How lasers work (in theory)
Summary
TLDRThis video explains how lasers work by exciting atoms to emit light. When one atom releases a photon, it stimulates others to do the same, creating a cascade of light. Trapping the light between mirrors increases its intensity as it bounces and stimulates more emissions. Photons naturally align with one another, sharing the same phase, polarization, and direction. When you release this concentrated light, it forms a coherent laser beam. The video also references a demonstration where you can see lasers in action and suggests other cool science videos to explore.
Takeaways
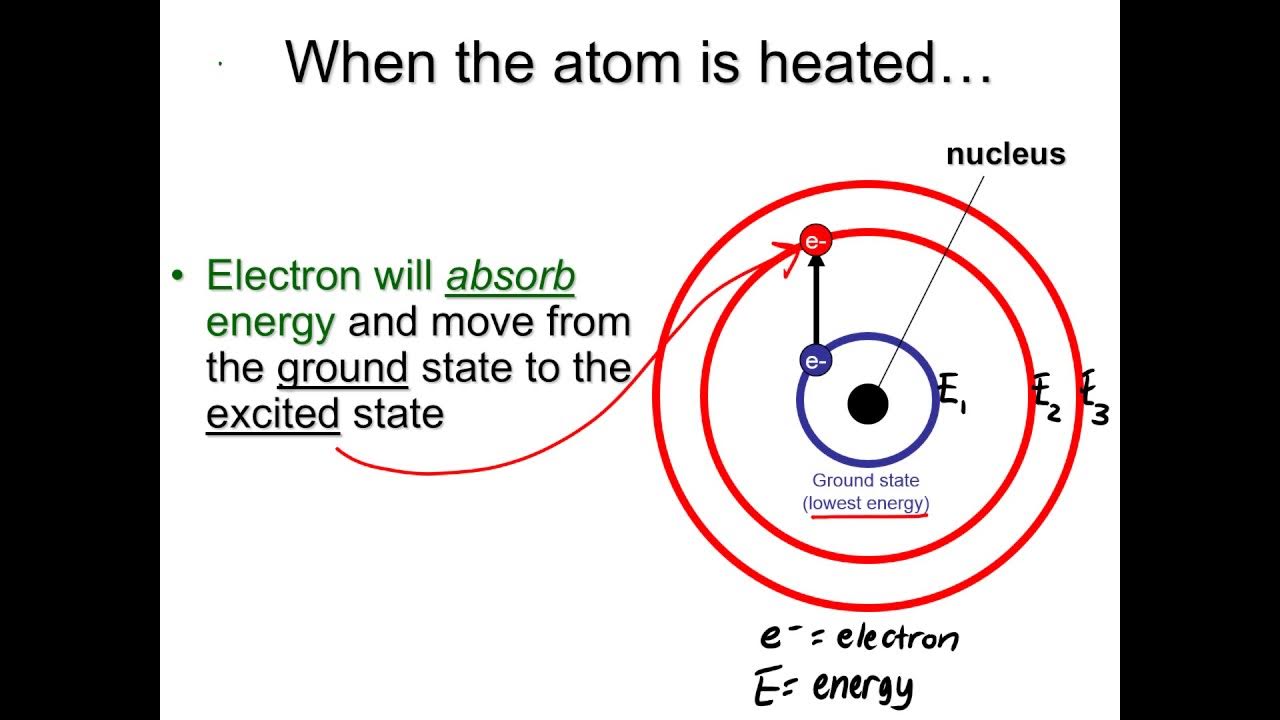
- 🔋 Lasers work by giving atoms enough energy to excite them and emit light.
- 💡 When one atom emits a photon, it stimulates others to emit photons, creating a cascade effect.
- 🔄 Trapping the light between two mirrors amplifies the laser’s power as the photons bounce back and forth.
- ✨ The passing light further stimulates the atoms to emit more light, creating a continuous emission process.
- ⚡ Atoms emit light when another photon passes by due to a tendency for photons to align in phase and direction.
- 🎲 Photons are more likely to exist in the same state (phase, polarization, direction) because they can't be distinguished from one another.
- 🤝 Photons prefer to be 'together,' and this leads to coherent light emission, even before the second photon exists.
- 🔭 A laser beam is created when photons are allowed to escape through a small hole in one of the mirrors.
- 👀 Lasers produce coherent light that is extremely powerful due to the alignment of photons.
- 📺 The script suggests checking out the 'Smarter Every Day' episode showing a laser you can interact with, and other cool science videos.
Q & A
What is the basic principle of how a laser works?
-A laser works by energizing a collection of atoms so that they are excited and ready to emit light. Once one of them spontaneously emits a photon, it stimulates others to emit light in a cascade effect.
Why is it important to trap the emitted light between two mirrors?
-Trapping the light between two mirrors allows it to bounce back and forth through the atoms, which stimulates more atoms to emit light. This amplifies the light, making the laser more powerful.
How do the atoms continue to emit light indefinitely?
-As long as the atoms are continuously re-excited with energy, they will keep emitting light. The light bouncing between the mirrors helps sustain this emission.
Why do atoms emit light when another photon passes by?
-Photons tend to want to be in the same state as other photons, sharing the same phase, polarization, and direction. This phenomenon encourages an excited atom to emit a photon when another photon passes by.
What is the probability that an excited atom will emit a photon when a solitary photon passes by?
-There’s a good chance that an excited atom will emit a photon when a photon passes by because photons tend to ‘want’ to be together, even before the second photon exists.
Why do photons prefer to be in the same state?
-Unlike flipping coins, where there are more ways for them to be in different states, photons have two ways to be in the same state and only one way to be different. This makes it more likely for photons to be in the same state.
What characteristics do photons share when they are in the same state?
-Photons that are in the same state share the same phase, polarization, and direction.
How does the laser produce a coherent beam of light?
-After a large number of photons are bouncing between the mirrors, a small hole is opened at the end to release a highly concentrated and coherent stream of light, which is the laser beam.
What does the term 'coherent light' mean in the context of lasers?
-Coherent light means that all the photons in the laser beam are in the same phase, have the same frequency, and travel in the same direction.
How can you see lasers in action as mentioned in the video?
-The video suggests watching an episode of 'Smarter Every Day,' which demonstrates a laser that you can stick your hand inside. It also offers other science videos for further exploration.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тариф5.0 / 5 (0 votes)