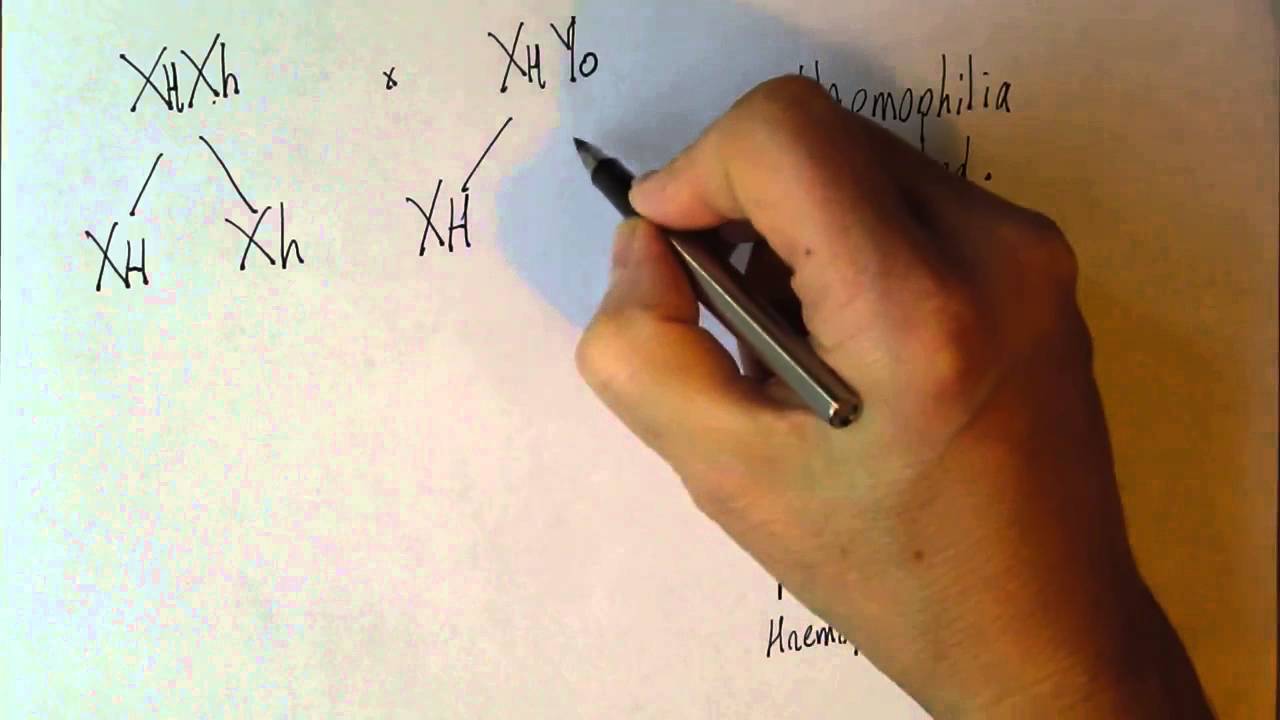What is X-linked Recessive Inheritance?
Summary
TLDRThis video script discusses the genetic inheritance of X-linked recessive conditions. A mother who is a carrier has a 50% chance of having unaffected children, a 25% chance of passing the mutation to a daughter who will likely be a carrier, and a 25% chance of passing it to a son, who will be affected. These conditions often manifest in childhood, potentially causing serious illness, intellectual and physical disabilities, and can reduce life expectancy or lead to early death.
Takeaways
- 🧬 A mother who is a carrier of a recessive condition has a 50% chance of having a child who inherits the normal gene and is unaffected.
- 👧 She has a 25% chance of passing on the mutated gene to her daughter, who will likely be a carrier.
- 👦 There is a 25% chance of passing the mutation to her son, who may be affected by the recessive condition.
- 🚹 In recessive conditions, males are typically affected more severely as they need only one copy of the mutation to exhibit symptoms.
- 🚺 Female carriers are generally healthy, but some may experience medical issues related to the condition.
- 👶 The diseases included in the panel usually manifest in childhood and can lead to serious health complications.
- 🧠 These conditions can potentially cause intellectual and physical disabilities in children.
- ⏳ They may also impact life expectancy, with some diseases leading to early death in severe cases.
- 🧪 Genetic testing can help identify carriers and affected individuals, allowing for informed family planning and medical management.
- 👨⚕️ Early diagnosis and intervention can be crucial for managing the symptoms and improving the quality of life for those with recessive conditions.
Q & A
What is the likelihood that a child of a carrier mother will inherit the normal gene and not be affected by the condition?
-A child of a carrier mother has a 50% chance of inheriting the normal gene and not being affected by the condition.
If a mother is a carrier, what is the probability that she will pass on the gene with the mutation to her daughter?
-There is a 25% chance that a carrier mother will pass on the gene with the mutation to her daughter.
What is the likelihood that a son will inherit the mutation in a recessive condition from a carrier mother?
-A son has a 25% chance of inheriting the mutation in a recessive condition from a carrier mother.
How does a recessive condition affect males compared to females?
-In recessive conditions, males are usually more severely affected than females because they need only one copy of the mutation to be affected.
Are female carriers of recessive conditions generally healthy?
-Female carriers with recessive conditions are generally healthy, although in some instances they can have medical problems.
At what age do the diseases included on the panel typically start?
-The diseases included on the panel usually start in childhood.
What potential health issues can these diseases cause in children?
-These diseases can potentially cause serious illness, intellectual and physical disability in children.
Can these diseases affect life expectancy?
-Yes, in some cases, these diseases can affect life expectancy.
What is the worst-case scenario for individuals with these diseases?
-In the worst-case scenario, the disease can lead to death at an early age.
What is the significance of the 50% chance mentioned in the script for a carrier mother's children?
-The 50% chance signifies that for each child a carrier mother has, there is an equal likelihood of inheriting either the normal gene or the gene with the mutation.
Why is it important for carrier mothers to understand the genetic risks associated with their condition?
-Understanding the genetic risks is important for carrier mothers to make informed decisions about family planning and to be aware of potential health issues their children may face.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифПосмотреть больше похожих видео
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)