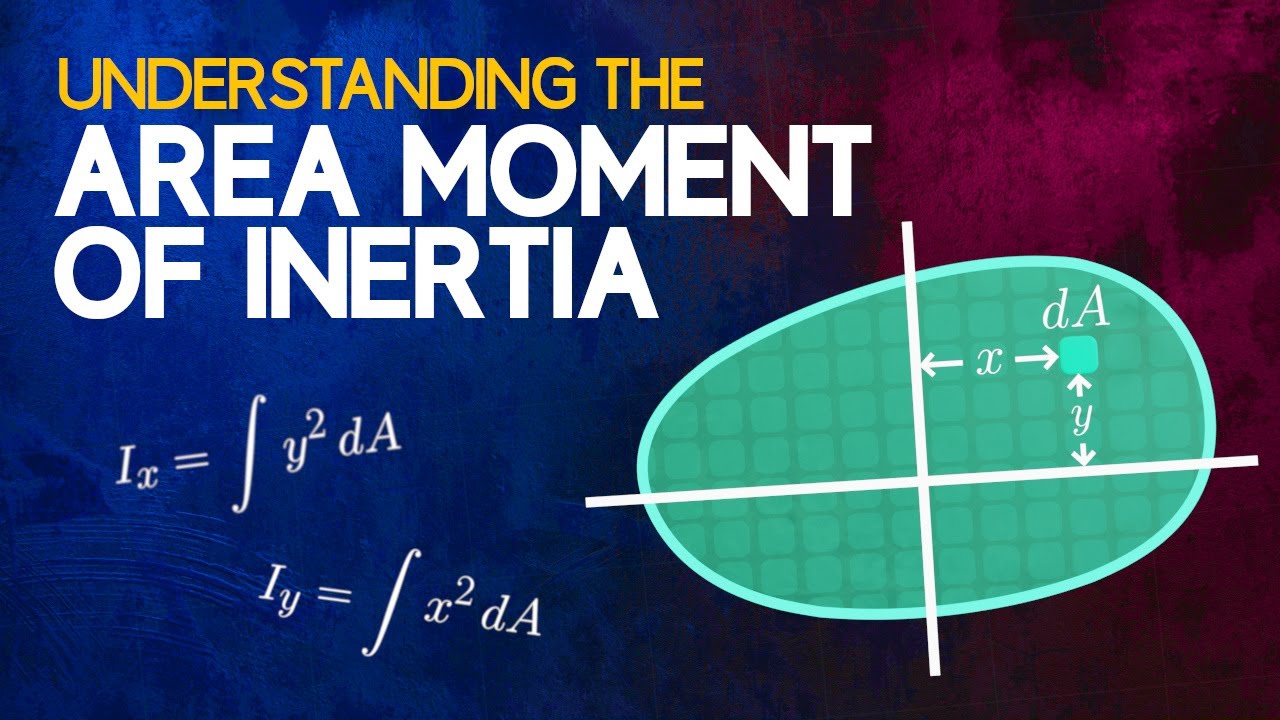
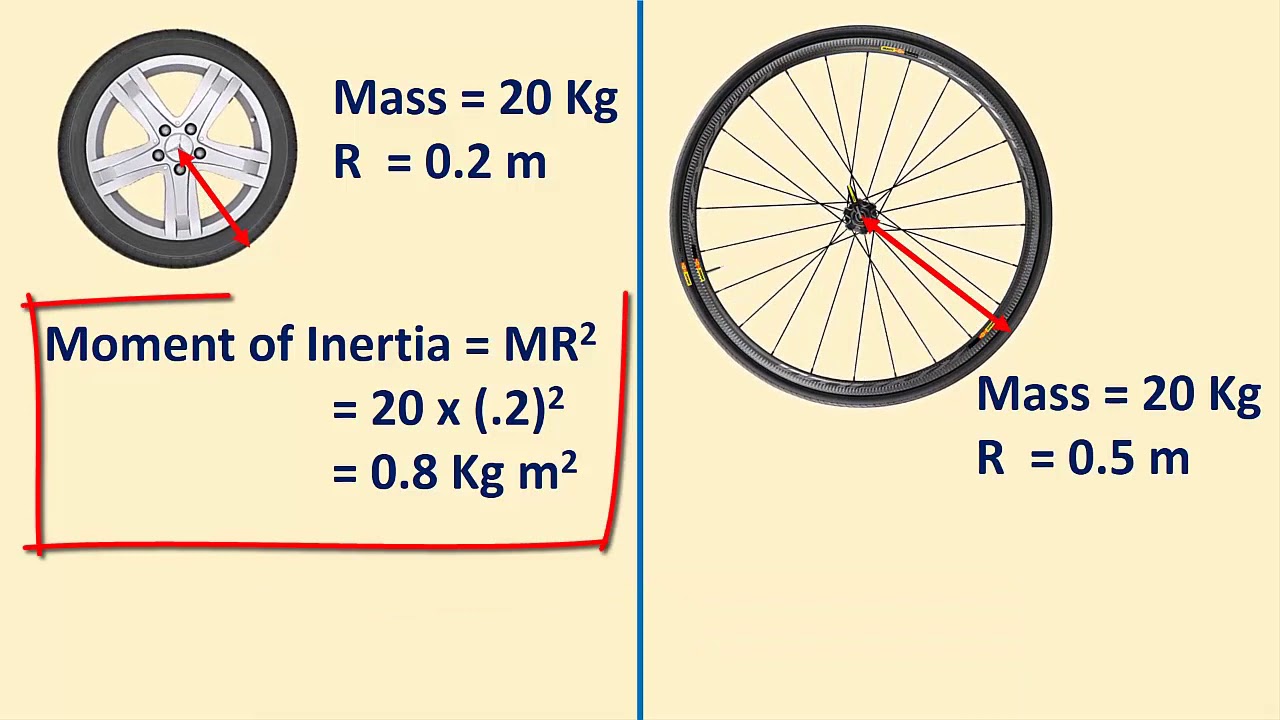
Eureka! Program 2: - Mass
Summary
TLDRThe script explores the concept of inertia through the lens of Eureka's 'The Story So Far'. It explains that inertia is not about size but mass, challenging the notion that bigger objects are inherently lazier. Using Styrofoam and lead cubes, it demonstrates that a small, dense object can have more inertia than a larger, lighter one. The script then delves into the scientific measurement of mass, referencing the international prototype of the kilogram in France, to illustrate how mass is quantified and its impact on inertia.
Takeaways
- 📚 Inertia is the resistance of an object to change its state of motion or rest; it's often associated with laziness.
- 🏋️♂️ Larger objects have more inertia and are harder to move or stop than smaller objects.
- 🤔 The misconception that all big things are lazier than small things is challenged by comparing a large Styrofoam cube with a small lead cube.
- 🔍 Inertia is not solely about size or volume; it's about the mass of an object.
- 🧠 A massive object, like a rock or a bulldozer, is hard to move or stop due to its high mass and therefore high inertia.
- 🔡 Scientists use the term 'mass' to quantify inertia, with greater mass corresponding to greater inertia.
- 🏛️ The kilogram (kg) is the international standard unit of mass, defined by a specific piece of platinum preserved near Paris, France.
- ⚖️ To determine the mass of an object, it can be compared to the standard kilogram using a balance scale.
- 📏 The mass of an object can be calculated by comparing it to the mass of the standard kilogram and counting the number of kilograms needed for balance.
- 📐 The lead cube example illustrates that it has a mass of 20 kg, significantly more than the 2 kg Styrofoam cube, highlighting the relationship between mass and inertia.
Q & A
What is the term used to describe an object's resistance to change in motion?
