What are CPU Registers? Types of Registers
Summary
TLDRThis video from Altec Queries delves into the intricacies of CPU registers, explaining their role as temporary storage units within the CPU. It outlines six types of registers and contrasts them with cache memory and RAM, illustrating their distinct functions in data processing. The analogy of an office environment helps clarify the differences, emphasizing registers' speed and cost relative to other storage options. The video is a valuable resource for anyone seeking to understand the inner workings of computer memory.
Takeaways
- 💡 CPU registers are temporary storage devices built inside a CPU used to store data, addresses, and instructions during processing.
- 🔍 There are six types of CPU registers based on their functions: Memory Address Register, Memory Buffer Register, Memory Data Register, Instruction Register, Program Counter, and Accumulator.
- 📚 Cache memory, RAM, and registers are all temporary storage devices, but they serve different stages of data processing.
- 🏢 Cache memory is like an office cabinet where frequently used data is stored for quick access.
- 📝 RAM stores data during the process, similar to keeping files on your working desk while analyzing them.
- 🔧 Registers store data before processing, akin to keeping project instructions on your desk before filing them away.
- 📏 The size of a register (1 byte, 2 bytes, 4 bytes, 8 bytes, or 16 bytes) determines how much information the CPU can store in it, affecting performance.
- ⚡️ CPU registers are faster than both cache and RAM, being the fastest type of storage in a computer.
- 💰 Registers are the most expensive type of computer memory due to their speed and performance.
- 👍 The video encourages viewers to like, subscribe, and follow All Tech Queries for more informative tech videos and tutorials.
Q & A
What are CPU registers?
-CPU registers are temporary storage devices built inside a CPU. They store data, addresses, and instructions while a process is being completed.
How many types of registers are there in a computer?
-There are six types of CPU registers based on their functions: Memory Address Register, Memory Buffer Register, Memory Data Register, Instruction Register, Program Counter, and Accumulator.
What is the primary function of a register?
-The primary function of a register is to hold data before processing, facilitating faster access and manipulation by the CPU.
How do cache memory, RAM, and registers differ in terms of data storage?
-Cache memory stores data after processing, RAM stores data during the process, and registers store data before processing.
Can you provide an analogy to explain the difference between cache memory and registers?
-An analogy is that cache memory is like cabinet desks where frequently used data is stored, while registers are like a working desk where new project instructions are kept for immediate analysis.
What determines the size of a register?
-The size of a register is determined by its capacity to store information, which can be 1 byte, 2 bytes, 4 bytes, 8 bytes, or 16 bytes.
How does the size of a register affect CPU performance?
-A larger size register can increase the performance of the CPU by allowing it to store more information, which can lead to faster processing.
Why are CPU registers considered the fastest type of storage in a computer?
-CPU registers are the fastest type of storage because they are located within the CPU itself, allowing for immediate access by the processor.
What is the cost implication of using larger registers in a CPU?
-Larger registers can increase the cost of a CPU due to the higher manufacturing complexity and the use of more silicon area on the CPU chip.
How do CPU registers compare to cache and RAM in terms of speed?
-CPU registers are faster than both cache and RAM because they are located within the CPU, providing the quickest access to data for processing.
What are some other platforms where All Tech Queries can be followed?
-All Tech Queries can be followed on other platforms as well, with links provided in the video description.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифПосмотреть больше похожих видео

Registers & Special Purpose Registers in Assembly Language Urdu/Hindi | Lecture # 2 | very Important

CPU Register
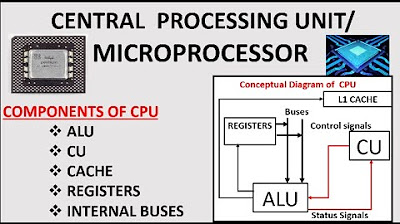
CPU and Its Components|| Components of MIcroprocessor
Primary Memory : Types and differences from Secondary Storage Memory

How Do CPUs Work?

L-1.3:Various General Purpose Registers in Computer Organization and Architecture
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
