Mpox (Monkeypox) Animation
Summary
TLDRMonkeypox is a rare, zoonotic orthopoxvirus infection that can spread from animals to humans through close contact, including sexual activity. It can also be transmitted via contaminated objects or surfaces. Symptoms include flu-like signs followed by a painful rash that evolves into pustules and eventually crusts over. High-risk groups include those with close contact with infected individuals or animals, and those not vaccinated against smallpox. If experiencing symptoms or seeking more information, consultation with a healthcare provider is advised.
Takeaways
- 🦠 Monkeypox is a rare disease caused by the orthopoxvirus, which is a group of closely related viruses including the variola virus that causes smallpox.
- 🐒 It is a zoonotic disease, meaning it can spread from animals to humans.
- 🤝 Transmission can occur through close skin-to-skin contact, including sexual activity, and is not limited to genital areas.
- 🛡 Using a condom alone may not prevent infection due to the virus's ability to spread through other body fluids and surfaces.
- 🤰 Pregnant women can pass the virus to their unborn child.
- 🤒 Initial symptoms are similar to flu, including fatigue, fever, and muscle aches, followed by a rash.
- 📈 The virus can spread through the bloodstream after entering the body, with an incubation period of one to two weeks without symptoms.
- 🚨 High-risk groups include those with close contact with infected individuals, lab workers, healthcare workers, and those in contact with potentially infected animals or surfaces.
- 💉 Individuals born after 1972 likely have not received the smallpox vaccine, which could provide some protection against monkeypox.
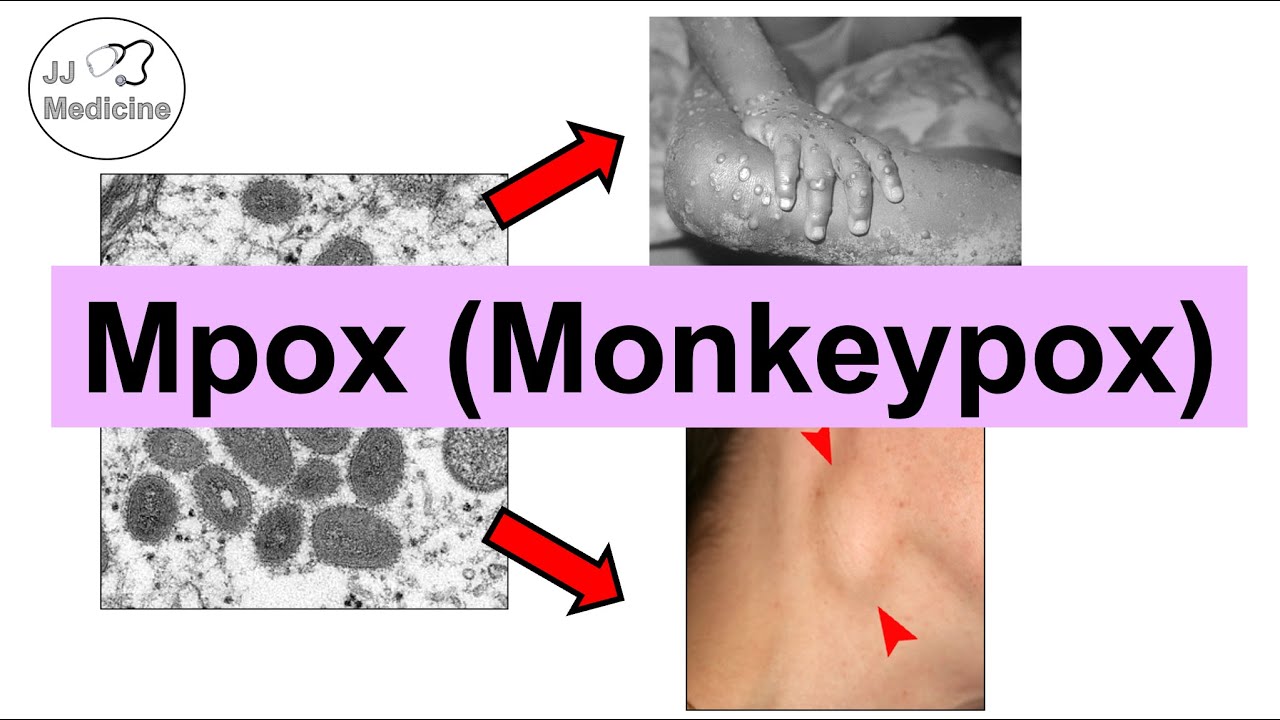
- 🌐 The rash associated with monkeypox typically appears on the genitals, anus, face, mouth, hands, feet, and chest, and can be very painful.
- 📢 If experiencing symptoms or seeking more information, one should consult a healthcare provider.
Q & A
What is monkey pox?
-Monkey pox is a rare disease caused by the monkey pox virus, which is a member of the orthopoxvirus group.
Which other viruses are closely related to the monkey pox virus?
-Other viruses in the orthopoxvirus group that can infect humans include the variola virus, which causes smallpox, the cowpox virus, and vaccinia.
What type of disease is monkey pox classified as?
-Monkey pox is classified as a zoonotic disease, meaning it can spread from non-human animals to people.
How can monkey pox be transmitted to humans?
-Monkey pox can be transmitted to humans through close skin-to-skin contact, including sexual activity with an infected person, as well as contact with rash, body fluids, or contaminated objects.
Is using a condom enough to prevent the transmission of monkey pox during sexual activity?
-Using a condom alone is probably not enough to prevent the transmission of monkey pox, as the virus can spread through contact with rash on non-genital parts of the body and other bodily fluids.
Can monkey pox be transmitted from a pregnant woman to her unborn child?
-Yes, a pregnant woman who has monkey pox can pass the virus to her unborn child.
What is the incubation period for monkey pox?
-The incubation period for monkey pox is one to two weeks, during which time the virus spreads in the bloodstream throughout the body without showing symptoms.
Who might be at a higher risk of catching monkey pox?
-Individuals at higher risk include those who have had close skin-to-skin contact with someone who has monkey pox, especially men who have sex with men in areas where monkey pox is spreading, lab workers, healthcare workers, and those who have contact with potentially infected animals or contaminated objects.
What are the initial symptoms of monkey pox?
-Initial symptoms of monkey pox may include flu-like symptoms such as exhaustion, chills, fever, headache, muscle aches, swollen lymph nodes, and a stuffy or sore throat.
How does the rash associated with monkey pox progress?
-The rash associated with monkey pox starts as a flat rash on certain areas of the body and then turns into raised, pimple-like sores filled with fluid or pus, which are often very painful and last for about a week before crusting over and falling off.
What should one do if they suspect they have monkey pox or want to learn more about it?
-If someone suspects they have monkey pox or wants to learn more about it, they should consult with their healthcare provider.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифПосмотреть больше похожих видео
Mpox (Monkeypox) | Transmission, Pathophysiology, Signs & Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment

MPOX 1.1

What Causes Monkeypox? | Monkeypox Outbreak 2022 | The Dr Binocs Show | Peekaboo Kidz

Mpox virus, maaaring makuha sa skin-to-skin at kontaminadong gamit; Sintomas, alamin!

Monkeypox Virus | Introduction #worldhealthorganization

Leptospirosis, Causes, Signs and Symptoms, Diagnosis and Treatment
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
