Understanding the Immune System in One Video
Summary
TLDRThis video offers a comprehensive overview of the immune system, dividing it into the innate and specific immune systems. The innate immune system provides immediate, generalized responses through physical and chemical barriers, macrophages, and the complement system. In contrast, the specific immune system involves specialized T and B cells that recognize and combat specific pathogens. The role of dendritic cells in antigen presentation and the activation of T helper and cytotoxic T cells is emphasized, alongside the production of antibodies by plasma cells. Overall, the video aims to enhance understanding of immunology for medical students.
Takeaways
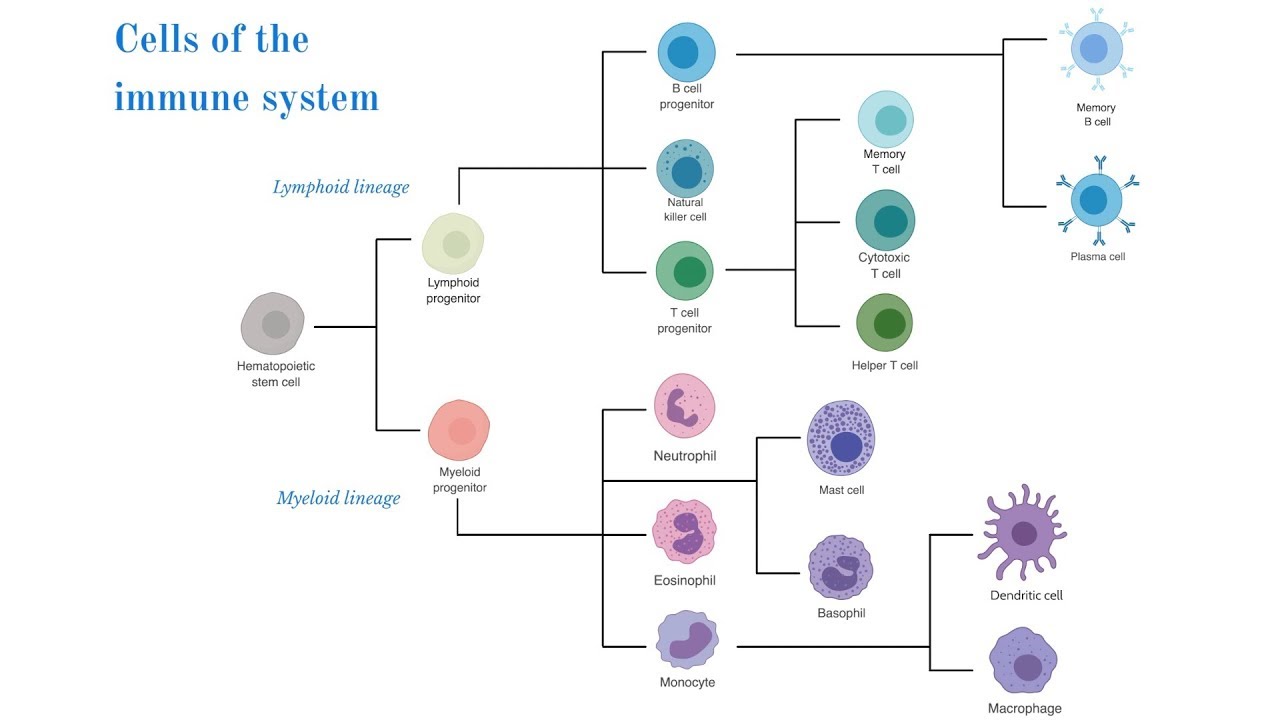
- 🦠 The immune system consists of two main components: the innate immune system, which provides immediate, generalized responses, and the specific immune system, which involves specialized T and B cells that respond to specific pathogens.
- 🛡️ The innate immune system includes physical barriers like skin and mucosa, as well as chemical barriers such as stomach acid and enzymes in tears that help destroy pathogens before infection occurs.
