O que o fisioterapeuta precisa saber sobre contrações musculares?
Summary
TLDRIn this video, Professor Bárbara explores the different types of muscle contractions, focusing on isometric, concentric, and eccentric contractions. She emphasizes their role in both movement and exercise prescription, highlighting the importance of understanding how muscles generate internal force and how external forces, like gravity, influence movement. Through practical examples, such as a squat with a barbell, the video explains how these contractions help maintain stability or control movements. The goal is to provide insight into how specific muscle contractions affect daily activities and how they can be used in rehabilitation and training.
Takeaways
- 😀 Muscle contractions can be classified into three types: isometric, concentric, and eccentric.
- 😀 Active movement requires internal muscle action, where muscles generate force to perform the movement.
- 😀 Passive movement is when external forces, like another person or mechanical equipment, move the body, without internal muscle activation.
- 😀 In active movement, we have pure active movement, assisted active movement, and self-assisted active movement.
- 😀 Muscle contractions can occur with or without external resistance, but gravity is always present as an external force.
- 😀 Isometric contractions occur when muscles contract without changing length, like holding a position or stabilizing the body.
- 😀 Concentric contractions happen when muscles shorten as they generate force, such as lifting a weight against gravity.
- 😀 Eccentric contractions happen when muscles lengthen while generating force, controlling movement, like when descending a step.
- 😀 For muscle control, eccentric contractions are important for managing downward movement and resisting gravity.
- 😀 The force from gravity should always be considered when prescribing exercises, as it affects muscle contraction and movement dynamics.
- 😀 Practical examples, like lifting a cup or holding a plank position, demonstrate the different types of muscle contractions in real-life scenarios.
Q & A
What is the main focus of this video?
-The main focus of the video is to explain and differentiate the various types of muscle contractions—specifically isometric, concentric, and eccentric contractions—along with their relevance in movement analysis and exercise prescription.
What is the difference between passive and active movement?
-Passive movement occurs when an external force or someone else moves the body without the individual's muscles generating internal force. Active movement, on the other hand, involves the individual's muscles generating internal force to produce the movement.
What are the three types of muscle contractions discussed in the video?
-The three types of muscle contractions discussed are isometric, concentric, and eccentric contractions. In isometric contractions, the muscle generates force without changing length. In concentric contractions, the muscle shortens while generating force. In eccentric contractions, the muscle lengthens while controlling the force.
What role does gravity play in muscle contractions during movement?
-Gravity is a constant external force that acts on the body, either aiding or resisting movement. When prescribing exercises, it's essential to consider how gravity interacts with the movement to understand the forces at play and the type of muscle contraction involved.
How is an isometric contraction defined?
-An isometric contraction occurs when the muscle generates force but its length does not change. The muscle remains contracted without moving, such as in exercises like the plank, where you hold a position without altering the muscle's length.
Can you provide an example of an eccentric contraction from everyday life?
-A common example of an eccentric contraction is when a person descends a step or a staircase. The quadriceps must control the descent of the body by gradually lengthening, resisting gravity and preventing a fall.
Why is the concept of external force important when prescribing exercises?
-Understanding external forces, like gravity or weights, is crucial in exercise prescription because they influence how muscles contract. The external forces determine the type of contraction needed to perform the movement effectively, whether it's isometric, concentric, or eccentric.
What is the difference between concentric and eccentric contractions?
-In concentric contractions, the muscle shortens as it generates force (e.g., lifting a weight). In eccentric contractions, the muscle lengthens while generating force (e.g., lowering a weight in a controlled manner). Both types of contractions involve active muscle engagement but have different effects on muscle length.
How can the concept of muscle contraction be applied to physical therapy?
-In physical therapy, understanding muscle contractions is critical for rehabilitation. For instance, eccentric contractions may be emphasized for controlling movements and preventing injury, while concentric contractions might be focused on strength building. Correctly identifying the type of contraction allows for better-targeted exercises for recovery.
Why does the video emphasize the importance of muscle activation in exercise prescription?
-The video emphasizes muscle activation because it is the foundation of any movement. Whether the movement is active, assisted, or active-assisted, muscle activation is necessary to produce internal force. This internal force is essential for controlling and performing movements during exercises and rehabilitation.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード関連動画をさらに表示

Exercise Physiology | Skeletal Muscle Force-Velocity Relationship

Muscle Contraction Types

Type of muscle contraction

Isotonic, Isometric, Eccentric and Concentric Muscle Contractions
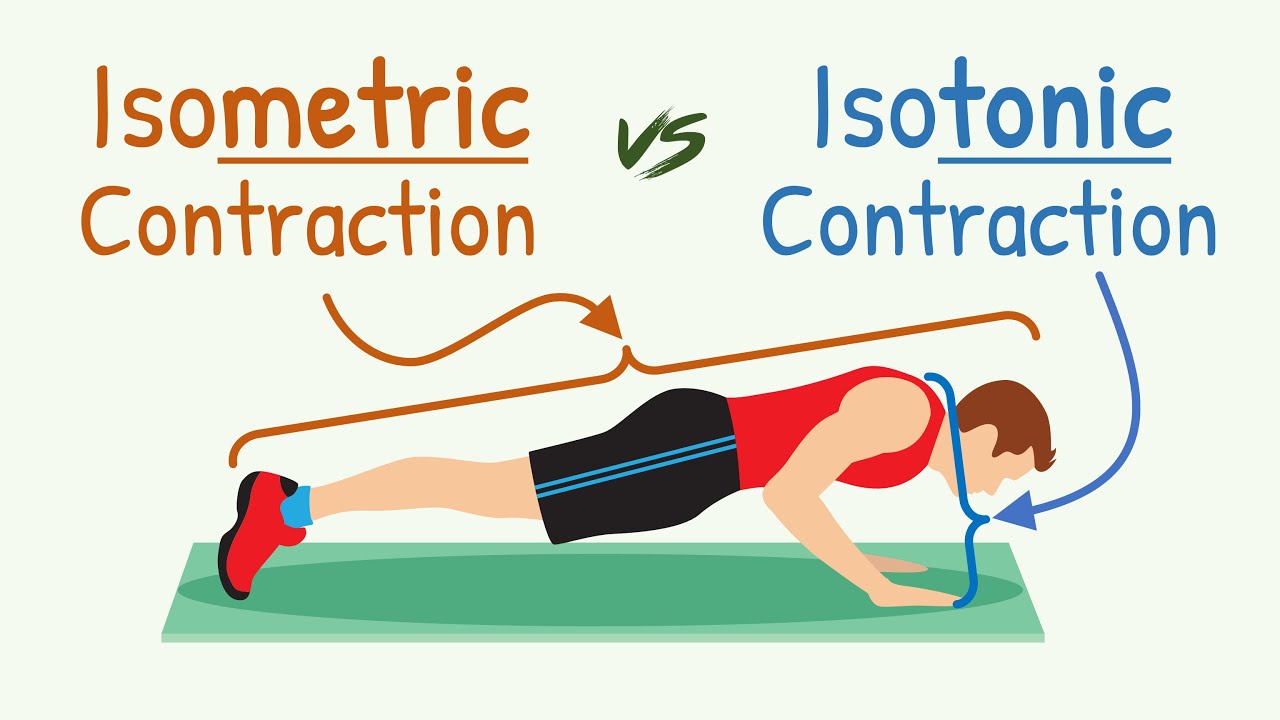
Isometric Contraction vs Isotonic Contraction || Physiology with Animation

Het bewegingsapparaat: Inleiding in de skeletspieren
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
