Teori Relativitas Khusus: 1. Pendahuluan
Summary
TLDRThis video introduces the theory of relativity, beginning with classical mechanics and the study of macroscopic objects with speeds far lower than the speed of light. It contrasts this with microscopic objects, such as atoms and particles, whose speeds approach light speed. The video delves into Einstein's theory of relativity, explaining the differences between classical Newtonian mechanics and special relativity, which uses Lorentz transformations. Key concepts like time dilation, length contraction, and the equivalence of mass and energy are explored, highlighting the relevance of relativity in understanding the physics of objects moving at high speeds.
Takeaways
- 😀 Classical mechanics studies macroscopic objects that move at speeds much slower than the speed of light.
- 😀 The speed of light (c) is approximately 3 x 10^8 meters per second and is significantly faster than macroscopic objects.
- 😀 Newton's laws of motion are applicable to macroscopic objects with small speeds, but fail for microscopic objects moving near the speed of light.
- 😀 Microscopic objects, like atoms and electrons, exhibit behavior that requires the theory of relativity to understand.
- 😀 Einstein's postulates form the foundation of the theory of relativity, which provides new insights into physics.
- 😀 A postulate is an assumption considered true without proof, which forms the basis for further study in physics.
- 😀 Classical mechanics addresses objects in low-speed conditions, while special relativity is needed for objects moving near the speed of light.
- 😀 The concept of relativity includes Newtonian relativity and special relativity, which are based on Galileo's and Lorentz's transformations, respectively.
- 😀 Galileo's transformation assumes that velocity is relative, while space and time are absolute.
- 😀 Lorentz's transformation, fundamental to special relativity, asserts that the speed of light is constant and space and time are relative.
- 😀 The theory of relativity is important for understanding the properties of objects moving at high speeds and has applications in various areas of physics, including length contraction, time dilation, and energy-mass equivalence.
Q & A
What is the main focus of the script?
-The script discusses the theory of relativity, focusing on both classical mechanics and special relativity, especially in relation to objects with speeds approaching the speed of light.
What is the speed of light mentioned in the script?
-The speed of light is approximately 3 × 10^8 meters per second.
What distinction does the script make between macroscopic and microscopic objects?
-Macroscopic objects are those visible to the naked eye and move at speeds much slower than the speed of light, while microscopic objects like atoms and subatomic particles can move at speeds close to the speed of light.
Why are Newton's laws insufficient for microscopic objects?
-Newton's laws cannot accurately explain phenomena involving microscopic objects moving at speeds close to the speed of light, which is where special relativity comes into play.
What is a postulate according to the script?
-A postulate, according to the script, is an assumption that is accepted as true without needing proof. In the case of relativity, Einstein's postulates are the foundation of the theory.
How does classical mechanics differ from the theory of relativity?
-Classical mechanics is applicable to macroscopic objects with speeds much slower than the speed of light, while the theory of relativity addresses phenomena at speeds approaching the speed of light and microscopic scales.
What are the two main transformations discussed in the theory of relativity?
-The two main transformations are Galileo's transformation, which assumes relative speed while treating space and time as absolute, and Lorentz's transformation, where the speed of light is absolute and space and time are relative.
What is the significance of Lorentz's transformation in special relativity?
-Lorentz's transformation is crucial in special relativity because it explains how time and space are affected by speeds close to the speed of light, resulting in phenomena like time dilation and length contraction.
What are some of the key topics covered in special relativity, as mentioned in the script?
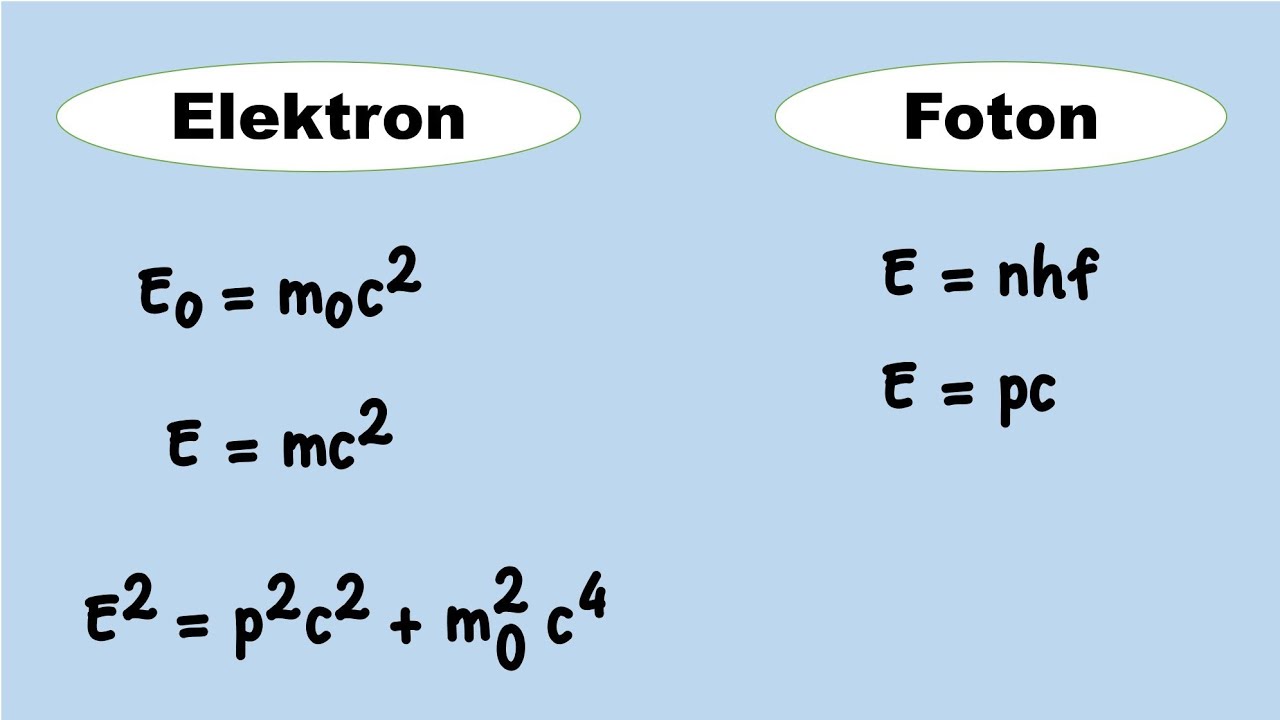
-Key topics in special relativity include length contraction, time dilation, mass-energy equivalence, relativistic velocity addition, and the conservation of relativistic energy and momentum.
What limitation is mentioned regarding the theory of relativity?
-The theory of relativity is limited in that it applies only to inertial reference frames, which are either at rest or moving at a constant velocity along a straight line.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード関連動画をさらに表示

MASSA, MOMENTUM DAN ENERGI RELATIVISTIK | Relativitas Einstein - Fisika Kelas 12

F278-Postulat Einstein dan konsep kecepatan relativistik,relativitas khusus

Teoria relativităţii pe înţelesul tuturor - 2
Konsep Dasar Fisika Modern-Kuantum

simplifying einstein's relativity

Theory of relativity explained in 7 mins
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
