5.1 INTRODUCTION TO OPERATIONS MANAGEMENT / IB BUSINESS MANAGEMENT / production, sustainability
Summary
TLDRThis introductory class to Unit 5 focuses on the role of operations management within a business. It defines operations management as a key business function responsible for improving the production process across all industry sectors. The class explores the input-output model, emphasizing the value-adding process managed by operations. It also discusses the interdependence of business functions, highlighting the collaborative nature of HR, finance, marketing, and operations management. Lastly, the concept of sustainability in business is introduced, urging operations managers to consider economic, environmental, and social impacts in their practices.
Takeaways
- 📚 Operations Management is a key area of management focused on developing, managing, and improving the production process.
- 🔑 It is one of the four business functions, alongside Human Resources, Finance, and Marketing, as covered in IB Business Management units 2, 3, 4, and 5.
- 🏭 Operations Management applies to all sectors of industry, including primary (extraction of raw materials), secondary (manufacturing), tertiary (services), and quaternary (intellectual pursuits).
- 🔄 The input-output model is central to understanding how businesses work, with operations management being the stage where inputs are processed and value is added to produce outputs.
- 🔗 There is an interdependence among all business functions, and operations management is no exception, needing to work in concert with HR, finance, and marketing for the overall success of the business.
- 🤝 The collaboration between operations management and HR is crucial for hiring the right people for production roles, ensuring the best fit for the operational needs of the business.
- 💰 Finance and operations management are interlinked, with the former setting realistic budgets based on the insights from the latter regarding production costs and processes.
- 📈 Marketing strategies are more effective when they are informed by the deep knowledge of product features and production processes that operations managers possess.
- 🌿 Sustainability is a core concept in business, encompassing economic, environmental, and social elements, and operations management plays a key role in ensuring sustainable practices within a company.
- 🌐 Sustainability in operations management involves finding ways to operate that benefit the local community, maintain financial health, and minimize environmental harm.
- 🎓 Understanding the role of operations management requires considering its definition, its place in the input-output model, its interdependence with other business functions, and its contribution to sustainability.
Q & A
What is the main focus of the first class of Unit 5?
-The main focus of the first class of Unit 5 is to learn about the role of operations management and how to explain it.
What are the four parts into which the role of operations management is broken down in the class?
-The role of operations management is broken down into four parts: defining operations management, reviewing the input-output model, discussing the interdependence of business functions, and talking about sustainability.
What is operations management and how does it relate to the four business functions?
-Operations management is an area of management responsible for developing, managing, and improving the production process. It is one of the four business functions along with HR, finance, and marketing.
Why is operations management important for all types of businesses, regardless of size or sector?
-Operations management is important for all types of businesses because it involves the core activities of producing goods or services, which is a universal requirement across all sectors and sizes of businesses.
What is the input-output model and how does operations management fit into it?
-The input-output model explains how businesses work by taking inputs (factors of production), processing them, adding value, and producing outputs (goods or services). Operations management specifically deals with the processing and value-adding stage of this model.
What is the concept of interdependence among business functions?
-The concept of interdependence among business functions refers to the idea that all business functions—HR, finance, marketing, and operations management—rely on each other and work together towards the same organizational goals.
How does operations management relate to human resource management in a business?
-Operations management works closely with human resource management to ensure that the right people are hired for the production process, with HR focusing on hiring and operations management focusing on the production itself.
What role does operations management play in the financial aspect of a business?
-Operations management plays a crucial role in the financial aspect of a business by working with finance managers to create realistic production budgets and ensure the financial well-being of the organization.
How is operations management connected to marketing in the context of a business?
-Operations management is connected to marketing through the shared knowledge of product features and production processes, which helps marketing managers devise appropriate promotional strategies.
What are the three elements of sustainability in business as discussed in the script?
-The three elements of sustainability in business are economic (maintaining financial well-being), environmental (not harming the environment), and social (benefiting the local community).
How should operations management consider sustainability in its practices?
-Operations management should consider sustainability by finding ways to operate that benefit the local community, maintain financial well-being, and do not harm the environment, potentially even improving it.
Outlines

