Interior of the Earth - Chapter 3 Geography NCERT Class 11
Summary
TLDRThis educational video script delves into the Earth's interior, exploring its layers—core, mantle, and crust—and the dynamic processes within. It distinguishes between endogenous forces like volcanic activity and exogenous ones such as erosion, shaping our landscapes. The script underscores the significance of understanding these processes for human settlement and disaster mitigation. It also discusses how scientists gather information about the Earth's interior through direct observations, like deep drilling, and indirect methods, including gravitational anomalies. The video concludes with an overview of earthquake types, their measurement, and effects, promising further exploration in linked videos.
Takeaways
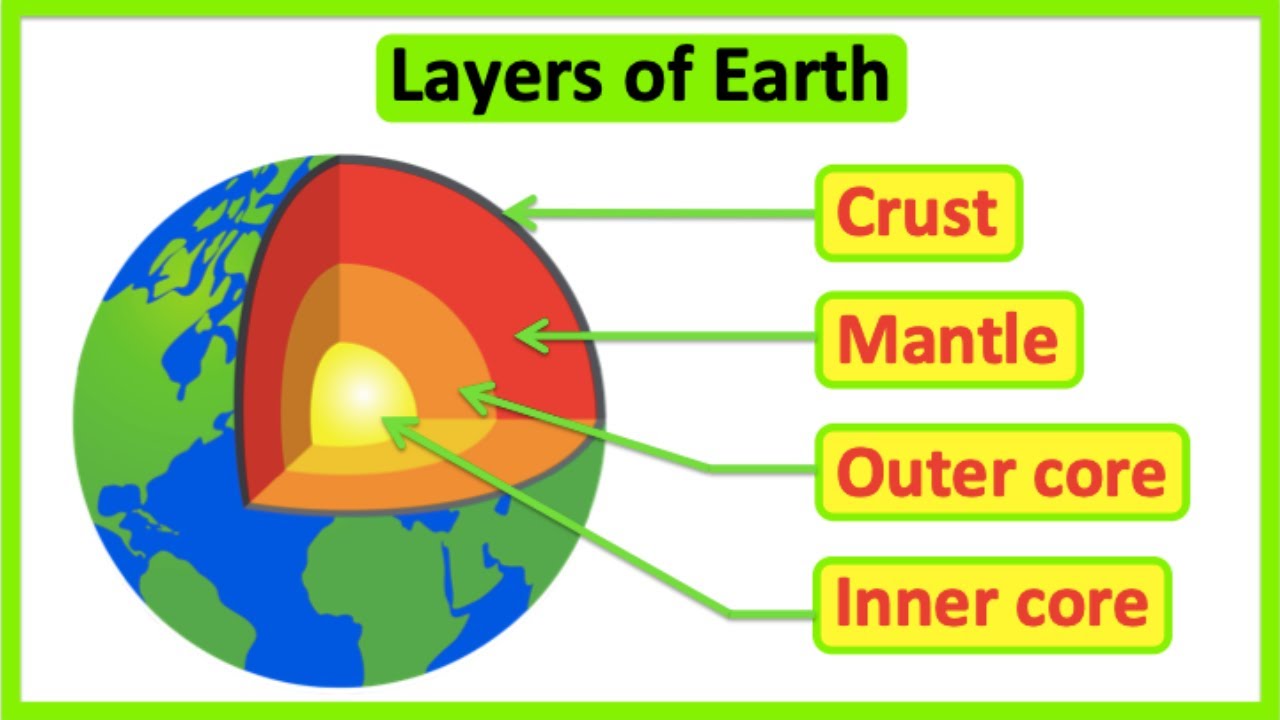
- 🌏 The interior of the Earth consists of the core, mantle, and crust, which are in a constant state of change.
- 🌋 Endogenous processes such as volcanic activity and tectonic plate movements shape the Earth's landscape, while exogenous processes like weathering and erosion modify its surface.
- 🏙️ Population density is higher in flat areas due to the influence of physiographic conditions on human settlement.
- 🌪️ Understanding the Earth's interior helps in predicting and mitigating the impact of natural disasters like earthquakes and tsunamis.
- 🔍 Direct observation of rocks and analysis of materials from deep drilling and volcanic eruptions provide insights into the Earth's interior.
- 📊 Indirect sources of information about the Earth's interior include temperature, pressure, and density changes with depth, as well as meteorite studies.
- 📉 Gravity anomalies indicate variations in the Earth's mass distribution, with higher gravity at the poles suggesting greater mass concentration.
- 💥 There are different types of earthquakes, including tectonic, volcanic, collapse, explosion, and reservoir-induced, each with unique causes and effects.
- 📈 Earthquakes are measured using the Richter scale for magnitude and the Mercalli scale for intensity.
- 🌋 Volcanoes release magma from the asthenosphere, leading to various volcanic landforms and the release of gases and pyroclastic materials.
Q & A
What are the three main layers of the Earth's interior?
-The three main layers of the Earth's interior are the core, mantle, and crust.
What are endogenous processes and how do they affect the landscape?
-Endogenous processes are internal geological activities such as volcanic activities, folding of the crust, and faulting due to plate tectonic activities. These processes change the landscape by shaping the Earth's surface features.
How do exogenous processes contribute to changes in the landscape?
-Exogenous processes are external activities like weathering, erosion, transportation, deposition, and denudation. These processes alter the outer physical shape of a landscape by wearing down and reshaping the Earth's surface.
