TDM, Statistical TDM & FDM
Summary
TLDRIn this video, Sunny explains the three main multiplexing techniques: Time Division Multiplexing (TDM), Statistical Time Division Multiplexing (STDM), and Frequency Division Multiplexing (FDM). TDM divides time into equal slots for different users, but STDM adapts time allocation based on demand and priority, making it more efficient. FDM, on the other hand, divides a channel into frequency bands for simultaneous signal transmission. Sunny also highlights the difference between baseband systems, which use TDM or STDM for digital signals, and broadband systems, which use FDM for analog signals, offering a clear understanding of their applications.
Takeaways
- 😀 TDM (Time Division Multiplexing) assigns equal time slots to users to send their data, ensuring fairness but not always efficiency.
- 😀 STDM (Statistical Time Division Multiplexing) adjusts the time allocation dynamically based on user needs, providing a more efficient solution than TDM.
- 😀 FDM (Frequency Division Multiplexing) works with analog signals, dividing the frequency spectrum into non-overlapping channels for simultaneous data transmission.
- 😀 TDM is ideal for digital signals in baseband systems, where only one signal is transmitted at a time.
- 😀 STDM offers more control over data allocation compared to TDM, especially when users have varying data volumes or priorities.
- 😀 FDM is commonly used in broadband systems, allowing multiple users to transmit data simultaneously over different frequency bands.
- 😀 In TDM, all users get the same amount of time regardless of their actual data needs or priority, which may not be cost-effective.
- 😀 Baseband systems, like Ethernet, use TDM or STDM and transmit only one signal at a time, occupying the entire bandwidth.
- 😀 Broadband systems, like optical or radio waves, use FDM because they support simultaneous transmissions across multiple frequencies.
- 😀 Understanding the differences between baseband and broadband systems is key to knowing when to use TDM, STDM, or FDM for data transmission.
Q & A
What is the main purpose of multiplexing in a network?
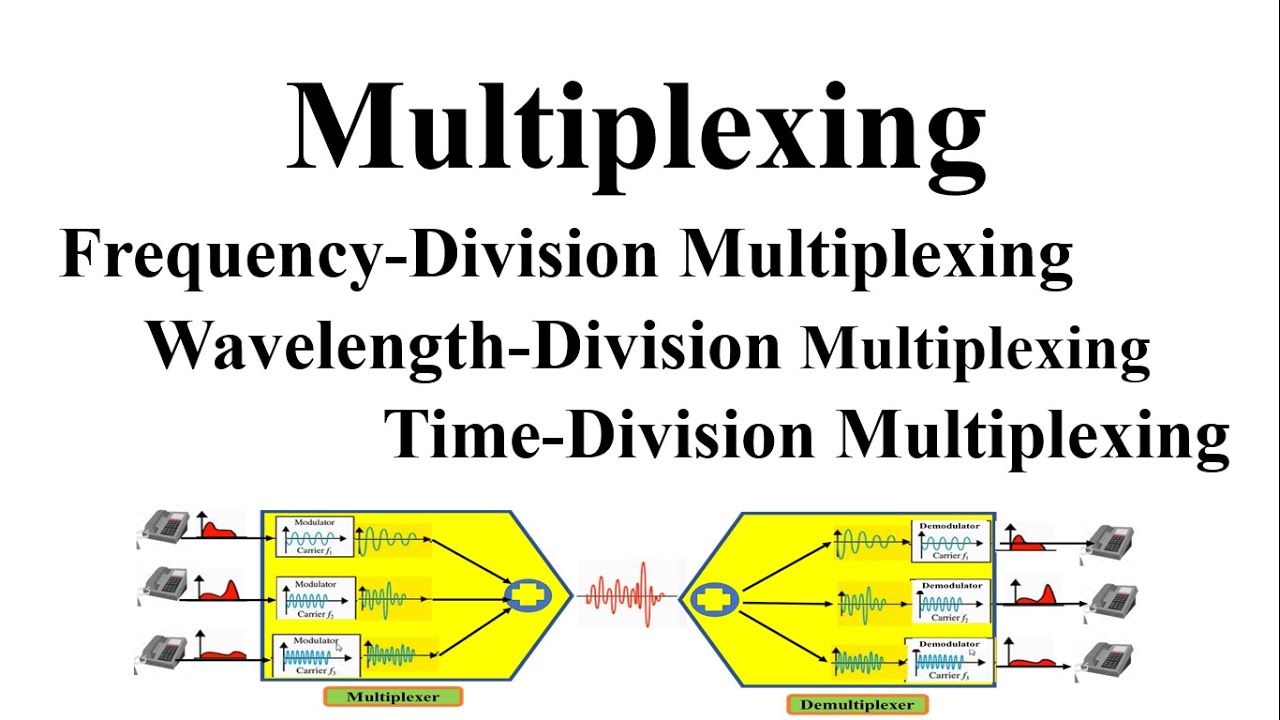
-The main purpose of multiplexing is to combine multiple signals into one and allow them to travel simultaneously over a single link, maximizing the use of available resources.
What is Time Division Multiplexing (TDM)?
-Time Division Multiplexing (TDM) is a method where time is divided into slots, and these slots are equally allocated to different users, allowing multiple users to share a single communication channel.
How does TDM handle users with different data requirements?
-TDM allocates equal time slots to all users regardless of their data needs, which can be inefficient in situations where some users require more bandwidth or have higher priority.
What is the issue with equal time slot allocation in TDM?
-The issue with equal time allocation in TDM is that it may not be cost-effective, as it doesn't consider varying data loads or priorities, leading to inefficiency when some users have more data to send than others.
What is Statistical Time Division Multiplexing (Statistical TDM)?
-Statistical Time Division Multiplexing (Statistical TDM) dynamically allocates time slots based on the statistical workload and priority of each user, making it more efficient than TDM.
How does Statistical TDM improve efficiency over traditional TDM?
-Statistical TDM improves efficiency by adjusting the allocation of time slots according to the data requirements or priority of each user, ensuring that users with higher needs or priority get more bandwidth.
What is Frequency Division Multiplexing (FDM) and when is it used?
-Frequency Division Multiplexing (FDM) is a technique used to combine analog signals into one channel by dividing the channel into non-overlapping frequency bands, each assigned to a different user. It is used for transmitting analog signals over broadband systems.
How does FDM differ from TDM?
-FDM differs from TDM in that it allocates different frequency bands to each user, allowing them to transmit simultaneously without overlapping, while TDM allocates separate time slots to each user.
What is the difference between baseband and broadband transmission systems?
-Baseband systems deal with digital signals and can only transmit one signal at a time using the entire channel's bandwidth, whereas broadband systems handle analog signals and allow multiple transmissions using different frequency ranges.
When should TDM be used over FDM?
-TDM should be used in baseband systems, which transmit digital signals over a single channel. FDM is more suitable for broadband systems, which transmit analog signals and need to share a channel by using different frequency ranges.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード関連動画をさらに表示
Frequency division multiplexing|Time division multiplexing|FDM|WDM| TDM| computer networks in detail

Multiplexing Tutorial - TDM, STDM, FDM Explained

Types of Multiplexing | FDM TDM WDM | Analog Digital | Computer Networks

Frequency Division Multiplexing (FDM) Explained

Serial Communications

CS601_Topic116
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
