UAD - Kuliah Online 1475530 Karakterisasi Material Lanjut (Lecture 2a - part 1)
Summary
TLDRThis video provides a comprehensive overview of spectroscopy and spectrophotometry, focusing on how light interacts with matter. It explains the three main types of interaction—absorption, reflection, and transmission—and how these principles are applied in a spectrophotometer. Key components such as light sources, monochromators, sample holders, and detectors are discussed, along with the importance of reference and blank samples for accurate measurements. The video also highlights the practical applications of spectrophotometry in various scientific fields, such as chemical analysis and biomedical testing.
Takeaways
- 😀 Spectroscopy is the study of light-matter interactions, focusing on how electromagnetic waves interact with material across specific wavelength ranges.
- 😀 The three main types of interactions in spectroscopy are absorbance, transmission, and reflection.
- 😀 In spectrophotometry, light passes through a sample and is detected after being transmitted or absorbed, with the device measuring these interactions.
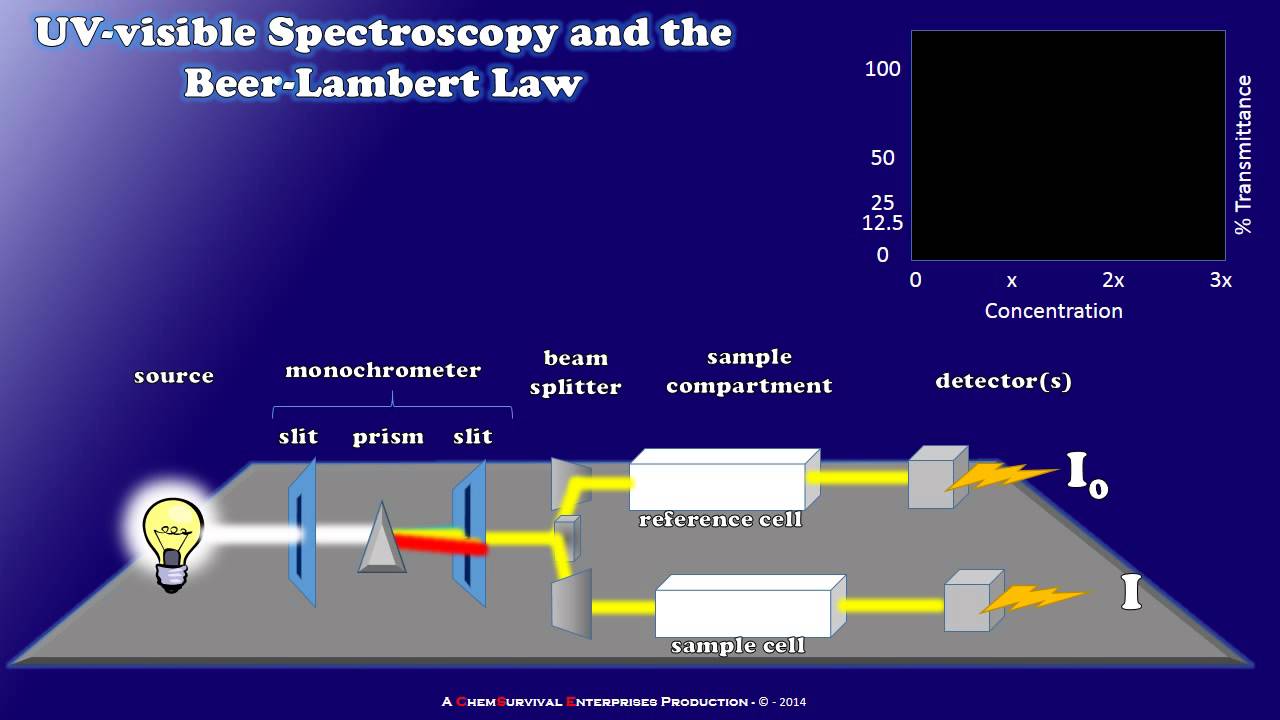
- 😀 The spectrophotometer includes a light source, monochromator, sample holder (cuvette), and detector to perform measurements.
- 😀 Different light sources such as tungsten (for visible light) and deuterium (for UV light) are used in spectrophotometry.
- 😀 A monochromator is used to isolate specific wavelengths of light from a polychromatic light source, enabling precise measurements.
- 😀 Quartz cuvettes are used for UV-visible measurements because they do not absorb in the UV range, ensuring accurate transmission data.
- 😀 A blank sample is essential for calibration in spectrophotometry, as it helps account for the transmission properties of the solvent or container material.
- 😀 Detectors in spectrophotometers measure transmitted light and convert it into an electrical signal for further analysis.
- 😀 Different materials and sample holders are used for specific applications, with considerations for transmission properties across the UV, visible, and infrared regions.
Q & A
What is the main principle behind spectroscopy?
-Spectroscopy is based on the interaction between light (electromagnetic waves) and matter. This interaction can take three primary forms: absorption, reflection, and transmission. These interactions allow us to analyze materials by studying how they respond to different wavelengths of light.
Why is transmission preferred over absorbance in spectrophotometric measurements?
-Transmission is often preferred because it is easier to measure compared to absorbance. While both methods provide valuable information, transmission directly measures the light passing through the sample, making it simpler to quantify.
What is a spectrophotometer, and what are its key components?
