Introduction to Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSP)
Summary
TLDRThis video introduces the concept of Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSP), a type of configuration search problem. It differentiates CSP from path search by emphasizing the goal state rather than the path. The script explains CSP's three main components: variables, domains, and constraints. It illustrates the process of formulating a CSP, assigning values to variables without violating constraints, and achieving a consistent and complete solution. Examples like the four queens puzzle and a diamond theft scenario are used to clarify the concept.
Takeaways
- 📚 The topic of the day is 'Constraint Satisfaction Problems' (CSP), which is a type of search problem.
- 🔍 CSP is distinguished from path search by focusing on achieving a goal state rather than finding a path to it.
- 👉 Two types of search techniques were discussed: path search and configuration search, with CSP belonging to the latter.
- 👣 In path search, the goal is to find a path from an initial state to a goal state, using techniques like BFS or DFS.
- 🧭 Informed search techniques use heuristics to guide the search towards more promising nodes.
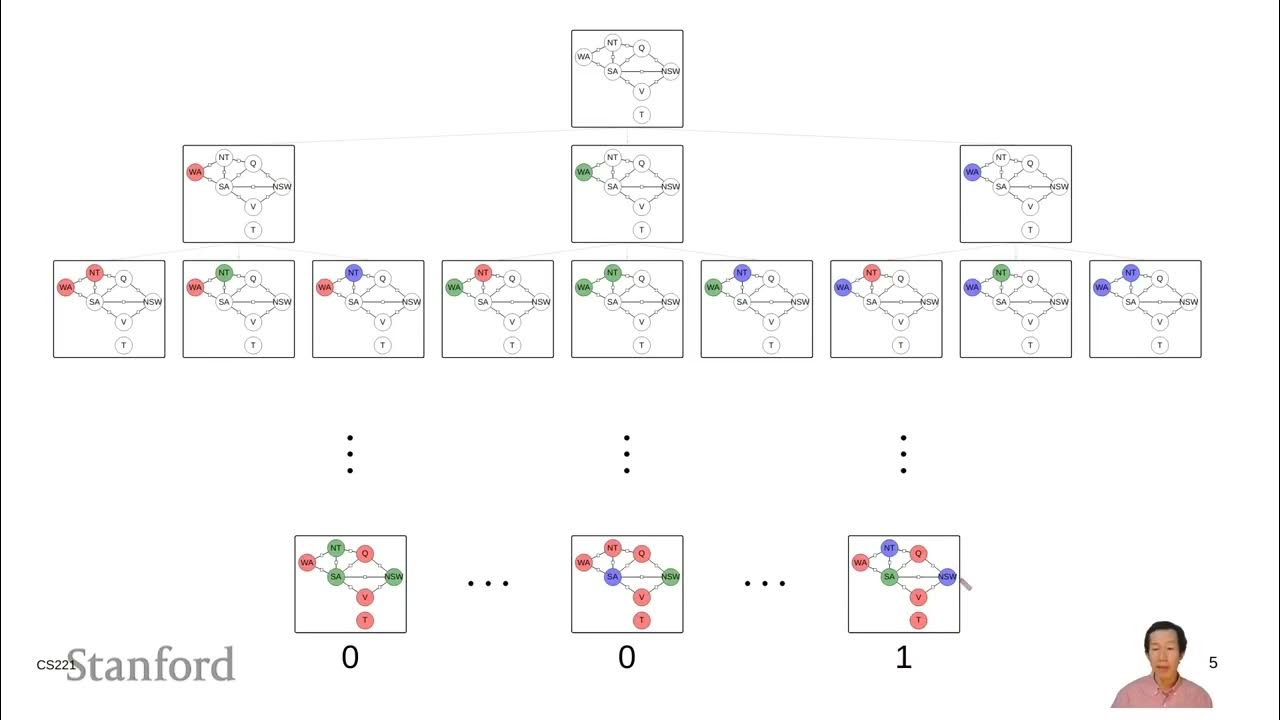
- 👑 The Four Queens problem was given as an example of a configuration search, where the arrangement of queens matters, not the sequence.
- 💎 Another example of configuration search is Ativ's diamond theft, where the path to the diamond is irrelevant; only possession of the diamond counts.
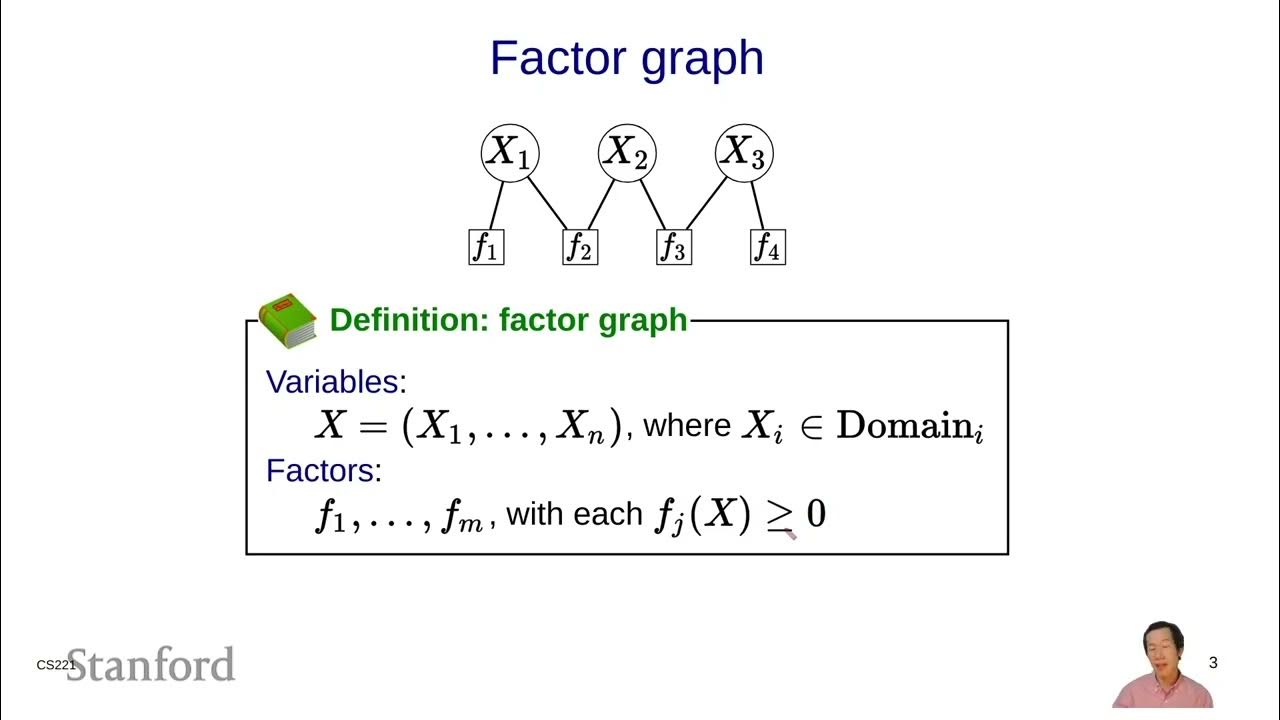
- 🔑 CSP consists of three components: variables, domains specifying possible values for variables, and constraints limiting valid value combinations.
- 📝 The initial state in CSP is an empty assignment, with no variables assigned values.
- 🎯 The successor function in CSP involves assigning values to unassigned variables, aiming for a consistent and complete solution.
- 🔒 Consistency in CSP means no constraints are violated, while completeness ensures all variables are assigned a value.
- 🚫 An example of an invalid solution was provided where assigning the same value to two variables violated the constraint of them being different.
Q & A
What is the main difference between path search and configuration search?
-Path search focuses on finding a path from an initial state to a goal state, while configuration search is concerned with finding a goal state itself, without the need to identify a path to reach it.
What are the two types of search techniques mentioned in the script?
-The two types of search techniques mentioned are uninformed search techniques like BFS (Breadth-First Search) or DFS (Depth-First Search), and informed search techniques which use heuristics to guide the search process.