-Inertia is the term used to describe an object's resistance to change in motion.
Why do larger objects tend to be harder to move or stop?
-Larger objects tend to be harder to move or stop because they have more mass, which results in greater inertia.
Is inertia directly related to the size or volume of an object?
-Inertia is not directly related to the size or volume of an object, but rather to its mass.
What is the difference between a massive object and a large object in terms of inertia?
-A massive object contains more matter and is harder to move or stop compared to a large object that may be less dense, like a large Styrofoam cube.
What is the scientific measure of inertia?
-The scientific measure of inertia is mass, which is the amount of matter in an object.
Why did scientists choose mass as the measure of inertia?
-Scientists chose mass as the measure of inertia because it is directly related to how difficult it is to change an object's state of motion.
Where is the standard kilogram kept, and why is it significant?
-The standard kilogram is kept near Paris in France. It is significant because it serves as the international prototype of the kilogram against which all other masses are measured.
How do you determine the mass of an object using the standard kilogram?
-You determine the mass of an object by balancing it on a scale against the standard kilogram or multiples of it until equilibrium is achieved.
What is the mass of the lead cube mentioned in the script?
-The mass of the lead cube mentioned in the script is 20 kilograms.
Why is the Styrofoam cube easier to move than the lead cube despite being larger?
-The Styrofoam cube is easier to move than the lead cube because it has less mass, making it less resistant to changes in motion.
What is the mass of the Styrofoam cube in comparison to the lead cube?
-The Styrofoam cube has a mass of 2 kilograms, which is 10 times less than the mass of the lead cube.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тариф5.0 / 5 (0 votes)