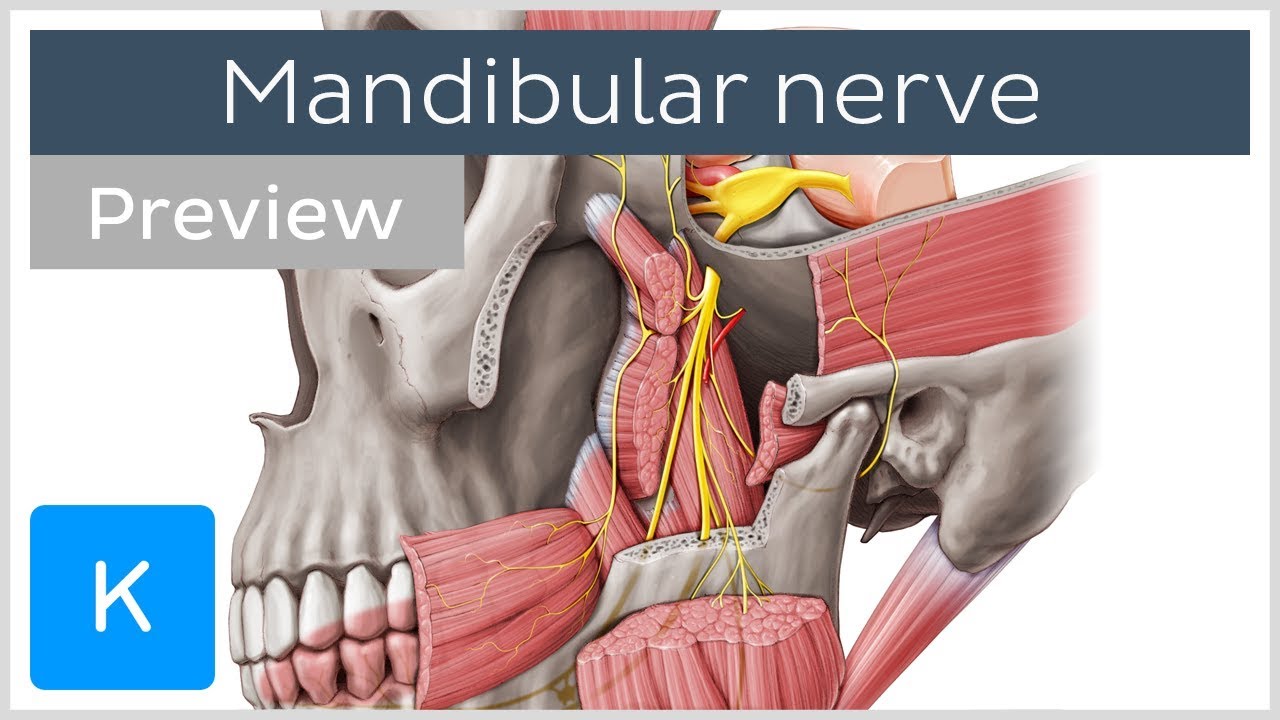
What is the Mandibular Nerve? (preview) - Human Anatomy | Kenhub
2-Minute Neuroscience: Trigeminal Nerve (Cranial Nerve V)
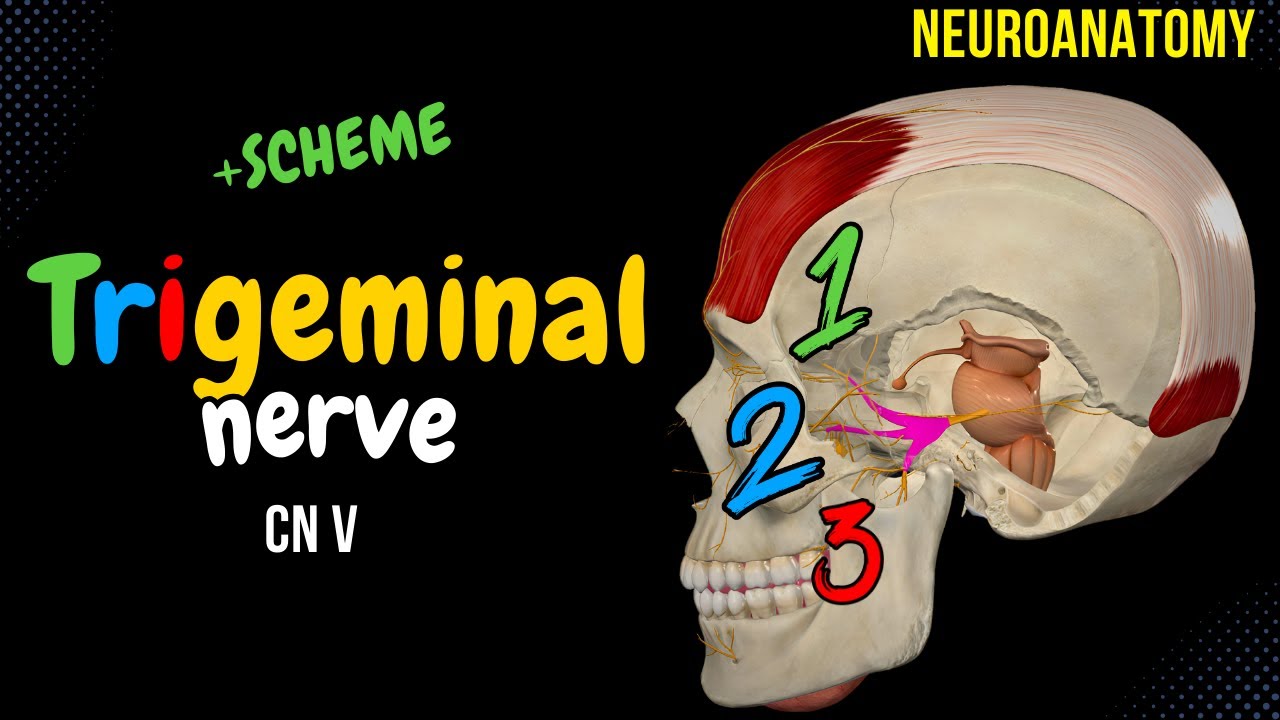
CN 5: Trigeminal Nerve (Scheme, Divisions, Pathway) | Neuroanatomy