What is the purpose of heuristics in informed search?
-Heuristics in informed search provide additional information to determine which node is more promising, helping to guide the search towards the goal more efficiently.
Can you explain the concept of a constraint in constraint satisfaction problems (CSP)?
-A constraint in CSP specifies which combinations of values the variables can take. It is a rule that must be satisfied for a solution to be valid, such as ensuring two variables do not have the same value.
What are the three components of a constraint satisfaction problem?
-The three components of a CSP are a set of variables, a set of domains that specify the possible values for each variable, and a set of constraints that define valid combinations of these values.
What does it mean for a solution in CSP to be 'consistent'?
-A solution is 'consistent' in CSP if it does not violate any of the given constraints among the variables that have been assigned values.
What does 'completeness' ensure in the context of CSP solutions?
-Completeness in CSP solutions ensures that every variable has been assigned a value, thus fulfilling the requirement for a solution to be fully determined.
How does the initial state in a CSP differ from that in path search?
-In CSP, the initial state is an empty assignment where no variables have been assigned values yet, whereas in path search, the initial state is a specific starting point from which a path to the goal is sought.
What is the role of the successor function in CSP?
-The successor function in CSP is responsible for assigning values to the unassigned variables, moving from the initial state towards a potential solution.
Can you provide an example of a constraint from the script?
-An example of a constraint given in the script is that variable x1 should not be equal to variable x2, ensuring that the two variables have different values.
What is the significance of the 'four queens problem' in the context of configuration search?
-The 'four queens problem' is a classic example of a configuration search problem where the goal is to place four queens on a chessboard so that none of them can attack each other, emphasizing the need to find a valid configuration rather than a path.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード関連動画をさらに表示

CS3491 AIML – Constraint Satisfaction Problem (CSP) with Example in tamil
Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSPs) 2 - Definitions | Stanford CS221: AI (Autumn 2021)

An Introduction To Constraint Programming - Jacob Allen
Constraint Satisfaction Problems (CSPs) 1 - Overview | Stanford CS221: AI (Autumn 2021)
AI - Ch03 - Uninformed search algorithms

Section 1 Worksheet Solutions: CSPs
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
