sistem pertahanan tubuh non spesifik internal - imun lapisan ke 2 bab sistem imun kelas 11 biologi
Summary
TLDRThis educational video explores the second layer of the body's immune defense system, focusing on non-specific internal immunity. It explains the roles of various immune cells such as phagocytes (neutrophils, monocytes, macrophages, dendritic cells) and non-phagocytes (basophils, mast cells, natural killer cells) in defending the body against pathogens. Additionally, the video delves into the role of defense proteins, including cytokines and complement proteins, in enhancing immune responses. The video also touches on the importance of inflammation reactions, and encourages viewers to subscribe for more educational content.
Takeaways
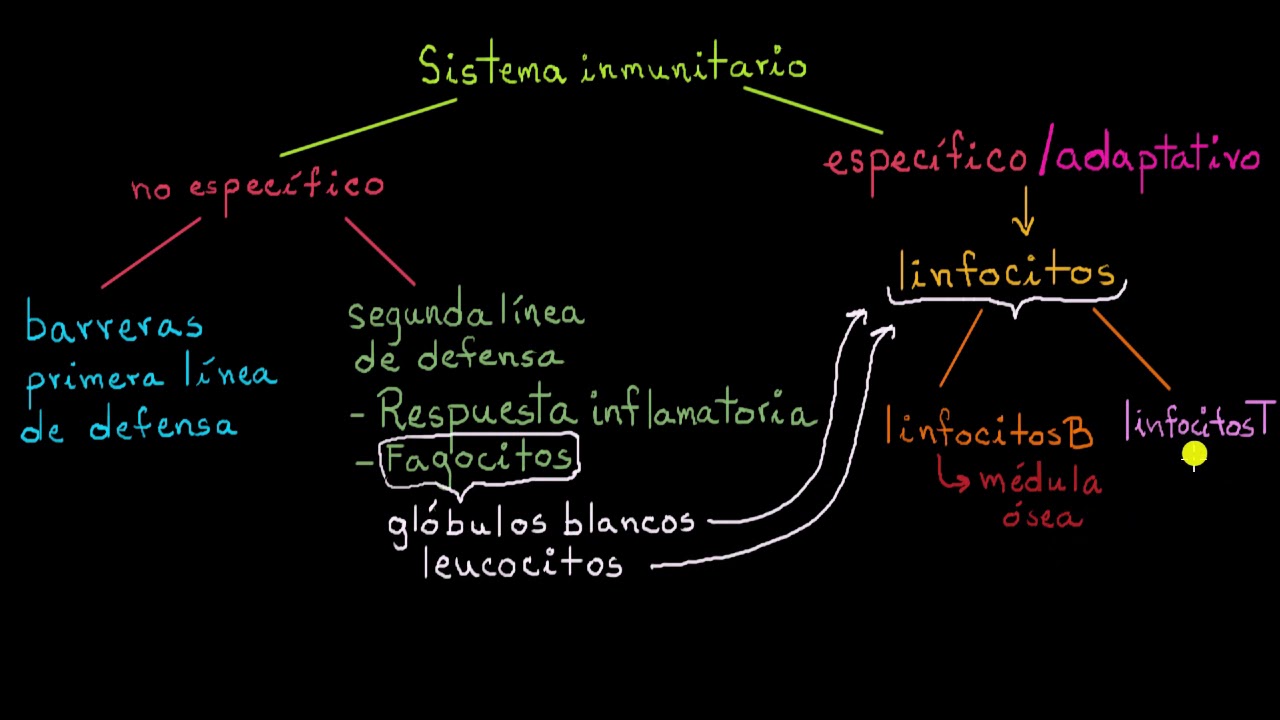
- 😀 The immune system has two main types of defense layers: external (non-specific) and internal (non-specific).
- 😀 External immunity prevents and attacks foreign particles outside the body, while internal immunity targets invaders already inside the body.
- 😀 Phagocytes are key components of internal immunity, as they ingest foreign particles or microbes through a process called phagocytosis.
- 😀 Different types of phagocytes include neutrophils, monocytes, macrophages, dendritic cells, and eosinophils, each with specific roles in fighting pathogens.
- 😀 Neutrophils are the most abundant phagocytes, circulating in the blood and responding quickly to infection.
- 😀 Monocytes can transform into macrophages once they enter tissues, where they continue to fight invaders.
- 😀 Dendritic cells are specialized for presenting antigens to T-cells, helping activate the adaptive immune response.
- 😀 Eosinophils target multicellular parasites and play a role in allergic responses, but their phagocytic activity is less significant.
- 😀 Non-phagocytic cells, like basophils, mast cells, and natural killer (NK) cells, do not ingest pathogens but release substances to kill or neutralize them.
- 😀 Proteins like cytokines and complement proteins are critical in internal immune defense, with roles in signaling, inflammation, and pathogen elimination.
Q & A
What is the primary focus of the video?
-The video primarily focuses on the second layer of the body's non-specific immune defense mechanisms, which includes internal defense against pathogens that have already entered the body.
How does the internal non-specific immune defense differ from the external defense?
-The internal non-specific immune defense targets and eliminates pathogens that have already entered the body, while the external defense prevents pathogens from entering in the first place.
What are the main components of the internal non-specific immune defense?
-The main components are phagocytic cells, non-phagocytic cells, and defense proteins, including cytokines and complement proteins.
What is the role of phagocytic cells in the immune response?
-Phagocytic cells, such as neutrophils, monocytes, and macrophages, engulf and digest foreign particles like bacteria, viruses, and debris through a process called phagocytosis.
What are neutrophils, and what is their function in the immune system?
-Neutrophils are the most common type of white blood cell in the bloodstream. They are essential for the body's defense against infection, especially bacterial infections, through phagocytosis.
What happens when monocytes migrate to tissues?
-Monocytes, after migrating to tissues, transform into macrophages, which are large cells that play a vital role in engulfing and digesting larger foreign particles.
What distinguishes dendritic cells from other phagocytic cells?
-Dendritic cells are specialized for antigen presentation. They capture pathogens and present them to T cells, which is crucial for initiating adaptive immunity.
What is the role of eosinophils in the immune response?
-Eosinophils primarily combat multicellular parasites and engage in phagocytosis, although their phagocytic activity is less significant than other cells like neutrophils.
What is the function of non-phagocytic cells like basophils and mast cells?
-Non-phagocytic cells, such as basophils and mast cells, release substances like histamine and heparin that play roles in allergic reactions, inflammation, and immune responses against parasites.
How do natural killer (NK) cells identify abnormal cells?
-NK cells identify and kill infected or abnormal cells by detecting the absence of MHC class I molecules on their surface, which distinguishes them from normal cells.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード関連動画をさらに表示

biologi bab sistem imun - Reaksi inflamasi sistem pertahanan tubuh. kelas 11 semester 2

SISTEM PERTAHANAN TUBUH - BIOLOGI KELAS 11 SMA

Sistem pertahanan tubuh non spesifik eksternal. sistem pertahanan tubuh lapis pertama. biologi SMA

Sistem Pertahanan Tubuh : (1) Pertahanan Eksternal dan Internal BIOLOGI 11 SMA

Respon imun bawaan: Proses Inflamasi
Tipos de respuesta inmune: Innata y adaptativa, humoral vs. celular | Khan Academy en Español
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
