Wave Characteristics
Summary
TLDRThis video explores the concept of vibrations and waves, focusing on mechanical waves like transverse and longitudinal waves. It explains how waves are generated through simple harmonic motion, with real-life examples like guitar strings and moving vehicles on bridges. The script covers key wave characteristics including wavelength, amplitude, frequency, and period. It also dives into wave speed, interference, diffraction, and energy transfer through waves. Through clear explanations and examples, the video aims to teach fundamental wave concepts, providing viewers with an understanding of how waves behave in various mediums.
Takeaways
- 😀 Vibrations occur in various objects, from guitar strings to bridges, due to atomic movements causing oscillations that generate waves.
- 😀 Simple harmonic motion is when an object moves back and forth, covering a definite path in equal intervals of time with equal displacement in both directions.
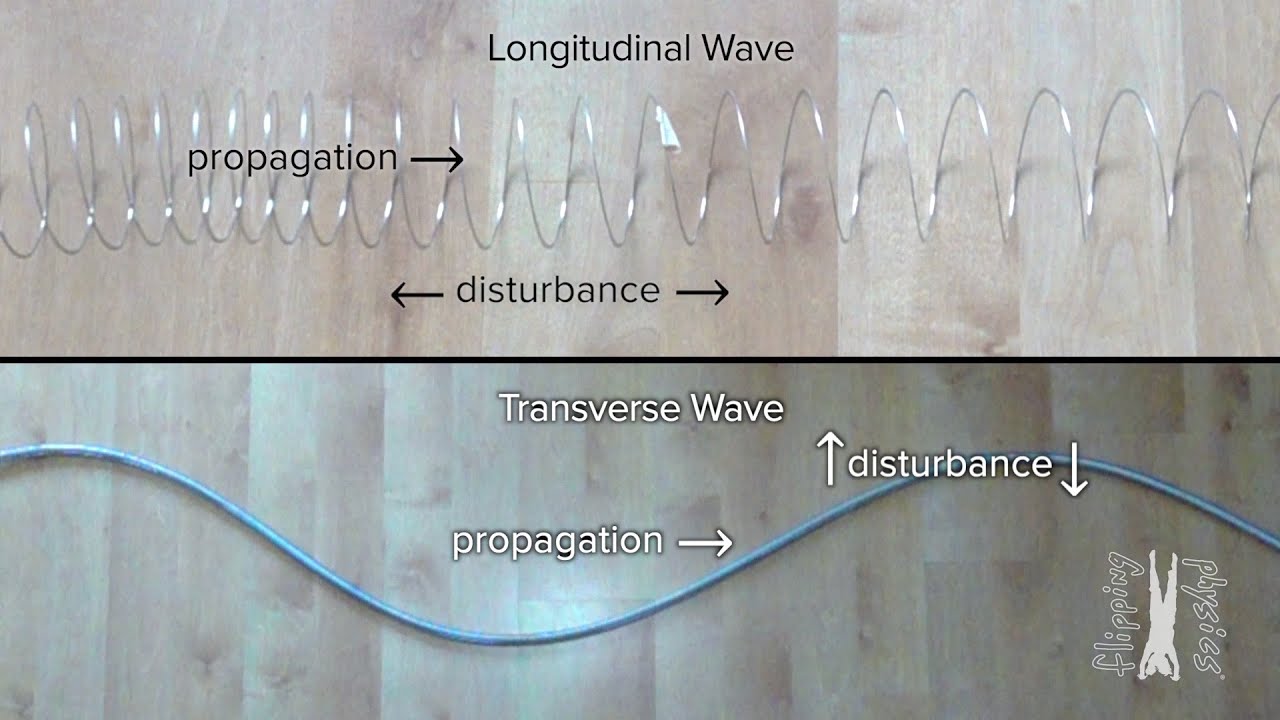
- 😀 Mechanical waves require a medium to travel through and can be classified as transverse or longitudinal waves based on how the medium particles move.
- 😀 Transverse waves occur when the medium moves perpendicular to the direction of the wave, while longitudinal waves occur when the medium moves parallel to the wave's direction.
- 😀 Compressional waves involve compressions (particles close together) and expansions (particles spread apart), similar to crests and troughs in transverse waves.
- 😀 Transverse waves cannot travel through gases due to widely separated gas particles, but longitudinal waves can propagate through gases.
- 😀 Surface waves, such as water waves, have both transverse and longitudinal properties, causing particles in the medium to move horizontally and vertically.
- 😀 Wavelength refers to the distance between two identical points on consecutive waves (crest to crest or trough to trough), and is denoted by the symbol λ.
- 😀 Amplitude measures the displacement of the medium from its rest position, indicating the wave's energy. The higher the amplitude, the more energy the wave carries.
- 😀 Frequency is the number of waves that pass a fixed point per second and is measured in Hertz (Hz). The frequency and period of a wave are inversely related (f = 1/T).
Q & A
What is the definition of vibration?
-Vibration refers to the repetitive motion of an object moving back and forth, caused by continuous oscillation of atoms within a molecule.
What is Simple Harmonic Motion (SHM)?
-Simple Harmonic Motion occurs when an object moves in a repetitive back-and-forth motion along a definite path with equal displacement in both directions and a constant time interval.
What are mechanical waves?
-Mechanical waves are waves that require a medium (solid, liquid, or gas) to travel through, and they can be classified into transverse and longitudinal waves based on the motion of the particles.
What is the difference between transverse and longitudinal waves?
-In transverse waves, the medium moves at right angles to the direction of the wave, while in longitudinal waves, the medium moves in the same direction as the wave.
What is the role of the spring in longitudinal waves?
-When a spring is pushed or pulled, it creates compressions (areas where coils are close together) and expansions (areas where coils are far apart), which correspond to the crests and troughs in a transverse wave.
Can transverse waves travel through gases?
-No, transverse waves cannot travel through gases because gas particles are too widely separated to vibrate in the manner required for transverse waves.
What is wavelength?
-Wavelength is the distance between one point on a wave and the exact same point on the next wave, typically measured from crest to crest or trough to trough.
What is amplitude and how is it represented?
-Amplitude is the maximum displacement of the medium from its rest position, and it is represented by the letter 'a.' It indicates how far the medium moves during the wave's motion.
How is frequency related to period?
-Frequency is the number of wave cycles that pass a fixed point per second, while period is the time it takes for one complete cycle. The frequency is the reciprocal of the period, meaning f = 1/t.
What is the wave speed formula and how is it applied?
-The wave speed formula is v = λ / t, where v is the wave speed, λ is the wavelength, and t is the period. It can also be written as v = λ * f, where f is the frequency.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード5.0 / 5 (0 votes)