📚 Derivada - Definição e Cálculo - Cálculo 1 (#16)
Summary
TLDRIn this video, viewers are introduced to the concept of derivatives, focusing on how to calculate the derivative of a function at a given point using its definition. The video explains the relationship between the tangent line and the derivative, demonstrating how the slope of the tangent is the derivative at that point. Examples are provided to clarify the process of finding derivatives through limits, including determining the slope of a tangent line for specific functions. The video emphasizes the importance of understanding these foundational concepts in calculus.
Takeaways
- 😀 The derivative of a function at a given point represents the slope of the tangent line at that point.
- 😀 The slope of the tangent line can be calculated using the limit definition of the derivative: m = lim(h -> 0) [f(x + h) - f(x)] / h.
- 😀 A secant line, which passes through two points on a curve, can be used to approximate the tangent line by making the two points infinitesimally close.
- 😀 The key concept behind the derivative is the limit process, where h approaches 0 to determine the slope of the tangent line.
- 😀 The coefficient of the tangent line (slope) is called the derivative at a specific point on the function.
- 😀 The concept of tangent and secant lines is essential for understanding the behavior of functions and calculating their derivatives.
- 😀 In geometry, the slope of a secant line is the ratio of the change in function values over the change in x-values (h).
- 😀 By using the limit definition, you can calculate the exact slope of the tangent line, which is the derivative of the function at a specific point.
- 😀 The derivative of a quadratic function (e.g., f(x) = x^2 - 2x + 1) can be calculated using the limit definition to determine the slope at a point.
- 😀 The equation of the tangent line can be derived once the derivative (slope) at a specific point is known, allowing for the complete equation of the line.
- 😀 Derivatives can initially be calculated using the limit process, but as you advance in calculus, derivative rules make the process much simpler.
Q & A
What is the geometric interpretation of a derivative?
-The geometric interpretation of a derivative is the slope of the tangent line to the graph of a function at a given point. This slope indicates the rate of change of the function at that point.
How can the derivative be calculated using limits?
-The derivative of a function at a point can be calculated by taking the limit of the difference quotient as the difference between two points approaches zero. The formula is: lim(h→0) [(f(x + h) - f(x)) / h].
What is the meaning of the 'm' in the tangent line equation?
-'m' represents the slope of the tangent line, which is equivalent to the derivative of the function at a given point.
How does the secant line relate to the tangent line?
-The secant line passes through two points on the graph of a function. As the points approach each other, the secant line becomes closer and closer to the tangent line, which represents the derivative at the point of contact.
What role does the variable 'h' play in the definition of the derivative?
-In the derivative formula, 'h' represents the difference in the x-values of two points on the function. As 'h' approaches zero, the secant line approaches the tangent line, and the slope of the tangent line is obtained.
Why is the process of finding the derivative using limits considered important?
-The limit process is crucial because it allows us to precisely define the instantaneous rate of change of a function, which is what the derivative measures, especially when dealing with curves.
What happens when 'h' tends to zero in the limit definition of the derivative?
-When 'h' tends to zero, the secant line's slope approaches the slope of the tangent line, allowing us to calculate the exact instantaneous rate of change (the derivative) at the given point.
How does the graph of a function help in understanding its derivative?
-The graph of a function helps visualize the slope of the tangent line at any given point, which is the derivative. By observing the curve's behavior, one can better understand how the function is changing at specific points.
How do you calculate the equation of the tangent line using the derivative?
-To find the equation of the tangent line, you first calculate the derivative at the point of interest to get the slope (m). Then, you use the point-slope form of a line (y - y1 = m(x - x1)) to write the equation of the tangent line.
What is the relationship between the function and its derivative at a specific point?
-At a specific point, the value of the function gives the coordinates of the point, and the derivative at that point gives the slope of the tangent line to the function's graph at that point. This slope indicates the rate of change of the function at that exact location.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード関連動画をさらに表示

Concavidad y puntos de inflexión para principiantes. Uso de la segunda derivada | Video 88
Konsep Dasar Turunan Fungsi Aljabar Matematika Wajib Kelas 11 m4thlab
Applying First Principles to x² (2 of 2: What do we discover?)
Derivatives... What? (NancyPi)

Definition of the Derivative
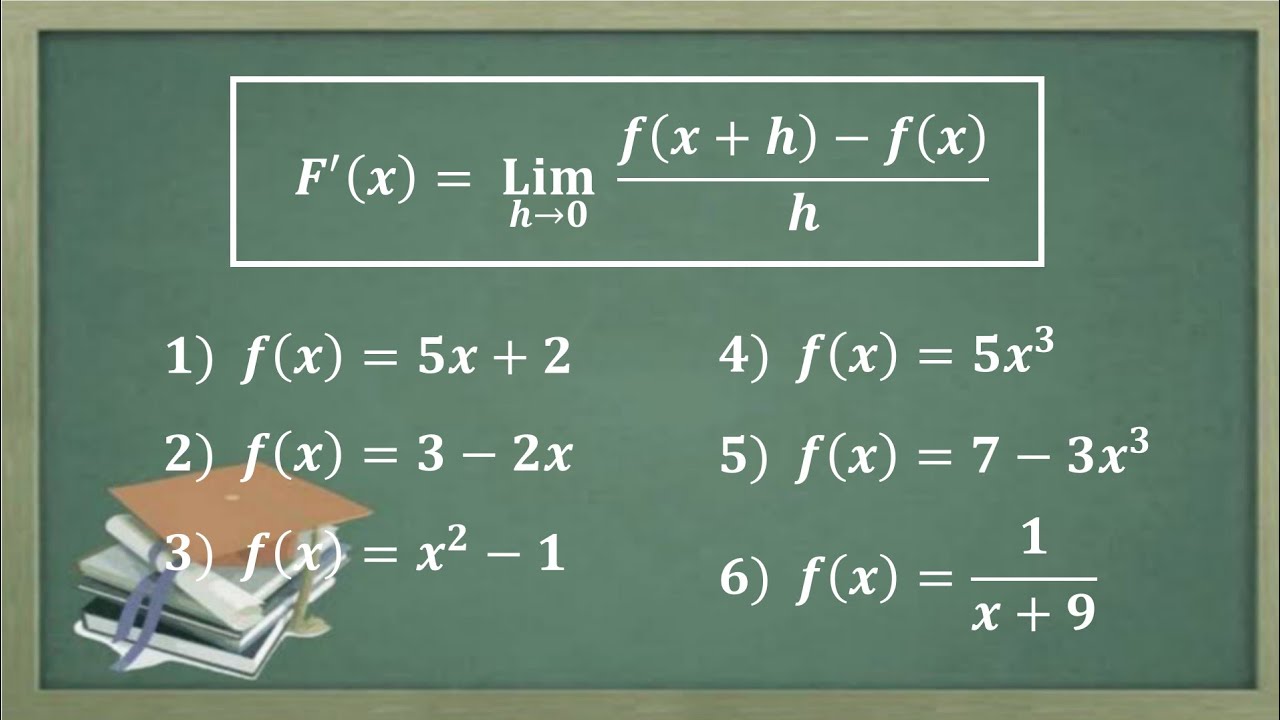
Turunan dengan menggunakan defnisi turunan Turunan menggunakan limit
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
