Gerak Relatif: Konsep, Rumus, dan Contoh
Summary
TLDRThis video explores the concept of relative motion, explaining how movement is always observed relative to a specific reference point. It covers real-world examples, such as the movement of vehicles (a red car and blue bus) and a boat moving in a river with a current. The video delves into the calculations of relative velocity using vector addition, showing how different reference frames can affect the perceived speed and direction of objects. The video serves as a practical introduction to kinematics, ideal for understanding relative motion in everyday scenarios.
Takeaways
- 😀 Relative motion means that an object's velocity can vary depending on the observer's frame of reference.
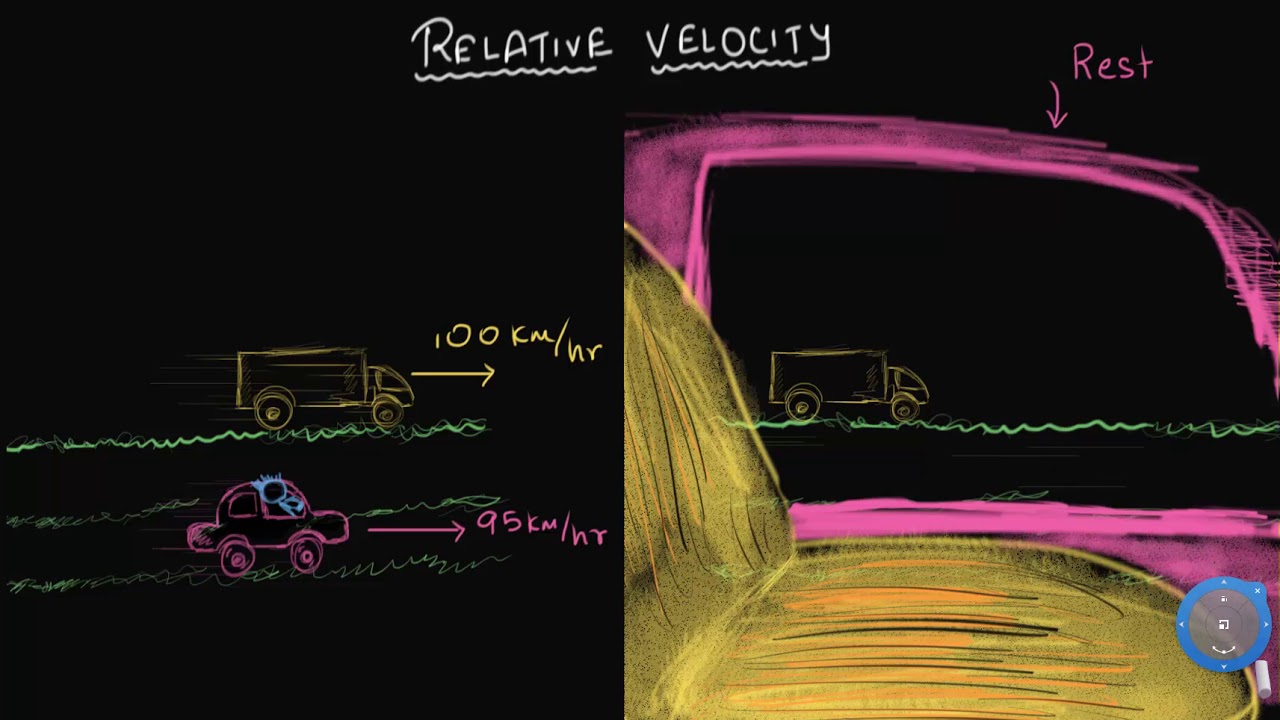
- 🚗 A person standing on the ground sees a red car moving at 50 km/h and a blue bus moving at 40 km/h.
- 🚙 If the observer is in the red car, they will see the blue bus moving backward because their own motion makes it appear slower.
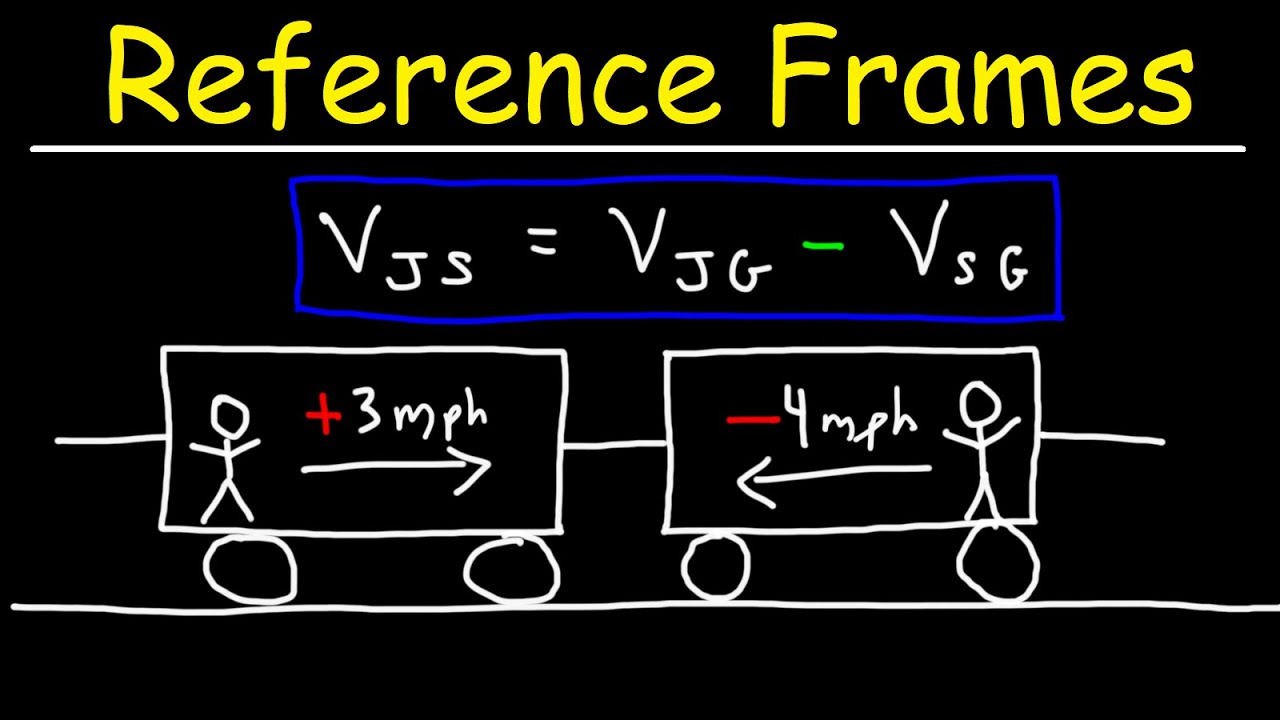
- 📏 The formula for relative velocity is: v21 = v2 + v1 (relative velocity of object 2 with respect to object 1).
