SATELIT, KOMET, ASTEROID, METEOROID, METEOR, METEORIT
Summary
TLDRThis video explores celestial bodies like moons, asteroids, comets, and meteoroids. It begins by explaining the concept of satellites, both natural and artificial, and how they orbit planets. It details various planets and their moons, highlighting the unique characteristics of Saturn’s numerous moons. The script also covers asteroids, their composition, and their location in the asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter. Further, it delves into comets, explaining how they develop tails due to sublimation as they approach the sun. Finally, it discusses meteoroids, meteors, and meteorites, explaining their journey and impact on Earth.
Takeaways
- 😀 A satellite is a celestial body that orbits a planet. There are two types: natural satellites (like moons) and artificial satellites (created by humans).
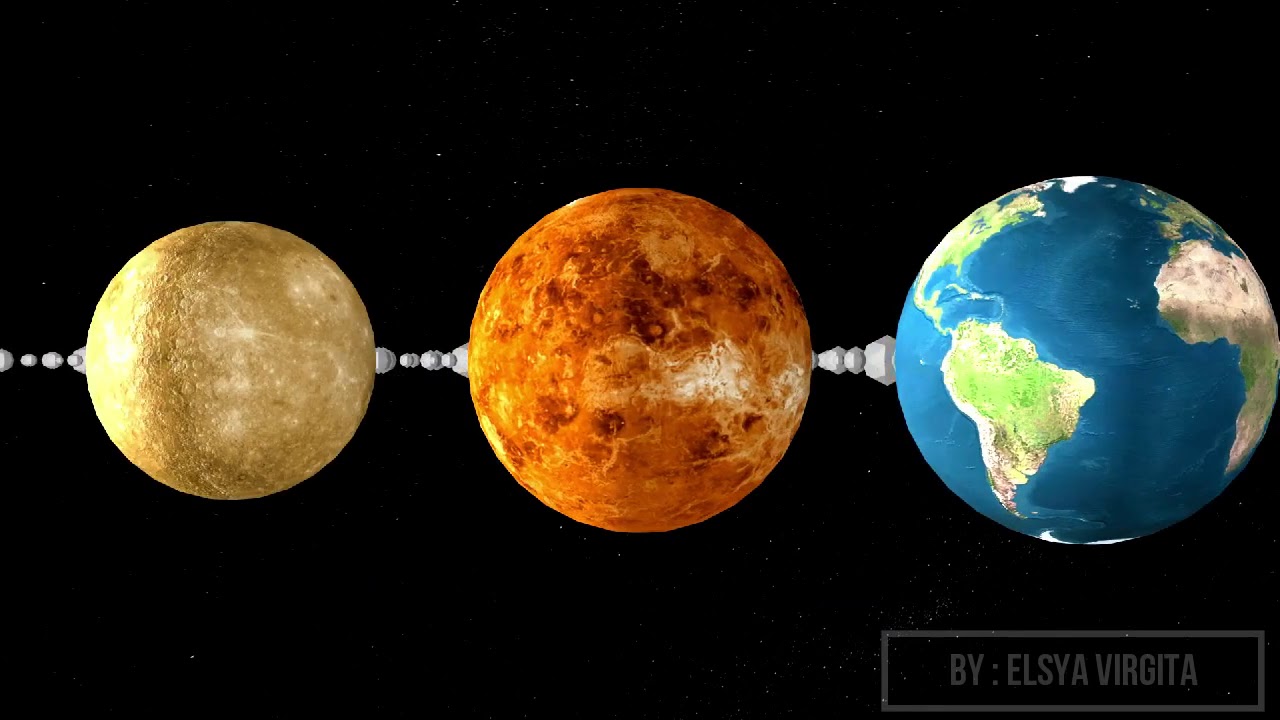
- 😀 Mercury and Venus do not have natural satellites due to their proximity to the Sun, which exerts a strong gravitational pull on any potential satellites.
- 😀 Earth has one natural satellite, the Moon, while Mars has two: Phobos and Deimos.
- 😀 Jupiter has over 79 moons, with the largest being the Galilean moons, including Ganymede, the largest moon in the solar system.
- 😀 Saturn has 82 moons, with Titan being the largest and the only moon in the solar system with a thick atmosphere and clouds.
- 😀 Uranus has 27 moons, with the largest ones being Miranda, Ariel, Umbriel, Titania, and Oberon.
- 😀 Neptune has 14 moons, with Triton being the largest. It is unique because it orbits Neptune in the opposite direction of the planet's rotation.
- 😀 An asteroid is a space object composed of rock and metal, primarily found in the asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter.
- 😀 A comet orbits the Sun in an elliptical path, and when it nears the Sun, its icy components sublimate, forming a visible tail that always points away from the Sun.
- 😀 Meteoroids are small rock fragments that float in space, and when they enter Earth’s atmosphere, they become meteors. If they survive and reach the surface, they are called meteorites. Meteorites can create craters on Earth’s surface, like the Barringer Crater in Arizona.
Q & A
What is a satellite?
-A satellite is a celestial object that orbits a planet. It can either be natural, like a moon, or artificial, like a man-made satellite.
What is the difference between natural and artificial satellites?
-Natural satellites are celestial objects like moons that are not created by humans and orbit planets, while artificial satellites are man-made objects that orbit other celestial bodies.
Why don't Mercury and Venus have natural satellites?
-Mercury and Venus don't have natural satellites because their proximity to the Sun means that the Sun's gravity is stronger than their own, preventing them from capturing any moons.
How many moons does Earth have, and what is it called?
-Earth has one natural satellite, which is called the Moon.
Which planet has the most natural satellites in the solar system?
-Saturn has the most natural satellites in the solar system, with 82 moons.
What is unique about Titan, Saturn’s largest moon?
-Titan is unique because it is the only natural satellite in the solar system known to have a thick atmosphere.
Where do most asteroids in our solar system reside?
-Most asteroids in the solar system are located in the Asteroid Belt, which lies between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter.
What happens when a comet approaches the Sun?
-When a comet approaches the Sun, some of its materials sublimate, forming a glowing coma and a tail that always points away from the Sun due to solar wind and radiation.
What is the difference between a meteoroid, a meteor, and a meteorite?
-A meteoroid is a small rock or particle in space. When it enters Earth's atmosphere and burns up, it creates a meteor. If it survives the atmospheric entry and hits the ground, it becomes a meteorite.
What is the Barringer Crater, and how was it formed?
-The Barringer Crater, located in Arizona, was formed by a large meteorite impact. The crater is about 1,400 meters in diameter and 170 meters deep.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード関連動画をさらに表示

SISTEM TATA SURYA - IPA

COMET, METEOR OR ASTEROID - The REAL difference.
VIDEO PEMBELAJARAN ANIMASI TATA SURYA KELAS VII SMP

El Sistema Solar

BAB 7 Bumi dan Tata Surya || Benda Langit Selain Planet -IPA Kelas 7 Kurikulum Merdeka

Sistem Tata Surya : Matahari - Planet - Komet - Meteoroid - Asteroid - Benda Langit
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
