Introduction to Sets || Mathematics in the Modern World
Summary
TLDRThis educational video explores the concept of sets in mathematics, using relatable examples like mobile game skins and kitchen utensils to illustrate how objects with similar properties are grouped. It explains the notation for sets and elements, introduces the roster and set builder methods for defining sets, and discusses interval notation. The video also covers cardinality, distinguishing between finite and infinite sets, and the null set. It concludes with a discussion on set equality, emphasizing that the order of elements and duplicates do not affect set equivalence.
Takeaways
- 😀 A 'set' is a collection of well-defined objects, often with similar properties, referred to as elements.
- 🎲 Sets are commonly denoted using uppercase letters, with elements enclosed in braces.
- 👥 The language of sets is used to study collections in an organized manner, such as grouping all kitchen utensils as a 'kitchen set'.
- 🔢 In mathematics, sets can be formed using numbers and their properties, like even numbers or integers.
- 📝 There are different ways to describe a set, including the roster method, which lists all members, and set builder notation, which describes the properties elements must have.
- 🌐 Interval notation is used to describe sets of real numbers within a certain range, using parentheses to indicate inclusion or exclusion of endpoints.
- 🔑 The cardinality of a set refers to the number of elements it contains and can be represented with specific symbols.
- 📉 Finite sets are countable, meaning all their elements can be listed, while infinite sets have elements that cannot all be listed.
- ❌ The null set is a unique set with no elements, often represented by a slash through a circle or empty braces.
- 🔀 Sets can be equal if they contain the same elements, regardless of the order in which they are listed.
Q & A
What does the term 'set' generally refer to in the context of the video?
-In the video, 'set' refers to a collection of well-defined objects or elements that often share similar properties or characteristics.
How are sets commonly denoted in mathematical notation?
-Sets are commonly denoted using uppercase letters, while the elements are enclosed within braces.
What is an example of a set given in the video?
-An example of a set given in the video is the set of 'Zojac skins' in the mobile legends game, which are based on the 12 fire signs of constellation.
What symbols are used to denote that an element is part of a set?
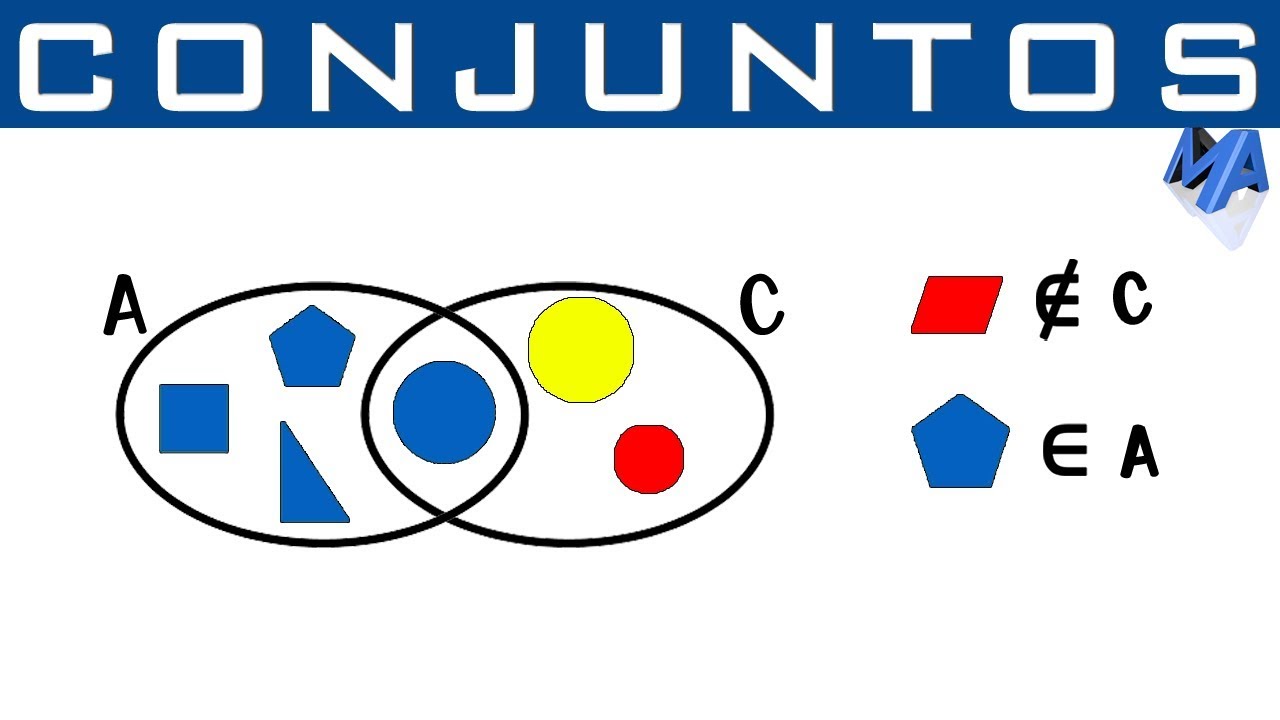
-The symbols used to denote that an element is part of a set are '∈' (element of) and '∉' (not an element of).
What is the roster method for describing a set?
-The roster method is a way to describe a set by listing all its members between braces.
How is a set described when its elements are too many to list?
-When the elements of a set are too many to list, the roster method can be used with ellipses to indicate the pattern, or set builder notation can be employed.
What is set builder notation and how is it used?
-Set builder notation is used to describe a set by stating the properties that the elements must have to be members of the set, rather than listing all the elements.
What is interval notation and how does it describe sets?
-Interval notation is used to describe sets of real numbers within a specified range, using parentheses to indicate whether the endpoints are included or not.
What is the cardinality of a set and how is it represented?
-The cardinality of a set is the number of elements it contains. It can be represented using the symbols '∣' or '∣∣' followed by the set name.
What is the difference between finite and infinite sets?
-Finite sets are sets with a countable number of elements that can be listed, while infinite sets have an unlimited number of elements that cannot be listed.
What is a null set and how is it represented?
-A null set is a set with no elements. It is represented with a circle and a slash or empty braces.
How are equal sets defined and what is the significance of the order of elements in determining set equality?
-Equal sets are sets that contain the same elements, regardless of the order of those elements. The order does not affect the equality of sets, as sets are unordered collections.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тариф5.0 / 5 (0 votes)