- 🧭 When two objects move in the same direction, the relative velocity between them is found by subtracting their speeds (e.g., 50 km/h - 40 km/h = 10 km/h).
- 🌊 A boat moving on a river experiences two components of velocity: one along the river's flow and one perpendicular to it.
- 🛶 When calculating the boat's velocity relative to an observer on land, vector addition is used to combine the two components of velocity.
- ⚡ The relative motion concept applies to many real-life scenarios, such as vehicles moving on roads and boats moving on rivers.
- 📊 The relative velocity formula allows us to calculate how fast one object appears to move relative to another object in different reference frames.
- 🎓 The speaker encourages viewers to stay tuned for more advanced explanations of vector addition and relative motion in future videos.
Q & A
What is the concept of relative motion as discussed in the video?
-Relative motion refers to the idea that motion is observed differently depending on the observer's point of reference. For example, a person sitting in a bus might appear to be stationary from the perspective of another person inside the bus, but in motion relative to an observer standing outside the bus.
How does the observer's reference point affect the perception of motion?
-An observer's reference point determines how motion is perceived. If the observer is on the ground, they see a vehicle moving at a certain speed. However, if the observer is inside a moving vehicle, they may perceive the relative speed of another vehicle differently, depending on whether it's moving faster or slower relative to their own movement.
What is the speed of the first car relative to an observer on the ground in the video?
-The speed of the first car (the red car) relative to an observer on the ground is 50 km/h, as stated in the video.
How is the speed of the second vehicle, the blue car, calculated relative to the observer on the ground?
-The speed of the second vehicle (the blue car) relative to an observer on the ground is 40 km/h, as mentioned in the video.
How do you calculate the speed of the second vehicle from the perspective of someone inside the first vehicle?
-To calculate the speed of the second vehicle relative to someone inside the first vehicle, you use the formula: v21 = v2t + v1t, where v2t is the speed of the second vehicle relative to the ground, and v1t is the speed of the first vehicle relative to the ground. In this case, v2t is 40 km/h, and v1t is -50 km/h, resulting in a relative speed of -10 km/h.
What does a negative relative speed indicate in this context?
-A negative relative speed indicates that the second vehicle (the blue car) is moving in the opposite direction from the perspective of someone inside the first vehicle (the red car). In other words, the second vehicle appears to be moving backward or away from the observer inside the first vehicle.
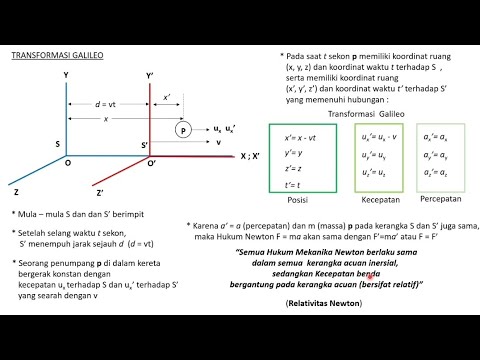
How does the relative motion of a boat on a river differ from the motion of vehicles on land?
-In the case of a boat on a river, the boat's motion is influenced by the current of the water. While the person inside the boat might perceive their movement relative to the boat itself (moving perpendicular to the current), an observer on the shore will see a combination of the boat's movement and the current's effect, resulting in a different trajectory.
What formula is used to calculate the relative velocity of a boat with respect to an observer on land?
-The formula for calculating the relative velocity of a boat with respect to an observer on land is: vP/L = vP/A + vA/L, where vP/L is the velocity of the boat relative to the land, vP/A is the velocity of the boat relative to the water, and vA/L is the velocity of the water (current) relative to the land.
What does the use of vectors in relative motion calculations help achieve?
-The use of vectors in relative motion calculations helps to account for the direction and magnitude of the velocities involved. By combining the velocity components in different directions (e.g., along the x and y axes), it is possible to determine the resultant velocity of an object from different reference points.
Why is the concept of relative motion important in understanding real-world motion scenarios?
-The concept of relative motion is crucial because in real-world scenarios, objects often appear to move differently depending on the observer's position. Whether it's a car moving along a road, a boat moving through water, or airplanes flying through the air, understanding relative motion allows for accurate predictions and analyses of how objects interact with each other in various contexts.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード関連動画をさらに表示
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)