Jaringan Otot
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the structure and function of muscle tissue in animals and humans. It covers the three main types of muscle tissue: skeletal muscle, smooth muscle, and cardiac muscle. The video details how each muscle type differs in structure, such as the arrangement of fibers and the presence of branching in cardiac muscle. It also explains how these muscles function, with skeletal muscle being voluntary, while smooth and cardiac muscles operate automatically. The presentation is designed to help viewers understand the key features of muscle tissues and their roles in movement and organ function.
Takeaways
- 😀 Muscle tissue is an active movement apparatus in animals and humans, found in both limbs and internal/external organs.
- 😀 Muscle tissue has the ability to contract and relax, enabling movement at its attachment points.
- 😀 Muscle fibers (miofibrils) are composed of muscle cells, and these fibers are wrapped in a membrane called the sarcolemma.
- 😀 The muscle cells contain a fluid called sarcoplasm.
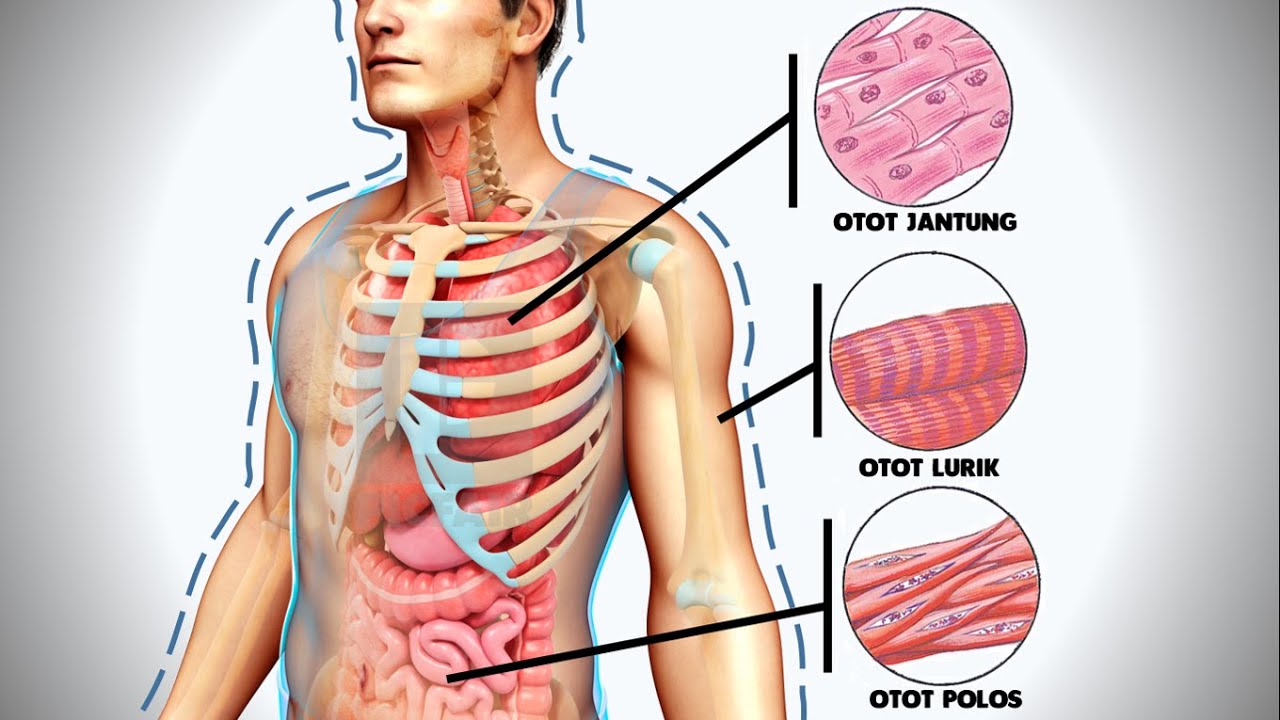
- 😀 Based on structure and function, muscle tissue is divided into three types: striated muscle, smooth muscle, and cardiac muscle.
- 😀 Striated muscle fibers have straight, orderly lines and are found in skeletal muscles, enabling voluntary movement.
- 😀 Smooth muscle fibers have a spindle-like shape, and they form the muscle tissue of organs like the intestines and lungs, working involuntarily.
- 😀 Cardiac muscle fibers have branched fibers, and they contract involuntarily, found in the heart.
- 😀 Striated muscle fibers have multiple nuclei located at the edges of the cells, while smooth and cardiac muscle cells have a single nucleus located centrally.
- 😀 Striated muscle is controlled voluntarily (e.g., writing, walking), whereas smooth and cardiac muscle are controlled involuntarily (e.g., heart beating, digestion).
Q & A
What is muscle tissue and why is it important in animals?
-Muscle tissue is the tissue responsible for movement in animals and humans. It is an active movement tool, allowing both voluntary and involuntary movements. It is found in all parts of the body, including limbs and internal organs.
What are the main types of muscle tissue?
-The three main types of muscle tissue are skeletal muscle, smooth muscle, and cardiac muscle. Each type differs in structure and function.
What is the structure of skeletal muscle tissue?
-Skeletal muscle tissue is made up of muscle fibers, which are bundles of myofibrils. These muscle fibers are enclosed by a membrane called the sarcolemma and contain a fluid called sarcoplasm.
How are skeletal muscle fibers structured?
-Skeletal muscle fibers are arranged in a way that they appear striated or striped under a microscope. This striation is due to the alignment of actin and myosin filaments.
What are the characteristics of smooth muscle tissue?
-Smooth muscle tissue consists of spindle-shaped, non-striated cells that are found in the walls of internal organs like the intestines, blood vessels, and bladder. Its cells are uninucleated and have a smooth appearance.
What is the structure of cardiac muscle tissue?
-Cardiac muscle tissue has striated fibers, similar to skeletal muscle, but its cells are branched and interconnected, forming a network. This allows the heart to contract as a unit. The cells also have a single central nucleus.
What is the function of the intercalated discs in cardiac muscle?
-Intercalated discs are specialized connections between cardiac muscle cells that allow for rapid communication and synchronization of muscle contraction. These discs are visible as dark lines under a microscope.
How do the locations of muscle tissues differ?
-Skeletal muscle is typically found attached to bones and allows for voluntary movement. Smooth muscle is found in the walls of internal organs and blood vessels, performing involuntary functions. Cardiac muscle is found exclusively in the heart and is responsible for its rhythmic contractions.
How do skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscles differ in terms of control?
-Skeletal muscle operates under voluntary control, meaning we consciously control its movements. Smooth muscle and cardiac muscle operate involuntarily, meaning their actions are automatic and not consciously controlled.
Can you explain the difference in the number and location of nuclei in muscle cells?
-In skeletal muscle, the nuclei are located at the edges of the cells and there are multiple nuclei per cell. In smooth muscle, the nucleus is centrally located, and there is only one nucleus per cell. In cardiac muscle, the nucleus is also centrally located, with each cell typically having one nucleus.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード5.0 / 5 (0 votes)