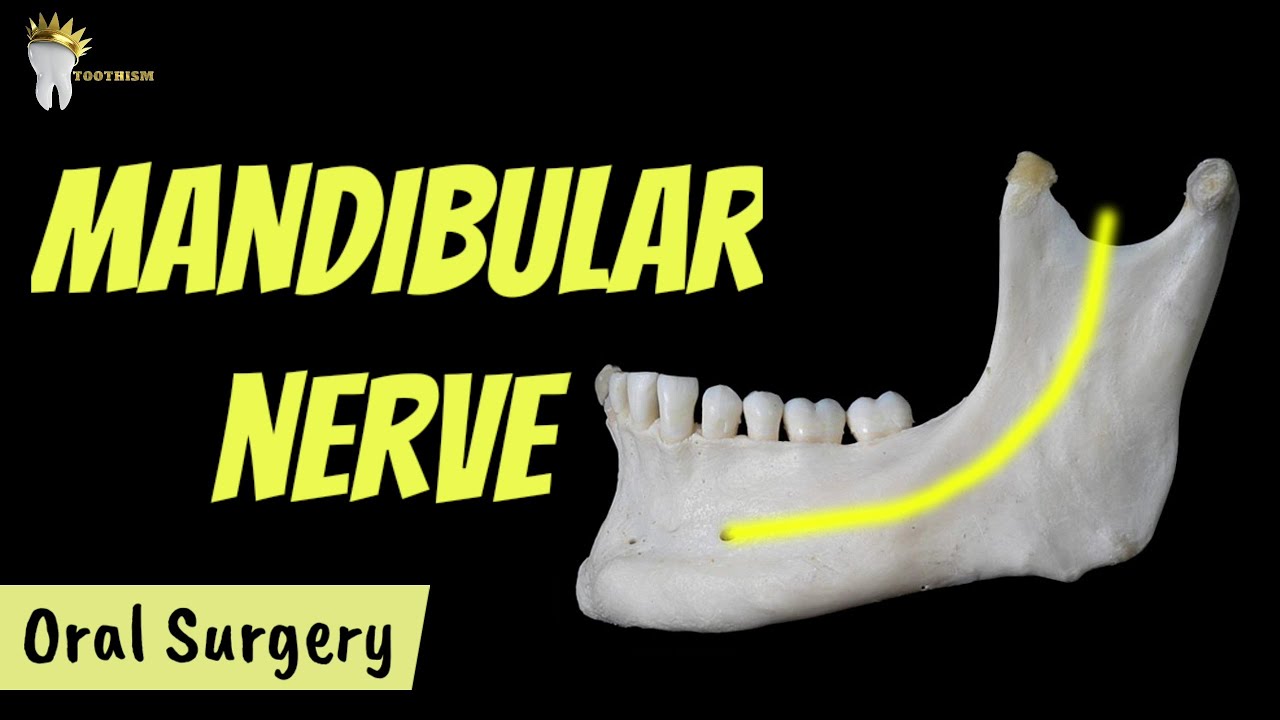
MANDIBULAR NERVE AND ITS BRANCHES
Maxillary division of Trigeminal nerve (V2 or Vb) / Maxillary nerve - Anatomy Animation

NERVE SUPPLY / INNERVATION OF MAXILLA AND MANDIBLE
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