-A spectrophotometer is an instrument used to measure the amount of light absorbed or transmitted by a sample. Its key components include the light source, monochromator (which separates light into different wavelengths), and detector (which measures the transmitted light).
What is the role of the monochromator in a spectrophotometer?
-The monochromator's role is to separate light from the source into individual wavelengths, allowing the spectrophotometer to focus on a specific range of wavelengths when measuring a sample's response.
How does a detector work in a spectrophotometer?
-The detector in a spectrophotometer measures the intensity of light that has passed through the sample. It works on the principle of the photoelectric effect, where absorbed light generates a current or voltage proportional to the light intensity.
Why is it necessary to use a reference sample in spectrophotometric measurements?
-A reference sample (or blank) is used to account for any light absorbed or transmitted by the solvent, cuvette, or other components, ensuring that only the light absorbed by the sample is measured.
What types of light sources are typically used in spectrophotometers?
-Common light sources in spectrophotometers include incandescent lamps (for visible light), deuterium lamps (for UV light), and tungsten lamps (for infrared light). The choice of light source depends on the desired wavelength range for the measurement.
What are the key factors to consider when selecting a cuvette for a spectrophotometric measurement?
-The key factors when selecting a cuvette include the material of the cuvette (e.g., quartz, glass) and its transparency to the specific wavelength range being measured. For UV measurements, quartz is typically used, as it allows UV light to pass through without significant absorption.
How does a spectrophotometer measure absorbance or transmission of a sample?
-A spectrophotometer measures absorbance or transmission by comparing the intensity of light that passes through the sample (transmission) to the initial intensity of light. The difference between these intensities gives a measure of how much light the sample absorbed or transmitted.
Why is the detection of very small concentrations or trace elements important in spectrophotometry?
-Spectrophotometry is crucial for detecting small concentrations or trace elements because it allows for highly sensitive measurements. This is especially useful in fields like biochemistry, environmental science, and pharmaceuticals, where detecting even minute quantities of a substance can be significant.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード関連動画をさらに表示

Prinsip dan Instrumentasi Spektrofotometer UV-Vis
How a Simple UV-visible Spectrophotometer Works

Introduction to spectroscopy | Intermolecular forces and properties | AP Chemistry | Khan Academy
UAD - Kuliah Online 1475530 Karakterisasi Material Lanjut (Lecture 2a - part 1)

Chemistry Class 12 | Chapter 12 | Topic 3b | UV-VIS Spectroscopy | in urdu | tutoria.pk

Spektroskopi Raman
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