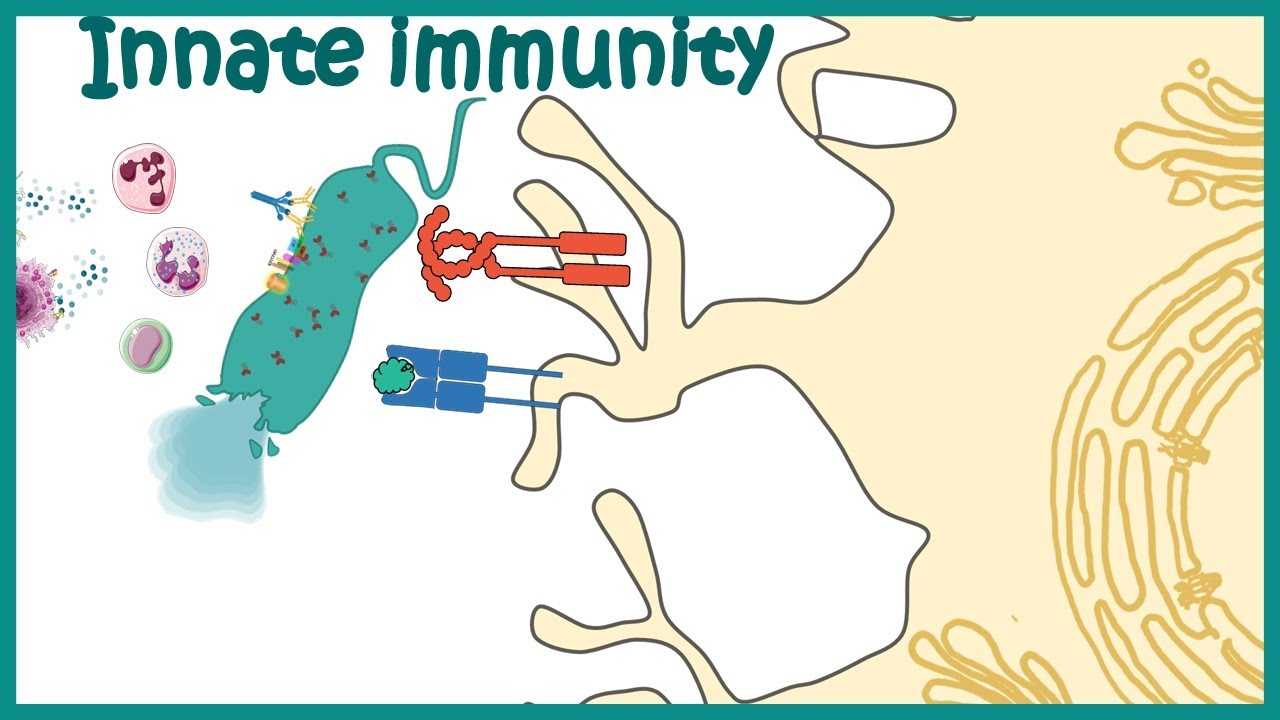
- 🔍 Macrophages and dendritic cells play crucial roles in the immune response; macrophages recognize pathogens and initiate the innate response, while dendritic cells activate the specific immune response by presenting antigens.
- ⚠️ When pathogens invade, macrophages perform phagocytosis, engulfing and digesting the pathogens, while releasing cytokines that trigger inflammation and recruit other immune cells.
- 🔥 Inflammation is a key aspect of the innate immune response, involving increased blood flow, vascular permeability, and the recruitment of additional immune cells like neutrophils and monocytes.
- 🌡️ Cytokines produced during inflammation can signal the brain to induce fever, which helps the body combat infections by creating unfavorable conditions for pathogens.
- 💡 The complement system works alongside the innate and specific immune systems, involving a cascade of proteins that enhance the immune response by marking pathogens for destruction and triggering inflammation.
- 📩 T and B cells, types of lymphocytes, circulate in the lymphatic system and blood, waiting to be activated by specific antigens presented by dendritic cells.
- 💉 Activated B cells differentiate into plasma cells that produce antibodies, which neutralize toxins, prevent viral infections, and facilitate the destruction of pathogens by immune cells.
- 🔗 Antibodies enhance the immune response by binding to pathogens, acting as opsonins that mark them for phagocytosis, neutralizing toxins, and preventing pathogens from invading healthy cells.
Q & A
What are the two main categories of the immune system?
-The two main categories of the immune system are the innate immune system and the specific immune system.
How does the innate immune system respond to infection?
-The innate immune system responds immediately with a generalized response using components already present at the infection site.
What are some examples of physical barriers that prevent infections?
-Examples of physical barriers include the skin and the mucosa of the respiratory, gastrointestinal, and urinary tracts.
What role do macrophages play in the immune response?
-Macrophages recognize pathogens using pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) and initiate phagocytosis to destroy them.
What are cytokines, and what is their function during an infection?
-Cytokines are signaling proteins that are released by macrophages to recruit and activate more immune cells, leading to inflammation.
What triggers the complement system, and what is its purpose?
-The complement system is triggered by pathogens through the lectin and alternative pathways, or by antibody-antigen complexes through the classical pathway, and it helps to destroy pathogens.
How do dendritic cells facilitate the specific immune response?
-Dendritic cells pick up antigens at the site of infection, present them to T and B cells in lymphatic tissues, and activate the specific immune response.
What are the functions of T helper cells in the immune response?
-T helper cells help activate B cells to produce antibodies, stimulate cytotoxic T cells to kill infected cells, and recruit other immune cells to the infection site.
What are antibodies, and how do they aid the immune system?
-Antibodies are proteins produced by plasma cells that can neutralize toxins, prevent viral infections, agglutinate pathogens, and act as opsonins to enhance phagocytosis.
What is the significance of memory B cells in the immune system?
-Memory B cells provide long-term immunity by remaining in the body and allowing for a quicker response upon future exposure to the same pathogen.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тариф5.0 / 5 (0 votes)