Transistor Biasing: What is Q-point? What is Load Line? Fixed Bias Configuration Explained
Summary
TLDRIn this video, the basics of transistor biasing are explained, focusing on its role in amplifier circuits. The process of biasing a BJT (Bipolar Junction Transistor) is explored, with a specific emphasis on the common emitter configuration. Key concepts like the operating point (Q-point) and load line are introduced, showing how proper biasing ensures optimal amplification without distortion. The importance of temperature stability in maintaining the Q-point is discussed, along with the fixed-bias configuration as a common method for setting the operating point. The video concludes with a preview of other biasing techniques for more stable performance.
Takeaways
- 😀 **Transistor Biasing:** The process of applying a DC voltage to a transistor (BJT) to set its operating conditions, allowing it to amplify AC signals effectively.
- 😀 **Importance of Biasing:** Without proper biasing, a BJT will not amplify an input signal, as it needs a DC supply to operate in the active region.
- 😀 **Common Emitter Configuration:** The most widely used transistor configuration for amplification, where the base-emitter junction is forward biased and the collector-base junction is reverse biased.
- 😀 **Q-point (Operating Point):** The point on the output characteristics curve where the transistor is operating, determined by the voltage Vce and current Ic, which should be in the active region for proper amplification.
- 😀 **Active Region Biasing:** Proper biasing keeps the transistor in the center of the active region, ensuring signal amplification without distortion.
- 😀 **Saturation and Cut-off Regions:** If the transistor is biased near the saturation or cut-off regions, it leads to non-linear distortion of the amplified signal.
- 😀 **Temperature Stability:** The operating point may change with temperature due to variations in the transistor's parameters, such as current gain and saturation current.
- 😀 **Stability Factor:** Measures how the operating point shifts with temperature variations, highlighting the importance of designing a stable biasing circuit.
- 😀 **Fixed-Bias Configuration:** A simple biasing circuit where the base resistor sets a fixed base current (Ib), defining the collector current (Ic) and the voltage Vce.
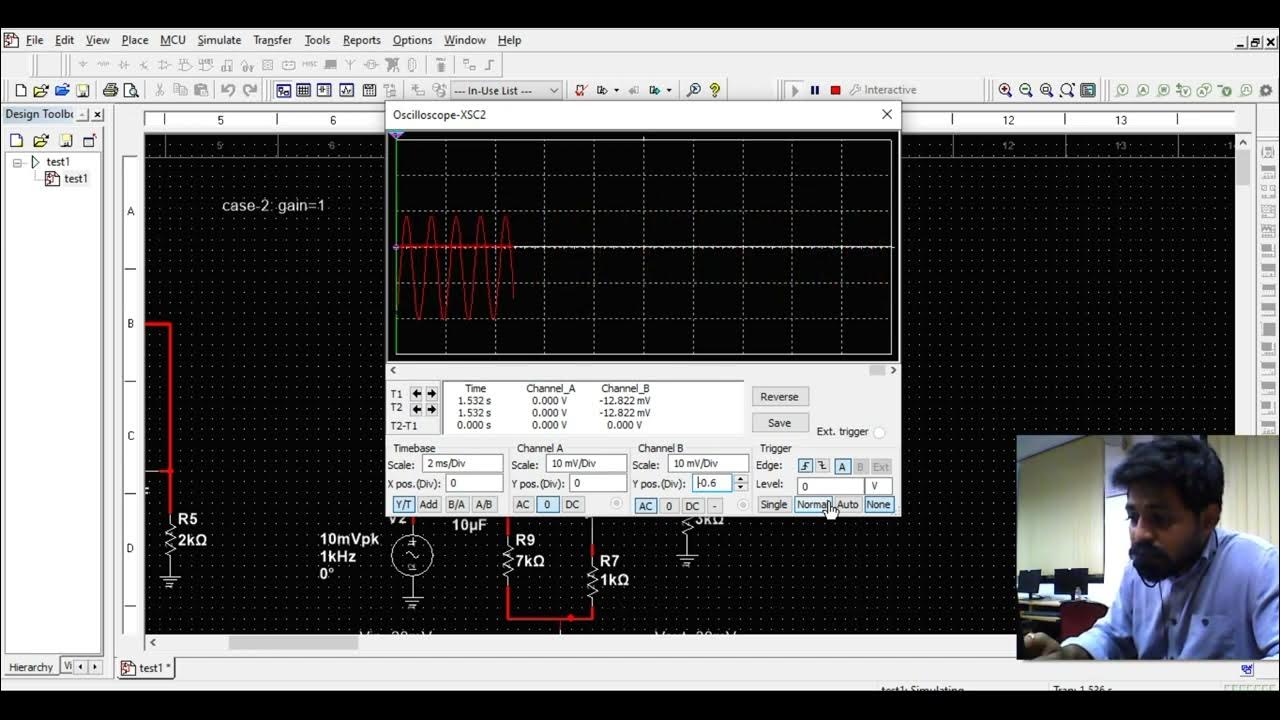
- 😀 **Load Line and Operating Point:** The load line, defined by the collector resistor (Rc), represents all possible operating points for a given Vcc. Changes in Rc, Vcc, or Ib affect the operating point.
- 😀 **Effect of Beta Variation:** A change in the transistor's current gain (β) due to temperature or transistor replacement can significantly affect the operating point, leading to variations in the collector current and voltage Vce.
Q & A
What is transistor biasing and why is it necessary?
-Transistor biasing refers to the process of applying a DC voltage to a transistor to set the operating point. It is necessary for the transistor to function properly as an amplifier, enabling it to amplify an AC input signal by providing the required operating conditions.