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифMindmap

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифKeywords

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифHighlights

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифTranscripts

Этот раздел доступен только подписчикам платных тарифов. Пожалуйста, перейдите на платный тариф для доступа.
Перейти на платный тарифПосмотреть больше похожих видео

3.1 INTRODUCTION TO FINANCE / IB BUSINESS MANAGEMENT / capital expenditure, revenue expenditure

PROTOCOLO E ARQUIVO

How a control unit works inside a CPU

What Are The 8 Business Functions? A Simple Explanation | Introduction to Business Studies
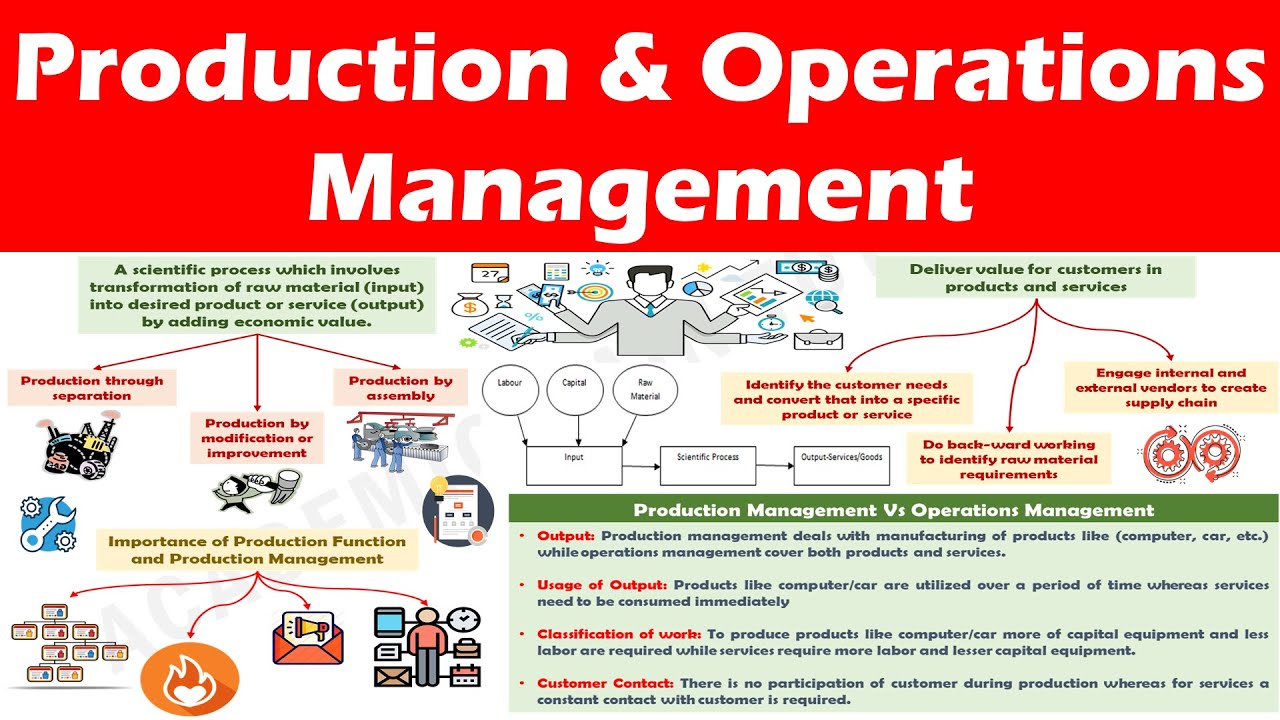
Production and Operations Management - Understanding the concept.

BUSINESS STUDIES | ll PUC | CH 01 | NATURE & SIGNIFICANCE OF MANEGEMENT - CHARACTERISTICS | S01
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
