3 Identification of Backtracking Problems
Summary
TLDRThe video provides an in-depth exploration of algorithmic strategies, focusing on approaches like backtracking and greedy algorithms. The speaker emphasizes the importance of understanding problem constraints, including time complexity and the number of choices. Backtracking is explained as a method where manually constructing a decision tree may be impractical due to high complexity. The speaker also discusses when to apply greedy algorithms, highlighting the need for careful consideration toGot it! Please let me know if there’s anything else you'd like me to do, and I’ll avoid failures. The video encourages critical thinking, practice, and intuition when choosing the best approach for algorithmic challenges.
Takeaways
- 😀 Understand the problem's constraints: Recognizing time complexity and the number of choices helps you choose the right approach.
- 😀 Recursion: It’s essential to grasp the recursive tree structure but avoid manually drawing it in complex cases as it becomes too cumbersome.
- 😀 Backtracking: Manually constructing a backtracking tree is impractical due to the large number of choices. Instead, rely on understanding the algorithm's structure and apply it programmatically.
- 😀 Greedy Algorithms: Don't apply greedy methods hastily. Carefully evaluate if the problem can be solved greedily, as this approach can fail in some cases.
- 😀 Test your intuition: Before attempting an algorithm, ask yourself if you can think of a greedy or recursive approach, and consider its potential failure points.
- 😀 Avoid overcomplicating problems: If you find yourself struggling to visualize a backtracking tree or an approach by hand, focus on the problem's core logic and use tools like recursion or backtracking in code.
- 😀 Recursive problems often grow exponentially. Be mindful of the time complexity when considering recursive solutions.
- 😀 Always validate your approach before diving into coding. Ensure you understand the theoretical foundation and the edge cases of the solution.
- 😀 Don't rush with greedy solutions. Take time to think through if the greedy strategy will always work or could lead to incorrect outcomes.
- 😀 Practical problem-solving is essential for developing algorithmic intuition. Testing different methods on a problem will help you understand which technique works best.
Q & A
What is the importance of understanding constraints in algorithmic problem-solving?
-Understanding constraints, such as time complexity and the number of choices, is crucial for determining the most efficient approach to solving a problem. It helps in deciding whether recursive or backtracking methods are feasible and ensures that the solution works within the problem’s limits.
Why is it not recommended to manually construct a backtracking tree by hand?
-Manually constructing a backtracking tree can be impractical because the number of choices or variables often increases exponentially, making it difficult to handle. Backtracking trees can become very large, making manual construction time-consuming and error-prone.
How can the number of choices in a backtracking problem affect the solution?
-The number of choices in a backtracking problem determines the complexity of the solution. As the number of choices increases, the potential solution space grows rapidly, which can make finding a solution slower and more computationally expensive.
What role does greedy thinking play in problem-solving?
-Greedy thinking is about making locally optimal choices at each step, with the hope that these choices will lead to a global optimum. However, it’s essential to critically assess whether a greedy approach is appropriate, as it may fail in cases where the global optimum cannot be reached by making such choices.
What should you do if you feel a greedy approach is not suitable for a problem?
-If you feel that a greedy approach might not be suitable, it’s important to consider alternative methods such as dynamic programming, recursion, or backtracking. Always question whether making a greedy choice will lead to a correct solution, and try to evaluate the problem from different perspectives.
What is the suggested approach to tackle a problem when backtracking is involved?
-The speaker suggests first approaching a problem with logical reasoning and trying to solve it without using backtracking. Once a basic understanding is achieved, you can then apply backtracking to see how it helps refine the solution and to better understand when it is needed.
Why is it important to practice backtracking through example problems?
-Practicing backtracking through examples allows you to gain a deeper understanding of its application and limitations. By doing so, you become more comfortable with recognizing when backtracking is the best approach and how to structure the problem-solving process effectively.
What does the speaker mean by 'you will feel it' when working on backtracking problems?
-When the speaker says 'you will feel it,' they mean that by working through problems and applying backtracking, you will intuitively understand when the method is appropriate and how it improves the problem-solving process. It’s about developing an instinctive sense of how backtracking works in practice.
How can recursive trees and backtracking trees differ in terms of problem-solving approaches?
-Recursive trees typically represent problems where each step leads to a single or a limited set of choices, often with a clear path to the solution. Backtracking trees, on the other hand, involve exploring multiple choices and paths, where not all choices may lead to a solution, and the process may require backtracking to find the correct path.
What advice is given for tackling problems that require both recursive and backtracking approaches?
-The advice is to first reason through the problem logically without relying on backtracking. Once you have a solid understanding of the problem, apply backtracking to explore possible solutions. This approach helps you gain clarity on how the two methods work together and when each is most effective.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード関連動画をさらに表示

