KESETIMBANGAN KIMIA KELAS 11_PART 1
Summary
TLDRThis lesson introduces the concept of chemical equilibrium, exploring the difference between irreversible and reversible reactions. Using relatable analogies, such as rusting nails and boiling water, the script demonstrates how equilibrium works in chemical processes. Key concepts like dynamic equilibrium, where reactions occur in both directions at equal rates, are explained. The lesson also touches on homogeneous and heterogeneous equilibria. Through simple examples and comparisons, students are guided to understand how equilibrium maintains balance in chemical reactions, leading to continuous, dynamic processes. The session sets the stage for further exploration in future lessons.
Takeaways
- 😀 Chemical equilibrium refers to a state where the rate of the forward and reverse reactions are equal, leading to no net change in the system.
- 😀 The concept of 'equilibrium' in chemistry can be likened to a fair balance, like a seesaw where both sides are equal.
- 😀 An irreversible reaction, such as rusting of iron, only proceeds in one direction and cannot revert back to its original state.
- 😀 A reversible reaction, such as the boiling and condensation of water, can go both forward and backward, reaching a state of dynamic equilibrium.
- 😀 The transition of water from liquid to gas (vaporization) and from gas back to liquid (condensation) is an example of a reversible reaction.
- 😀 The process of freezing and melting ice (H2O) is another example of a reversible reaction where both phases (solid and liquid) coexist at equilibrium.
- 😀 In a chemical reaction, reactants are the substances that undergo change, while products are the result of the reaction.
- 😀 A dynamic equilibrium in chemistry means that the concentration of reactants and products remains constant over time.
- 😀 Chemical equilibrium can be categorized into two types: homogeneous and heterogeneous equilibrium, based on whether all substances are in the same phase or different phases.
- 😀 Understanding equilibrium in daily life can be related to examples like a seesaw, where balance or equilibrium is achieved through position adjustments rather than identical weights.
Q & A
What does the term 'setimbang' mean in the context of chemistry?
-In the context of chemistry, 'setimbang' refers to a state of balance or equilibrium. It suggests a stable position where the forward and reverse reactions are occurring at the same rate, and no net change is observed in the system.
What is the significance of the arrow symbol in chemical reactions?
-In chemical reactions, a single arrow (→) indicates an irreversible reaction, meaning the reaction proceeds in one direction only, like the rusting of iron. A double-headed arrow (↔) represents a reversible reaction, where the system can reach equilibrium between reactants and products, such as water freezing and melting.
Can rusted iron (paku yang sudah berkarat) revert back to its original form?
-No, once iron has rusted (forming Fe(OH)₃), it cannot revert back to its original state through a simple reaction. This process is irreversible, represented by a single-direction arrow in the reaction.
What happens when water is boiled in a closed pot?
-When water is boiled in a closed pot, it turns into steam (gas). The steam condenses upon touching the lid of the pot and returns to liquid form, creating a dynamic equilibrium where the liquid and gas phases are constantly changing.
How does the melting and freezing of ice demonstrate chemical equilibrium?
-The melting of ice and freezing of water represent a reversible process. Ice can melt to form water, and water can freeze back into ice, showing a dynamic equilibrium where both processes occur continuously in a closed system.
What does the concept of 'dynamic equilibrium' mean?
-Dynamic equilibrium refers to a state where the rate of the forward reaction equals the rate of the reverse reaction. In such a state, there is no net change in the concentration of reactants and products over time, even though the reactions continue to occur.
What is the difference between homogeneous and heterogeneous equilibrium?
-Homogeneous equilibrium occurs when all reactants and products are in the same phase (solid, liquid, or gas), while heterogeneous equilibrium involves reactants and products in different phases, such as a solid reacting with a gas or liquid.
What is required for a system to be in a state of equilibrium?
-For a system to be in equilibrium, the rates of the forward and reverse reactions must be equal, and the concentrations of reactants and products must remain constant over time.
Why is the balancing of a seesaw used as an analogy for chemical equilibrium?
-The balancing of a seesaw is used as an analogy to explain chemical equilibrium because, just like a seesaw needs equal weight on both sides to balance, a chemical system needs equal rates of forward and reverse reactions to achieve equilibrium.
What does the term 'reversible reaction' mean in chemistry?
-A reversible reaction is one in which the products can react to form the original reactants, and this process occurs in both directions, leading to a dynamic equilibrium where the system can shift back and forth between the reactants and products.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード関連動画をさらに表示

