MATATAG ARALING PANLIPUNAN 7 Q4 Week 1 - Ang Pagtatatag ng ASEAN with PowerPoint and DLL
Summary
TLDRThe transcript discusses the formation and history of ASEAN (Association of Southeast Asian Nations), founded on August 8, 1967, to promote economic, social, and cultural development, as well as peace and stability in Southeast Asia. It highlights the contributions of key figures such as Narciso Ramos, Adam Malik, and Tun Abdul Razak, and details the challenges faced by Southeast Asian countries in uniting for collective progress. It also covers ASEAN's objectives, key principles, member countries, and the organizational structure, along with its motto and role in regional and international diplomacy.
Takeaways
- 🌏 ASEAN (Association of Southeast Asian Nations) was officially established on August 8, 1967 through the Bangkok Declaration to promote regional cooperation and unity in Southeast Asia.
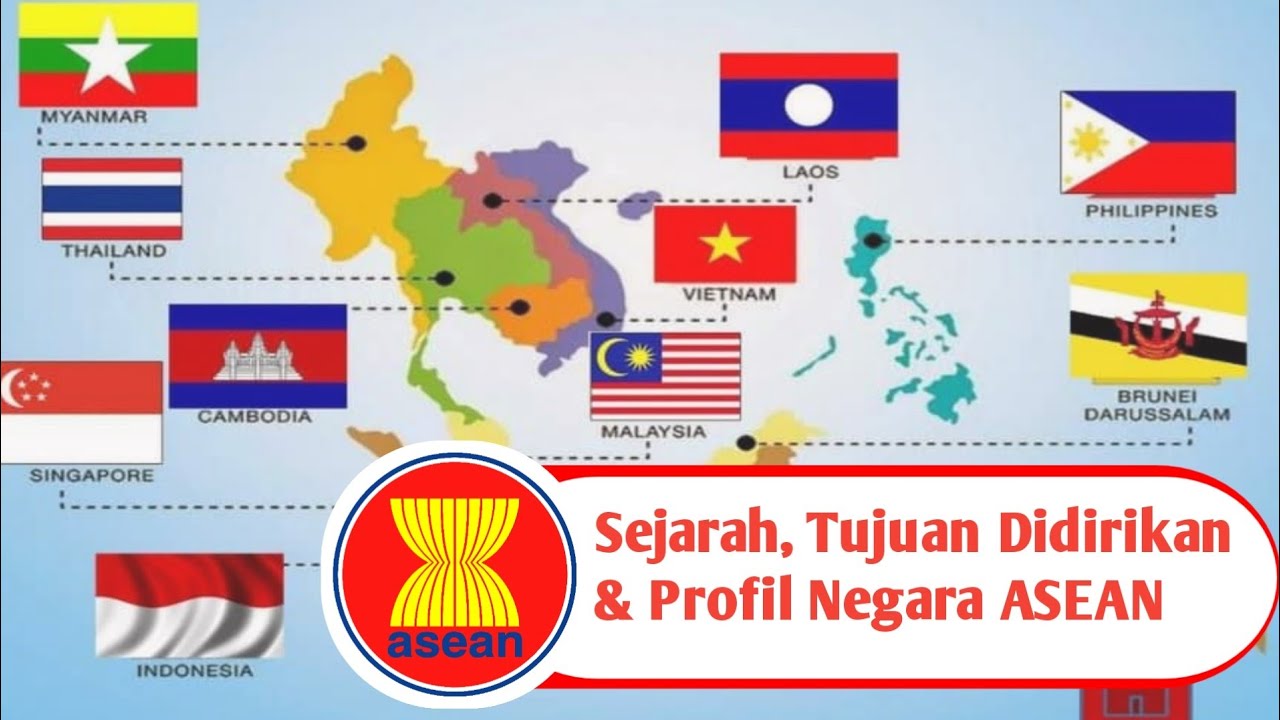
- 🤝 The five founding member states of ASEAN are Indonesia, Malaysia, the Philippines, Thailand, and Singapore, represented by their foreign ministers known as the founding fathers of ASEAN.
- 📜 The Bangkok Declaration laid the foundation for ASEAN’s goals, including economic growth, social progress, cultural development, and regional peace and stability.
- 🕊️ ASEAN was formed in the context of post–World War II challenges, regional conflicts, and the desire of Southeast Asian nations to strengthen sovereignty and avoid external interference.