What is the role of the Q-point in transistor biasing?
-The Q-point, or operating point, defines the transistor's operating voltage and current. It is crucial because it ensures the transistor is in the active region, where it can amplify signals without distortion.
What happens if the Q-point is set in the saturation or cutoff region?
-If the Q-point is set in the saturation or cutoff region, parts of the amplified signal may get clipped, leading to non-linear distortion in the output waveform. This is because the transistor cannot fully respond to the input signal within these regions.
How does the temperature affect the transistor's operating point?
-Temperature variations can alter the transistor's parameters, such as the current gain (beta) and reverse saturation current. This can cause shifts in the operating point, affecting the transistor's performance.
What is the stability factor in transistor biasing?
-The stability factor is a measure of how much the operating point changes with temperature. A well-designed biasing circuit aims to minimize this variation, maintaining stable performance across temperature fluctuations.
What is the fixed-bias configuration in transistor biasing?
-The fixed-bias configuration involves applying a DC base voltage through a resistor to set a fixed base current. This base current then controls the collector current. It is simple but less stable, as changes in temperature or transistor properties can shift the operating point.
What is the significance of the load line in the fixed-bias configuration?
-The load line represents the relationship between the collector current (Ic) and collector-emitter voltage (Vce) in the circuit, given specific values for the supply voltage (Vcc) and collector resistance (Rc). It shows the possible operating points of the transistor based on these parameters.
How does changing the base resistor (Rb) affect the operating point?
-Changing the base resistor (Rb) alters the base current (Ib), which in turn shifts the operating point along the load line. An increase in Ib moves the operating point upwards, while a decrease moves it downwards.
What happens when the transistor's current gain (beta) varies?
-A change in the transistor's current gain (beta) significantly affects the collector current (Ic) and, consequently, the operating point. For example, if beta decreases, the collector current drops, and if beta increases, the collector current rises, shifting the operating point accordingly.
Why is it important to ensure a stable operating point in transistor amplifiers?
-A stable operating point is essential for consistent amplifier performance. If the operating point shifts due to temperature changes or transistor variations, the amplifier's output may become distorted or less effective, reducing signal fidelity and amplification quality.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード関連動画をさらに表示
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)