Overview and Anatomy & Physiology | Endocrine System (Part 1)
Summary
TLDRThis educational video series introduces the endocrine system, focusing on its role in regulating the body's internal environment through various glands and hormones. It differentiates between endocrine and exocrine glands, explains the types of hormones, and their mechanisms of action. The series will cover endocrine disorders, such as Addison's vs. Cushing's and diabetes, providing foundational knowledge for understanding these conditions. The host, Eddie Watson, encourages viewers to subscribe for more critical care educational content.
Takeaways
- 📚 The video introduces a new series focused on the endocrine system, aiming to provide a solid foundation for understanding various endocrine-related disorders.
- 🔬 The endocrine system is responsible for regulating the body's internal environment through the secretion of hormones by endocrine glands into the bloodstream, as opposed to exocrine glands which secrete substances into ducts.
- 🧠 The nervous and endocrine systems work closely together to regulate growth, reproduction, metabolism, and homeostasis, with the nervous system reacting quickly and the endocrine system having a slower, widespread effect.
- 💉 Hormones are chemical messengers that affect distant target cells and can be categorized into endocrine, paracrine, and autocrine hormones, each with different mechanisms of action.
- 🔑 Hormones bind to specific receptor sites on target cells, acting like a lock-and-key mechanism to initiate a response, with some cells having multiple receptor sites for different hormones.
- 🌟 Hormones can be classified into peptides (water-soluble), steroids (lipid-soluble), and amines (amino acid derivatives with variable behavior), each interacting with receptors in different ways.
- 🔄 Feedback mechanisms, primarily negative feedback, regulate hormone release, maintaining balance by reducing stimulation for hormone production once a certain effect is achieved.
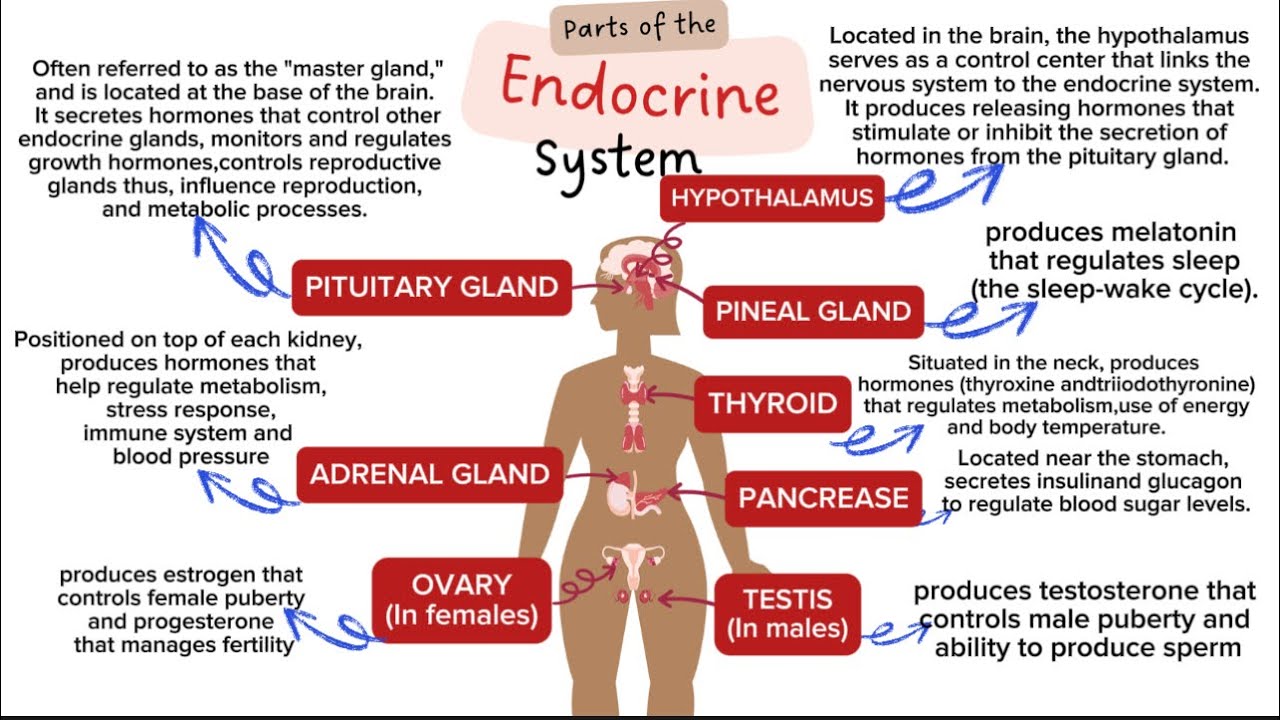
- 🧠 The hypothalamus acts as the control center of the endocrine system, linking the central nervous system with the pituitary gland, which in turn controls other endocrine glands.
- 🌐 The pituitary gland, often referred to as the 'master gland,' releases hormones that stimulate or inhibit the function of other endocrine glands, with distinct hormones from its anterior and posterior parts.
- 🚀 The endocrine system includes various glands such as the thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal glands, and gonads, each with specific roles in metabolism, calcium regulation, stress response, and sex hormone production.
- 🌱 Other organs like the heart, kidneys, stomach, and intestines also release hormones, but their primary function is not endocrine, and they contribute to broader physiological processes.
Q & A