- 🏛️ The Treaty of Amity and Cooperation (1976) established ASEAN’s core principles such as non-interference, peaceful settlement of disputes, respect for sovereignty, and mutual cooperation.
- 🌱 ASEAN gradually expanded its membership to include Brunei, Vietnam, Laos, Myanmar, Cambodia, and later granted Timor-Leste observer status, completing Southeast Asia’s regional grouping.
- 👥 ASEAN operates through key institutions such as the ASEAN Summit, ASEAN Coordinating Council, ASEAN Community Councils, and the ASEAN Secretariat based in Jakarta, Indonesia.
- 📊 The three main pillars of ASEAN are the Political-Security Community, the Economic Community, and the Socio-Cultural Community, each addressing different aspects of regional integration.
- 🌐 ASEAN strengthens global engagement through dialogue partnerships, including major powers and organizations, as well as frameworks like ASEAN Plus Three, ASEAN Plus Six, and the ASEAN Regional Forum.
- 🚩 The ASEAN emblem and flag symbolize unity, peace, cooperation, and shared prosperity, with rice stalks representing collective growth and solidarity among member states.
- 🧭 The ASEAN motto, 'One Vision, One Identity, One Community,' reflects the shared aspiration of Southeast Asian nations to move forward together as a unified and cooperative region.
- 📈 ASEAN plays a crucial role in improving economic development, trade, education, and cultural exchange while maintaining peace and stability across Southeast Asia.
Q & A
What is the ASEAN, and why was it established?
-ASEAN, or the Association of Southeast Asian Nations, was established on August 8, 1967, to promote regional cooperation, economic growth, and political stability among Southeast Asian countries. Its founding was driven by the desire to strengthen economic ties, ensure peace, and enhance cultural understanding within the region.
Who were the founding fathers of ASEAN?
-The founding fathers of ASEAN were Narciso R. Ramos (Philippines), Adam Malik (Indonesia), Thanat Khoman (Thailand), Tun Abdul Razak (Malaysia), and S. Rajaratnam (Singapore). They signed the Bangkok Declaration in 1967, which laid the foundation for ASEAN.
What is the significance of the ASEAN emblem and its symbolism?
-The ASEAN emblem represents unity and cooperation among the member states. The blue background symbolizes peace and stability, the rice stalks symbolize the shared aspirations of the founding members, and the colors blue, yellow, white, and red symbolize peace, prosperity, cleanliness, courage, and vitality.
What were the main challenges ASEAN faced in its early years?
-ASEAN faced challenges such as regional conflicts, political tensions, and the need to unify countries with diverse political systems, cultures, and histories. Early efforts included attempts to form smaller regional groups like ASA and MAPHILINDO, which were ultimately unsuccessful due to internal disagreements.
Which countries joined ASEAN after its founding, and when?
-Brunei joined ASEAN on January 7, 1984, Vietnam on July 28, 1995, Laos and Myanmar on July 23, 1997, Cambodia on April 30, 1999, and East Timor (Timor-Leste) gained observer status on November 11, 2022.
What is the ASEAN motto, and what does it represent?
-The ASEAN motto is 'One Vision, One Identity, One Community.' It reflects the goal of achieving a united and integrated region that works together for collective peace, stability, and prosperity.
What are the main purposes of ASEAN as outlined in its declaration?
-The main purposes of ASEAN include accelerating economic growth, promoting social progress and cultural development, ensuring regional peace and stability, fostering cooperation in areas of mutual interest, and enhancing collaboration with international organizations.
What is the ASEAN Charter, and why is it important?
-The ASEAN Charter, adopted on December 15, 2008, provides a legal and institutional framework for ASEAN. It formalized the organization's structure, principles, and objectives, ensuring greater accountability, transparency, and effectiveness in ASEAN's operations.
What are the three main pillars of ASEAN?
-The three main pillars of ASEAN are: the ASEAN Political-Security Community (APSC), focused on peace and stability; the ASEAN Economic Community (AEC), aimed at creating a single market and competitive economy; and the ASEAN Socio-Cultural Community (ASCC), which strives to improve the lives of people in the region through social and cultural cooperation.
What role does the ASEAN Summit play in the organization?
-The ASEAN Summit is the highest decision-making body within ASEAN. It meets twice a year and is composed of the heads of state or government of ASEAN member countries. The summit sets policies, discusses major regional issues, and provides guidance on the overall direction of ASEAN's initiatives.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード5.0 / 5 (0 votes)