1 Backtracking Course Overview

03. Berpikir Komputasional - Solusi Optimal dengan Algoritma Pintar - Informatika Kelas XII
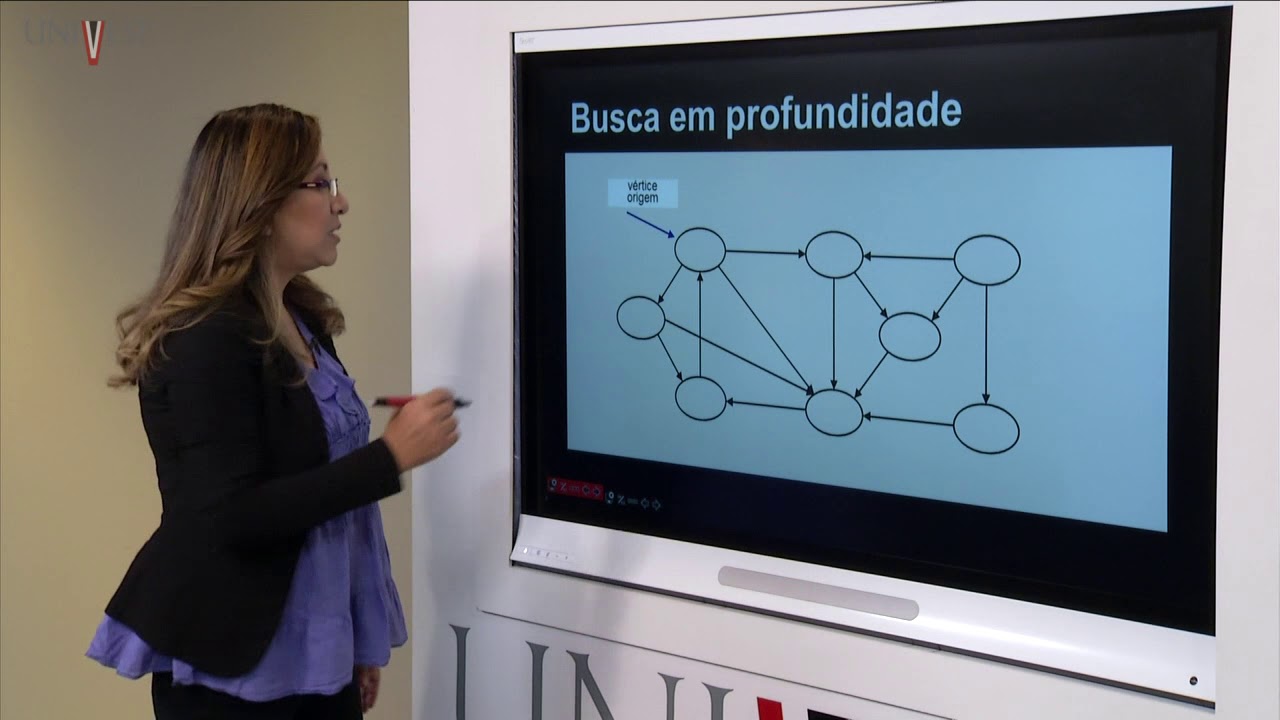
Projeto e Análise de Algoritmos - Aula 12 - Algoritmos de busca em largura e profundidade em grafos

Algorithmic Thinking with Python | Module - 1 Part - 1 | B.Tech. KTU 2024 Scheme | Semester - 1 |

Meraih Potensi Unik : Pendidikan Individual untuk Anak Berkebutuhan Khusus.
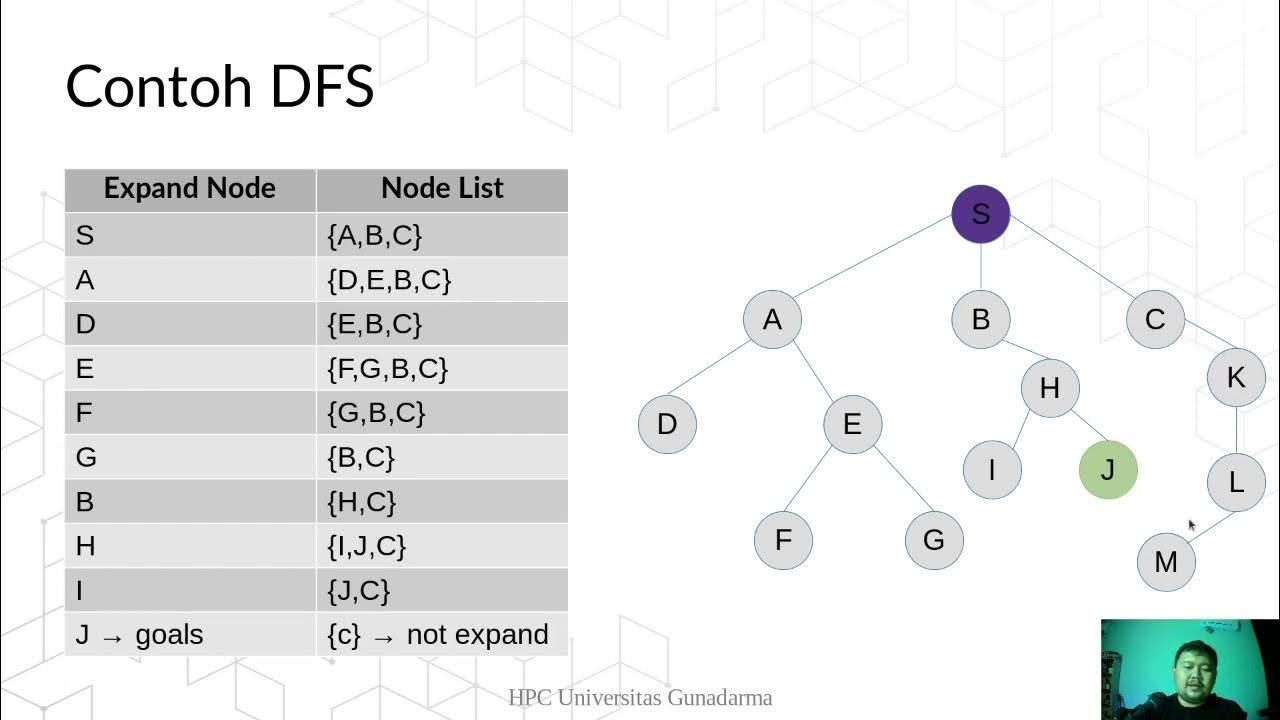
DFS -Depth First Seach
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