What is the main function of the endocrine system?
-The main function of the endocrine system is to regulate the body's internal environment through the secretion of hormones by endocrine glands.
How does the endocrine system differ from the exocrine system?
-The endocrine system secretes hormones directly into the bloodstream, while the exocrine system secretes substances into ducts that lead to external places.
What is the role of the hypothalamus in the endocrine system?
-The hypothalamus acts as the control center and the link between the central nervous system and the endocrine system, regulating hormone release through signals to the pituitary gland.
Why is the pituitary gland referred to as the 'master gland'?
-The pituitary gland is called the 'master gland' because it controls the release of hormones from almost all other endocrine glands in the body.
What are the three subcategories of hormones?
-The three subcategories of hormones are endocrine, paracrine, and autocrine hormones, each with different mechanisms of action and target cells.
How do hormones interact with target cells?
-Hormones interact with target cells by binding to specific receptor sites on the cell surface or inside the cell, leading to a specific response.
What are the three main categories of hormones based on their chemical nature?
-The three main categories of hormones are peptides (protein hormones), steroids, and amines (amino acid derivatives).
How do feedback mechanisms regulate hormone release in the endocrine system?
-Feedback mechanisms, primarily negative feedback, regulate hormone release by adjusting the secretion of hormones based on the effects they have on target cells.
What is the primary function of the thyroid gland?
-The primary function of the thyroid gland is to release hormones T3 and T4, which regulate metabolism, tissue growth, and help maintain blood pressure.
What are the roles of the adrenal glands?
-The adrenal glands have two parts: the cortex, which produces steroid hormones like cortisol and aldosterone, and the medulla, which produces catecholamines like adrenaline and norepinephrine.
What is the significance of the gonads in the endocrine system?
-The gonads (ovaries in females and testes in males) are responsible for releasing sex hormones, which are crucial for secondary sexual characteristics, puberty, and menopause.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифПосмотреть больше похожих видео
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM : What It Is, Parts and Functions of the Endocrine System.

tugas Ilmu Biomedik Dasar, tentang sistem endokrim. Kelompok 2

Sistema Endócrino: Introdução | Anatomia e etc

Biologi Bab. sistem endokrin /hormonal - perkenalan apa itu sistem endokrin kelas 11

GCSE Biology - Endocrine System & Hormones #59

SISTEM ENDOKRIN : BIOLOGI SMA KELAS 11
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
