Introduction to Microprocessors || History || Evolution || Generations || of Microprocessor
Summary
TLDRThis video provides an introduction to microprocessors, explaining their purpose, history, and evolution. It covers the role of the microprocessor as the brain of a computer, specifically focusing on how it executes programs and interacts with input, memory, and output devices. The script outlines the components of a computer, such as the ALU and control unit, and details the history of Intel's microprocessors, including the 4004, 8008, 8080, 8085, and 8086. Key characteristics like address bus size, memory capacity, and clock frequency are discussed, highlighting the advancements in microprocessor technology over time.
Takeaways
- 😀 Microprocessors are the brain of a computer, also known as the CPU, responsible for executing programs and performing tasks like playing movies or games.
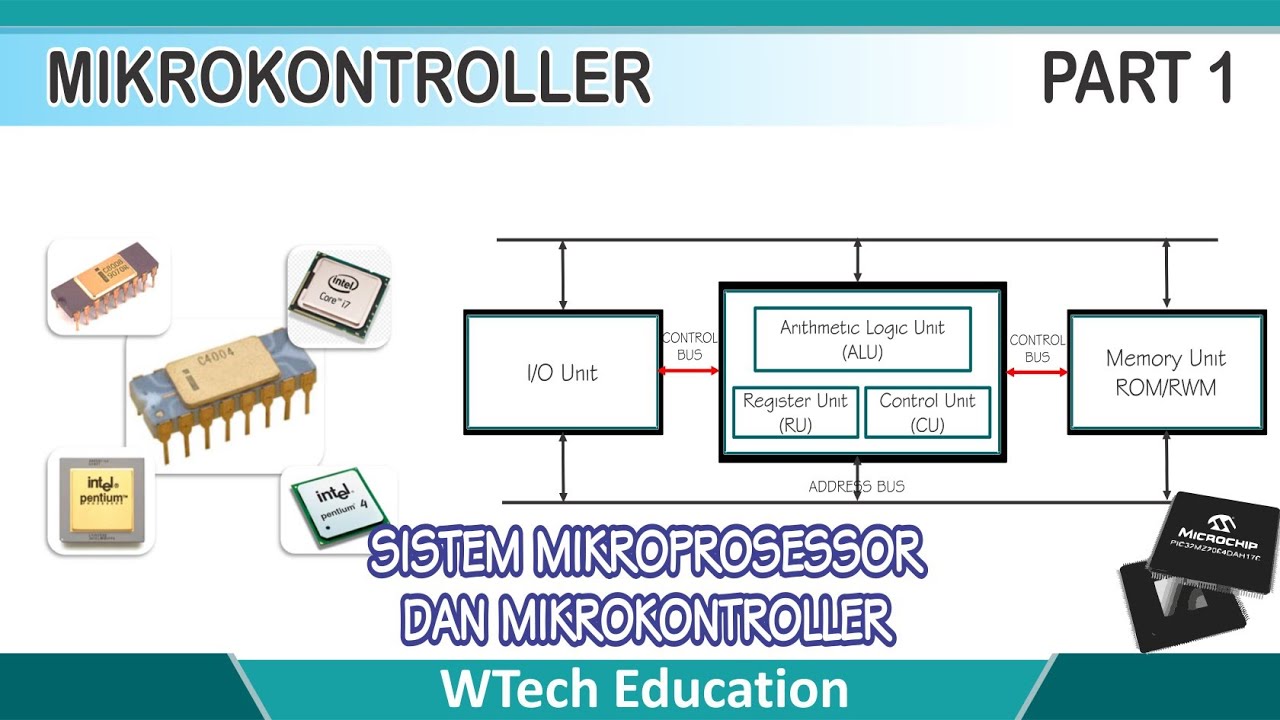
- 😀 A microprocessor is a combination of the Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) and Control Unit (CU), which work together to execute and manage operations.
- 😀 Input devices, such as keyboards and mice, provide data to the computer, while output devices, like monitors and printers, display the processed information.
- 😀 Memory in a computer is split into secondary (non-volatile) memory, such as hard disks, and main (volatile) memory, such as RAM, which is needed for executing programs.
- 😀 A microprocessor can only execute a program stored in the main memory (RAM), as it cannot access secondary memory like hard disks directly.
- 😀 The first microprocessor, the Intel 4004, was introduced in 1971 and started the development of modern computing.
- 😀 The evolution of microprocessors includes advancements in size, processing capacity, address and data lines, memory capacity, and clock frequency.
- 😀 Early microprocessors like the Intel 4004 were 4-bit processors, while later models like the Intel 8086 were 16-bit processors with the capability to process larger amounts of data.
- 😀 The address bus size determines the memory capacity of a microprocessor; for example, the Intel 8086 with a 20-bit address bus could access up to 1MB of memory.
- 😀 Clock frequencies of early microprocessors ranged from 740 kHz (Intel 4004) to 10 MHz (Intel 8086), with newer processors today operating at much higher speeds.
- 😀 The Intel 8086 microprocessor was a significant development in the 16-bit era, offering more advanced processing capabilities and higher performance than its predecessors.
Q & A
What is the purpose of a microprocessor?
-The microprocessor, also known as the CPU, is responsible for executing programs and handling tasks such as playing movies, games, and processing input from devices like the keyboard and mouse.
What are the main components of a computer, as explained in the video?
-The main components of a computer include input devices (e.g., keyboard, mouse), the microprocessor (a combination of the ALU and control unit), memory (main and secondary), and output devices (e.g., monitor, printer).
What is the function of the ALU in a microprocessor?
-The ALU, or Arithmetic Logic Unit, performs all arithmetic operations, logical operations, and shift operations within the microprocessor.
How does the control unit (CU) assist the microprocessor?
-The control unit (CU) decodes instructions and determines which operation the ALU should perform, such as addition, subtraction, logical operations, or shifts.
What is the difference between secondary memory and main memory?
-Secondary memory (e.g., hard disk) is non-volatile and stores data permanently, while main memory (e.g., RAM) is volatile and stores data temporarily during program execution.
Why can't the CPU execute a program directly from secondary memory?
-The CPU can only execute a program if it resides in main memory (RAM). It cannot directly execute programs stored in secondary memory, such as a hard disk.
What is the significance of the microprocessor in the functioning of a computer?
-The microprocessor is the brain of the computer, executing programs and controlling the interactions between the different components (ALU, CU, memory, and I/O devices).
What are the key microprocessors discussed in the video, and what are their characteristics?
-The key microprocessors discussed are the Intel 4004, 8008, 8080, 8085, and 8086. They vary in data line size (from 4-bit to 16-bit), address bus size, memory capacity, pin count, and clock frequency.
What was the first microprocessor, and when was it developed?
-The first microprocessor was the Intel 4004, developed in 1971. It was a 4-bit processor with a 10-bit address bus and a 740 kHz clock frequency.
What is the maximum memory capacity supported by the 8086 microprocessor?
-The 8086 microprocessor, with its 20-bit address bus, supports a maximum memory capacity of 1MB.
How does the clock frequency of microprocessors relate to their performance?
-The clock frequency determines how fast a microprocessor can process instructions. Higher clock frequencies allow for faster execution of tasks. For example, the 4004 operated at 740 kHz, while the 8086 could operate at up to 10 MHz.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード5.0 / 5 (0 votes)