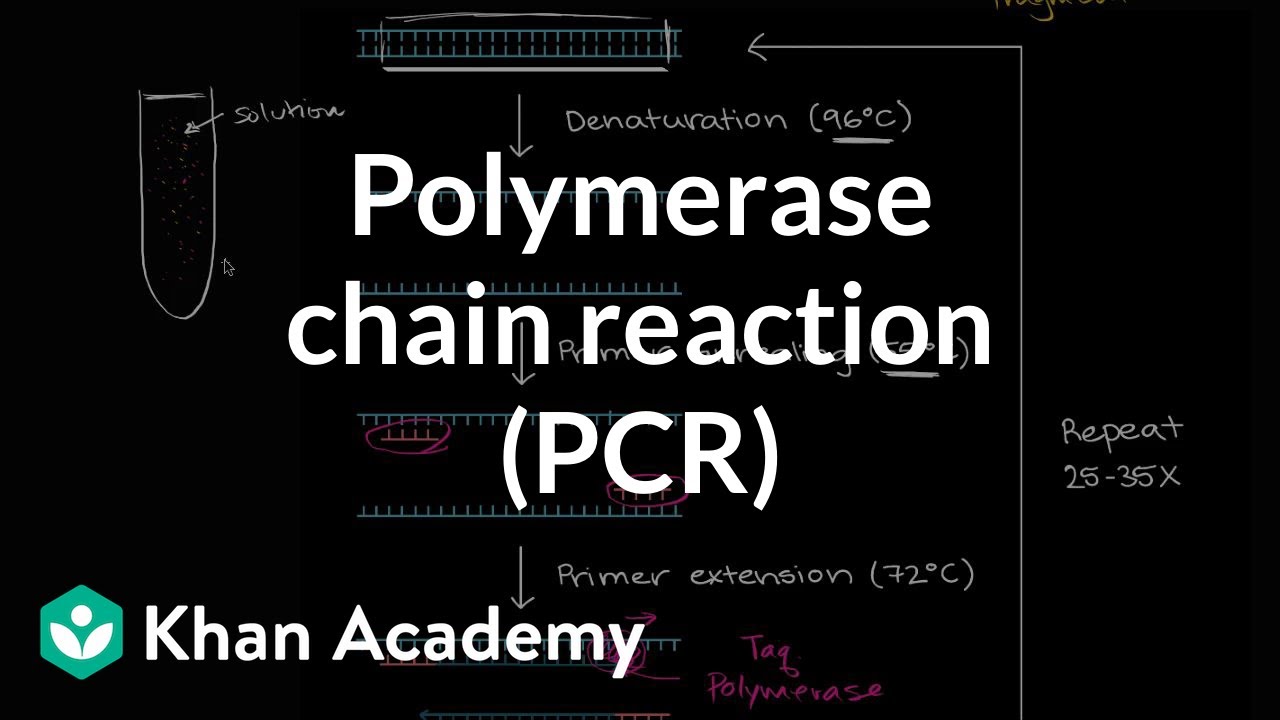
qPCR (real-time PCR) protocol explained
Summary
TLDRQuantitative PCR (qPCR), also known as real-time PCR, is a powerful technique used to detect and quantify specific gene sequences in a sample. It is commonly used in diagnostics, including viral infections like COVID-19. By monitoring fluorescence during PCR cycles, qPCR provides real-time data on gene amplification. This method uses two main assays: the SYBR Green assay, which binds to double-stranded DNA, and the TaqMan assay, which employs specific probes for enhanced detection. The cycle threshold (Ct) value indicates the concentration of DNA, with lower Ct values correlating to higher DNA amounts. qPCR is widely used in gene expression analysis and pathogen detection.
Takeaways
- 😀 qPCR (quantitative PCR) is the gold standard technique for detecting viral infections like COVID-19.
- 😀 A swab sample is taken, and RNA is extracted, then reverse transcribed into DNA for analysis with qPCR.
- 😀 Unlike conventional PCR, qPCR uses fluorescent reporters to monitor the accumulation of the amplification product in real-time.
- 😀 In qPCR, the fluorescence increases with each cycle, generating a classic qPCR curve, and the threshold cycle (Ct) value is used to determine the presence of the target gene.
- 😀 A lower Ct value indicates a higher DNA concentration, while a higher Ct value indicates a lower DNA concentration.
- 😀 The qPCR process involves two main assays: the SYBR Green assay (uses an intercalating dye) and the TaqMan assay (uses probes).
- 😀 In the SYBR Green assay, the dye binds to double-stranded DNA, emitting fluorescence as amplification occurs.
- 😀 In the TaqMan assay, specific probes bind to the target sequence, and fluorescence is emitted when the probe is cleaved during amplification.
- 😀 Both assays generate a fluorescence curve during amplification, allowing for quantitative gene expression analysis.
- 😀 qPCR is widely used in diagnostics for detecting pathogens and in gene expression studies to compare multiple genes.
- 😀 The Ct value helps quantify gene expression by showing at which cycle the signal intensity reaches the threshold.
Q & A
What is qPCR and why is it important?
-qPCR (quantitative PCR), or real-time PCR, is a technique used to quantitatively measure the presence of a specific DNA or RNA sequence in a sample. It is widely used for diagnostics, especially in detecting viral infections like COVID-19, and for gene expression analysis.
How does qPCR differ from conventional PCR?
-In conventional PCR, DNA amplification is observed at the end of the process, while in qPCR, amplification is monitored continuously during the reaction. This allows qPCR to measure the accumulation of DNA in real-time, providing quantitative data.
What is the significance of the CT value in qPCR?
-The CT (cycle threshold) value represents the point at which the fluorescent signal generated by the PCR product exceeds a set threshold. A lower CT value indicates a higher concentration of the target sequence, while a higher CT value suggests a lower concentration.
What are the main types of qPCR assays?
-The two main types of qPCR assays are the SYBR Green assay and the TaqMan assay. The SYBR Green assay uses a dye that binds to double-stranded DNA, while the TaqMan assay uses a specific probe with a fluorescent reporter and a quencher to detect the target sequence.
How does the SYBR Green assay work?
-In the SYBR Green assay, the dye binds to double-stranded DNA during amplification, and the fluorescence is monitored after each cycle. The increase in fluorescence corresponds to the accumulation of DNA, which is tracked to provide quantitative results.
How does the TaqMan assay work?
-In the TaqMan assay, a specific probe is used that binds to the target DNA sequence. This probe contains a fluorescent reporter and a quencher. During amplification, the probe is cleaved, separating the reporter from the quencher, leading to the emission of fluorescence, which is detected.
Why is qPCR considered the gold standard for viral infection testing?
-qPCR is highly sensitive and allows for the accurate detection and quantification of viral genetic material, making it ideal for diagnosing infections like COVID-19. Its ability to detect viral RNA even in low quantities makes it the gold standard.
What is the process for conducting qPCR with a viral sample?
-In a qPCR test for viral infections, a swab sample is taken from the patient. The RNA is extracted, reversed transcribed into complementary DNA (cDNA), and then analyzed through qPCR to detect the viral genetic material.
How does qPCR help in gene expression analysis?
-qPCR allows researchers to compare the expression levels of different genes by measuring the CT values. A lower CT value indicates higher gene expression, while a higher CT value suggests lower expression.
What is the role of the DNA polymerase in qPCR?
-The DNA polymerase in qPCR is responsible for amplifying the target DNA. In the case of TaqMan assays, the polymerase also has a 5' exonuclease activity that cleaves the TaqMan probe during amplification, releasing the fluorescent signal.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード関連動画をさらに表示
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)