Kimia - ANIMASI PERCOBAAN PENGARUH KONSENTRASI DAN VOLUME PADA PERGESERAN KESETIMBANGAN
Summary
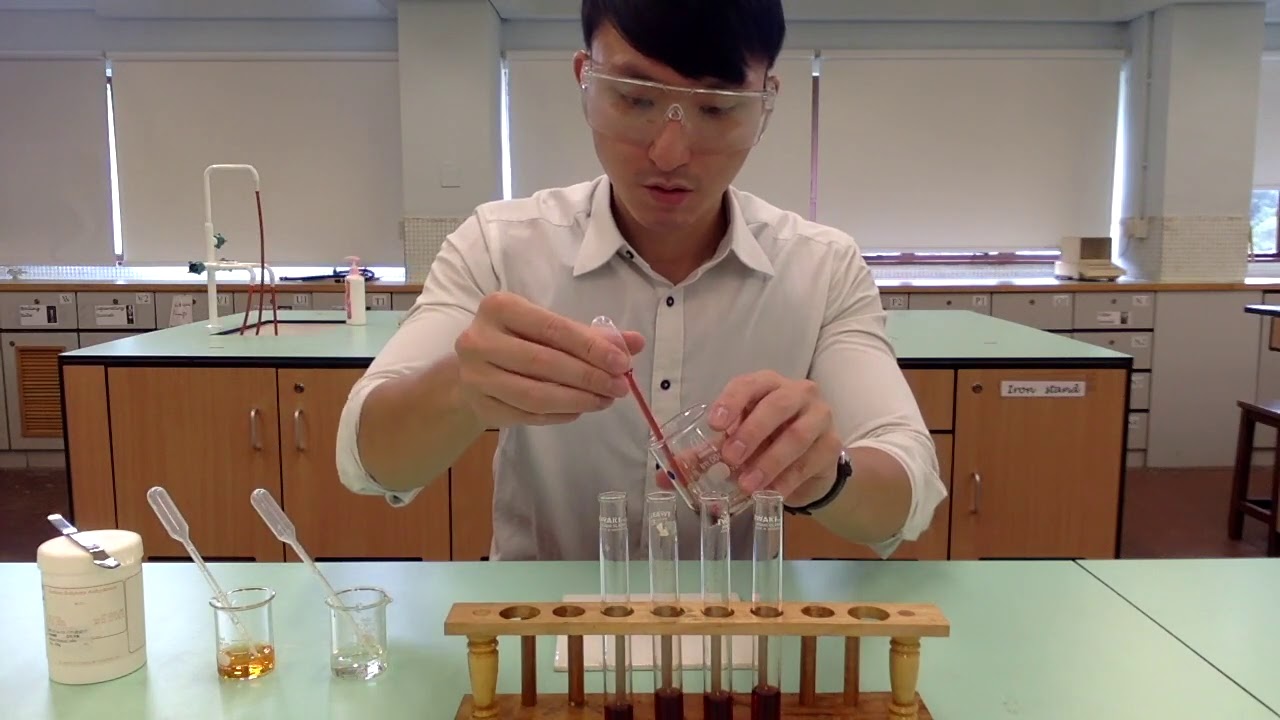
TLDRThis experiment demonstrates the principles of chemical equilibrium and Le Chatelier's Principle using a reaction between FeCl3 and KSCN. When mixed, they form a red-colored complex, Fe(SCN)3. The video explores how altering concentrations of FeCl3, KSCN, and Na2HPO4, as well as changing the volume by adding water, affects the equilibrium. The color changes provide visible evidence of shifts in the equilibrium position: more FeCl3 or KSCN causes a shift to the right (darker red), while Na2HPO4 and increased volume shift it to the left (lighter red). This experiment showcases how chemical systems respond to various changes in concentration and volume.
Takeaways
- 😀 The reaction between FeCl3 (brownish-orange) and KSCN (colorless) produces a red solution (FeSCN2+), demonstrating an equilibrium reaction.
- 😀 According to Le Chatelier's principle, if the equilibrium is disturbed, the system will shift to counteract the change.
- 😀 When the concentration of FeCl3 is increased by adding more of it, the equilibrium shifts to the right, resulting in a darker red solution.
- 😀 Adding more KSCN also shifts the equilibrium to the right, resulting in a darker red color as well.
- 😀 When Na2HPO4 is added, it binds Fe3+ ions, causing a decrease in Fe3+ concentration, and the equilibrium shifts to the left, making the red color fade.
- 😀 In this equilibrium system, adding a substance shifts the balance toward the side that doesn't have the added substance.
- 😀 Decreasing the concentration of one of the substances also causes the equilibrium to shift toward the side with the reduced substance.
- 😀 If water is added to the red solution, the color lightens, showing that increasing the volume shifts the equilibrium to the side with more molecules.
- 😀 If the volume is reduced, the equilibrium shifts to the side with fewer molecules, which can be seen by the intensifying red color.
- 😀 This experiment illustrates how changes in concentration and volume can impact equilibrium reactions, following the principles of Le Chatelier.
Q & A
What is the color change observed when FeCl₃ is mixed with KSCN?
-The mixture of FeCl₃ (which is brownish orange) and KSCN (which is colorless) results in a red solution, which indicates the formation of a complex compound, Fe(SCN)₃.
How does Le Chatelier's principle apply to the changes in the equilibrium of this reaction?
-Le Chatelier's principle states that when a system at equilibrium is disturbed by an external change (such as a change in concentration or volume), the system will shift to counteract that change and restore equilibrium.
What happens when additional FeCl₃ is added to the system?
-When FeCl₃ is added to the solution, the concentration of Fe³⁺ increases. According to Le Chatelier's principle, this causes the equilibrium to shift to the right, towards the formation of more Fe(SCN)₃, resulting in a darker red color.
What is observed when KSCN is added to the system?
-Adding KSCN to the solution increases the concentration of SCN⁻ ions. As a result, the equilibrium shifts to the right, producing more Fe(SCN)₃ and deepening the red color of the solution.
What effect does adding Na₂HPO₄ have on the equilibrium?
-Adding Na₂HPO₄ decreases the concentration of Fe³⁺ ions by binding to them, causing the equilibrium to shift to the left to compensate for the decrease in Fe³⁺, which lightens the red color of the solution.
What happens when water is added to the equilibrium system?
-Adding water increases the volume of the solution, which dilutes the concentrations of all ions. The equilibrium shifts to the left (toward the side with more ions) and the red color fades.
How does the volume of the solution affect the equilibrium?
-When the volume is increased (by adding water), the equilibrium shifts to the side with more molecules, which, in this case, is the left side. Conversely, reducing the volume would shift the equilibrium to the side with fewer molecules.
What is the role of the glass beaker in the experiment?
-The glass beaker is used to contain the solution during the experiment, providing a stable environment for mixing the chemicals and observing the changes in the color and equilibrium of the solution.
What did the experiment show about the effect of concentration changes on equilibrium?
-The experiment demonstrates that increasing the concentration of a reactant (like FeCl₃ or KSCN) causes the equilibrium to shift toward the products, while decreasing the concentration of a reactant (such as by adding Na₂HPO₄) shifts the equilibrium toward the reactants.
How can this experiment help understand Le Chatelier's principle in real-life applications?
-This experiment illustrates how concentration and volume changes can affect chemical equilibria, which is essential in fields like industrial chemistry, where controlling equilibrium is crucial for optimizing product yields.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード5.0 / 5 (0 votes)