11 клас. Хімія. Необоротні та оборотні хімічні реакції. Хімічна рівновага. Принцип Ле Шательє
6. Chemical Reactions (Part 3) (3/5) (Cambridge IGCSE Chemistry 0620 for 2023, 2024 & 2025)
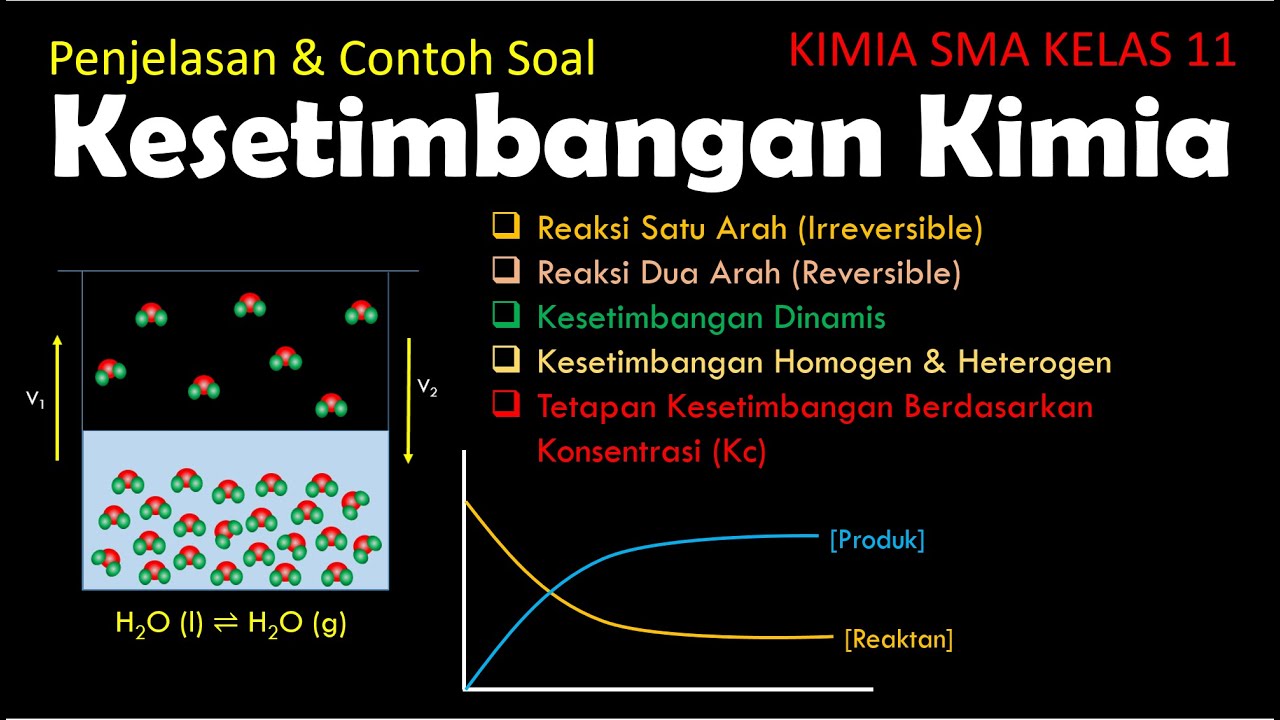
KESETIMBANGAN KIMIA ( KIMIA SMA KELAS 11 )

Kesetimbangan Kimia| Kimia SMA | Tetty Afianti

Part 1 Kesetimbangan Kimia: Reaksi Irreversible, Reaksi Reversible dan Konsep Kesetimbangan Dinamis.
Chemical Equilibrium Grade 12 Chemistry
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
