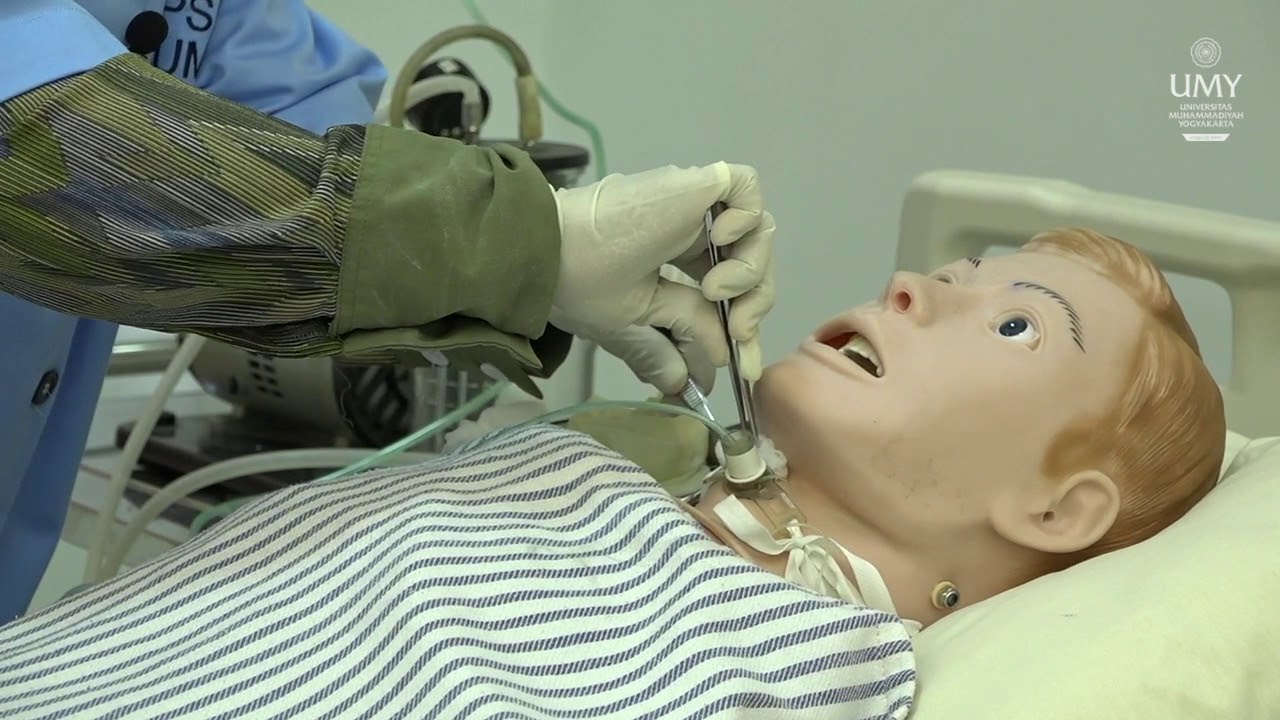
SUBGLOTTIC SUCTIONING | SUBGLOTTIC ASPIRATION | SUBGLOTTIC DRAINAGE
Summary
TLDRThis educational video introduces subglottic suctioning, a critical procedure for removing secretions above the cuff of an endotracheal or tracheostomy tube in ventilated patients. It explains the importance of this technique in preventing ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP) and outlines when and how to perform it, including manual and automated methods. The video emphasizes the need for suction in patients on mechanical ventilation over 72 hours and the use of a subglottic suction line for effective management.
Takeaways
- 😷 Subglottic suctioning is a technique used to remove secretions from above the cuff of an endotracheal or tracheostomy tube.
- 🔔 It's important to subscribe to the channel and enable notifications for instant updates on similar topics.
- 🌐 The process is crucial for preventing ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP), also known as VAP Bundle.
- 💉 The suctioning is indicated for patients on mechanical ventilation for over 72 hours, especially when using a tube with a subglottic suction line.
- 🕒 Subglottic suction should be performed every two to four hours, depending on the volume of secretions.
- 🍼 A 5 ml syringe is typically used for the aspiration of secretions during subglottic suctioning.
- 👶 The frequency of suctioning may vary based on the amount of secretions: every four hours for less than 5 ml, and every two hours for more than 5 ml.
- 🛏️ Subglottic suction is also done before extubation, patient positioning, and before deflating the endotracheal tube cuff.
- 🔧 There are different methods of subglottic suctioning, including manual, continuous, intermittent, and automated intermittent suctioning.
- 🧰 Understanding the parts of the endotracheal tube, such as the evacuation port and the subglottic suction line, is essential for manual suctioning.
- 🤖 Automated intermittent subglottic suction devices offer a closed system that eliminates the need for manual suctioning and helps prevent cross-contamination.
Q & A
What is the main purpose of subglottic suctioning?
-The main purpose of subglottic suctioning is to remove oropharyngeal secretions from above the cuff of the endotracheal or tracheostomy tube to prevent ventilator-associated pneumonia (VAP) and facilitate mechanical ventilation.
Why can't patients with an endotracheal tube naturally clear secretions above the cuff?
-Patients cannot naturally clear secretions above the cuff because the endotracheal tube prevents glottic closure, which is necessary for the natural expulsion of secretions.
What is the potential consequence of inadequate endotracheal tube cuff pressure?
-Inadequate cuff pressure may allow secretions to slip down into the trachea, potentially leading to ventilator-associated pneumonia.
Why is subglottic suction included in the VAP bundle?
-Subglottic suction is included in the VAP bundle as one of the interventions to reduce the risk of ventilator-associated pneumonia by preventing the accumulation of secretions above the endotracheal tube cuff.
For whom is subglottic suction indicated?
-Subglottic suction is indicated for patients requiring mechanical ventilation for more than 72 hours, and it is recommended that the endotracheal tube should have a subglottic suction line in such cases.
How often should subglottic suction be performed?
-Subglottic suction should be performed every two to four hours using a 5 ml syringe, with the frequency adjusted based on the amount of secretions: every four hours if less than 5 ml, and every two hours if more than 5 ml.
When should subglottic suction be done before extubation?
-Subglottic suction should be done before extubation to clear secretions from above the cuff and reduce the risk of aspiration.
What are the different methods of performing subglottic suction?
-Subglottic suction can be performed manually, continuously, intermittently, or using an automated intermittent suction device.
What is the role of the evacuation port in the endotracheal tube during subglottic suctioning?
-The evacuation port is an opening on the endotracheal tube used to connect to the subglottic suction line and aspirate the accumulated secretions.
How does an automated intermittent subglottic suction device improve patient care?
-An automated intermittent subglottic suction device eliminates the need for manual suctioning, provides consistent suctioning, and helps maintain a closed system to prevent cross-contamination.
What is the importance of understanding the parts of the endotracheal tube before performing subglottic suction?
-Understanding the parts of the endotracheal tube, such as the cuff, pilot balloon, and subglottic suction line, is crucial for correctly performing subglottic suction and ensuring patient safety.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тариф5.0 / 5 (0 votes)