Why is it important to understand the interior of the Earth in relation to human settlements?
-Understanding the interior of the Earth is important because human settlements are largely based on the physiographic conditions of a region. Knowledge of these conditions can help predict and mitigate risks from natural calamities such as floods and landslides.
What are the two ways scientists collect information about the Earth's interior?
-Scientists collect information about the Earth's interior through direct observations and analysis of materials. This includes studying rocks from the surface and mining areas, as well as materials that come out from the interior, such as magma during volcanic eruptions.
What is the significance of the Cola deep drill in Arctic Ocean?
-The Cola deep drill in the Arctic Ocean is significant because it is the deepest drill to date, reaching a depth of 12 km. This is an important effort to gather information about the Earth's interior, although it is still only half the depth of the continental crust.
How do indirect sources of information contribute to our understanding of the Earth's interior?
-Indirect sources of information, such as changes in temperature, pressure, and density with depth, meteorites, and variations in the Earth's gravitational field, contribute to our understanding of the Earth's interior by providing data that scientists can analyze to estimate the conditions within the Earth.
What are the different types of earthquakes mentioned in the script?
-The script mentions five types of earthquakes: tectonic, volcanic, collapse, explosion, and reservoir-induced earthquakes.
How are the strength and intensity of an earthquake measured?
-The strength or magnitude of an earthquake is measured using the Richter scale, while the intensity is determined by the Mercalli scale, which ranges from 1 to 12.
What is the role of the asthenosphere in volcanic activity?
-The asthenosphere, part of the upper mantle, contains molten rock called magma that moves and causes instability in the crust. This movement can lead to seismic activities and is the source of magma that erupts from volcanoes as lava.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифПосмотреть больше похожих видео

GRADE 10 SCIENCE QUARTER 1, MODULE 2 WEEK 2, EARTHQUAKE AND TYPES OF WAVES MELC BASED.

Materi Dinamika Litosfer (Lapisan Bumi) : Materi Geografi SMA dan SIMAK UI | Part 1

Day-8 || BA 1st semester geography Unit-1 ( Interior of Earth 🌍) by Mukul Sir #geography #earth

Earthquakes and Seismology in Earth’s Interior

Seperti Apa Kira-Kira Perjalanan ke Inti Bumi?
Layers of the Earth | Structure of the Earth | Educational Science Lesson
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
