Farmacologia - Farmacocinética de forma FÁCIL│ Medicina Resumida
Summary
TLDRThis video provides an in-depth overview of pharmacokinetics, explaining the four essential processes a drug undergoes in the body: absorption, distribution, biotransformation (metabolism), and elimination. The speaker emphasizes the importance of understanding these processes for both medical professionals and students. The video also highlights the impact of drug properties on its effectiveness and how different factors can influence drug absorption and elimination. Additionally, the speaker promotes a pharmacology course, encouraging viewers to subscribe, like, and share the video for further educational content.
Takeaways
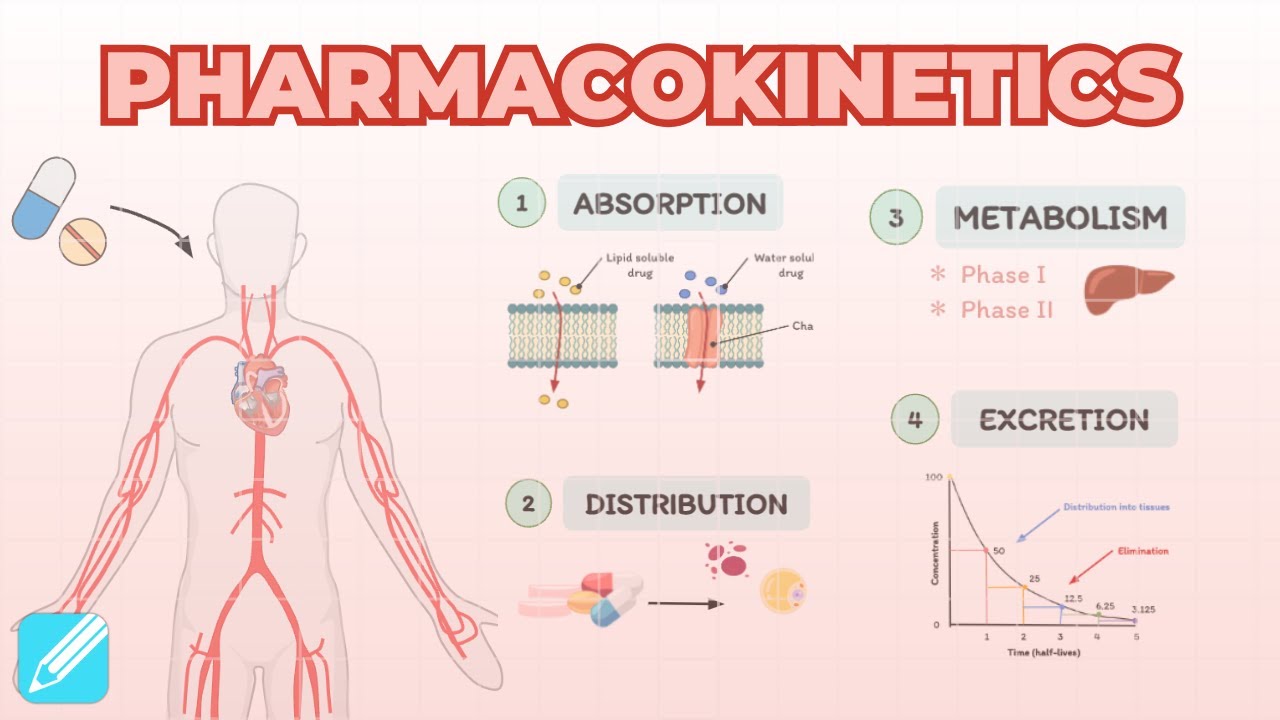
- 😀 Absorption is the process where a drug enters the bloodstream after being administered, such as when a patient swallows a drug.
- 😀 Distribution refers to the process by which the drug is carried through the bloodstream to various organs and tissues in the body.
- 😀 Some organs, like the brain, liver, and kidneys, receive a higher concentration of the drug due to better blood circulation.
- 😀 Drugs may have either beneficial or harmful effects depending on where they accumulate in the body.
- 😀 Metabolism involves the transformation of the drug into active or inactive metabolites, primarily occurring in the liver.
- 😀 First-pass metabolism in the liver can reduce the effectiveness of orally administered drugs compared to intravenous administration.
- 😀 Elimination is the process of the body removing the drug through urine, feces, or sweat.
- 😀 Lipid-soluble drugs may need to be metabolized into water-soluble forms for easier excretion through the kidneys.
- 😀 The liver plays a significant role in processing and eliminating drugs from the body.
- 😀 The video promotes a course on pharmacology, where topics like adrenergic, cholinergic, and other drug classes are explained in detail.
- 😀 The speaker encourages viewers to engage by liking, commenting, and sharing the video, as well as signing up for the pharmacology course.
Q & A
What is the main focus of the video script?
-The video focuses on explaining pharmacokinetics, specifically the four main stages: absorption, distribution, biotransformation, and elimination of drugs in the body.
What is pharmacokinetics and why is it important for a student to understand?
-Pharmacokinetics refers to the actions of the body on a drug, including its absorption, distribution, metabolism, and elimination. It is crucial for students to understand because it helps in predicting how a drug will behave in the body and its therapeutic effects.
What are the four stages of pharmacokinetics explained in the video?
-The four stages of pharmacokinetics are absorption, distribution, biotransformation (metabolism), and elimination.
Can you explain the process of drug absorption?
-Absorption occurs when a drug is taken into the body and passed into the bloodstream. For example, if a drug is ingested, it travels through the esophagus, stomach, and into the duodenum where it is absorbed into the blood. If a drug is administered via a patch, it is absorbed through the skin into the bloodstream.
How does drug distribution vary across different tissues in the body?
-Drug distribution depends on blood flow to different tissues. For example, drugs reach the brain, liver, and kidneys with higher intensity due to better blood flow, while tissues like the skin and adipose tissue receive lower amounts of the drug.
What happens during biotransformation (metabolism) of a drug?
-Biotransformation is the process where the body alters a drug, usually inactivating it or converting it into a less active metabolite. This often happens in the liver and can sometimes activate the drug into a more potent form.
What is 'first-pass metabolism' and how does it affect drug effectiveness?
-First-pass metabolism refers to the process where a drug is metabolized in the liver before it reaches the rest of the body. This can reduce the drug's effectiveness because some of it is inactivated in the liver before it can be distributed.
Why do intravenous drugs have higher bioavailability than oral drugs?
-Intravenous drugs bypass the digestive system and first-pass metabolism, delivering the full dose directly into the bloodstream, resulting in higher bioavailability compared to oral drugs that may be partially metabolized before reaching circulation.
What role does elimination play in pharmacokinetics?
-Elimination is the final stage of pharmacokinetics, where the drug is removed from the body, typically through the kidneys (urine), liver (bile), sweat, saliva, and other bodily fluids.
Why can't lipophilic drugs be eliminated by the kidneys directly?
-Lipophilic (fat-soluble) drugs cannot be eliminated by the kidneys directly because they can pass through lipid membranes and be reabsorbed into the bloodstream. The liver metabolizes these drugs into hydrophilic (water-soluble) forms, allowing them to be eliminated through urine.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード関連動画をさらに表示
Pharmacokinetics: Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism & Excretion

Farmakokinetika Obat

Pharmacology - PHARMACOKINETICS (MADE EASY)
Pharmacokinetics MADE EASY FOR BEGINNERS

Farmacocinética - Absorção, Distribuição, Biotransformação e Eliminação (Farmacologia) - Bio Aulas
Major Pharmacokinetic Processes animation
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
