What is metallic glass? - Ashwini Bharathula
Summary
TLDRMetallic glass is an innovative material that combines the best qualities of steel and plastic. Stronger than most metals and easily moldable like plastic, it offers a range of impressive applications, from sports equipment to electronics. Its unique atomic structure—amorphous rather than crystalline—gives it exceptional strength and resistance to corrosion. Though initially challenging to produce, advancements in manufacturing have led to the development of bulk metallic glasses (BMGs), which are thicker and more versatile. However, their high cost and brittleness prevent widespread use in large-scale infrastructure. The future of BMGs is promising as scientists work to overcome these limitations.
Takeaways
- 😀 Steel is strong but hard to shape, while plastic is easy to mold but lacks strength. The need for a material combining both strengths led to the creation of metallic glass.
- 😀 Metallic glass is a revolutionary material that is as strong as steel and as moldable as plastic, with a variety of potential applications.
- 😀 Unlike traditional metals, metallic glass has an amorphous atomic structure, which provides unique properties like enhanced strength and flexibility.
- 😀 Metallic glasses are resistant to corrosion and can be cast into complex shapes with mirror-like surfaces in a single molding step.
- 😀 The ability of metallic glass to store and release elastic energy makes it ideal for use in sports equipment like tennis racquets, golf clubs, and skis.
- 😀 Metallic glass is stronger than most metals and can withstand high amounts of force without getting bent or dented.
- 😀 Most metals are crystalline, but metallic glass lacks the regular atomic arrangement, which gives it its remarkable properties.
- 😀 The first metallic glass was made in 1960 from a gold and silicon alloy, but early versions were thin and impractical for most uses.
- 😀 Advances in metallic glass production, such as blending metals with different atomic sizes, have made it possible to create thicker bulk metallic glasses (BMGs).
- 😀 BMGs are still expensive and require high purity to avoid crystallization, which limits their large-scale use, but ongoing research aims to make them more affordable and durable for broader applications.
Q & A
What is metallic glass and why is it considered a breakthrough material?
-Metallic glass is a type of material with an amorphous atomic structure, meaning the atoms are randomly arranged, unlike most metals which have a crystalline structure. It is considered a breakthrough because it combines the strength of steel with the moldability of plastic, offering unique properties like high strength, resistance to corrosion, and the ability to store and release elastic energy.
How does metallic glass differ from traditional metals in terms of atomic structure?
-Traditional metals are crystalline, meaning their atoms are arranged in a regular, repeating pattern. In contrast, metallic glasses have an amorphous structure, where the atoms are randomly arranged, similar to the internal structure of a liquid. This lack of a regular atomic arrangement gives metallic glasses unique properties.
What are some practical applications of metallic glass?
-Metallic glasses are used in a variety of applications due to their unique properties. These include ultrasharp scalpels, strong electronics cases, sports equipment (such as tennis racquets, golf clubs, and skis), and components like hinges and screws. Their resistance to corrosion and ability to store elastic energy make them ideal for high-performance uses.
What is the main challenge in producing bulk metallic glasses (BMGs)?
-The main challenge in producing BMGs lies in their production cost and the need for high purity. BMGs are often made from expensive metals like palladium and zirconium, and any impurities can cause them to crystallize, losing their amorphous structure. This makes them expensive and difficult to use in large-scale applications.
How do metallic glasses compare to traditional metals in terms of strength and formability?
-Metallic glasses are much stronger than traditional metals, allowing them to withstand more force without getting bent or dented. Additionally, they are highly formable, capable of being molded into complex shapes with smooth, mirror-like surfaces, which is a property traditional metals often lack due to their crystalline structure.
What makes metallic glass particularly useful for sports equipment?
-Metallic glass is particularly useful for sports equipment due to its ability to store and release elastic energy efficiently. This makes materials like tennis racquets, golf clubs, and skis more durable and responsive. Additionally, its strength and resistance to wear make it ideal for high-performance sporting gear.
What is the process of creating metallic glass?
-Metallic glass is created by rapidly cooling molten metal at an extremely fast rate (a million degrees Kelvin per second) so that the atoms do not have time to arrange into a crystalline structure. This results in an amorphous solid with a random atomic structure, unlike traditional metals that crystallize as they cool.
Why do metallic glasses lack grain boundaries and what effect does this have?
-Metallic glasses lack grain boundaries, which are the weak points in crystalline metals where atoms are less orderly. The absence of grain boundaries makes metallic glasses stronger and less susceptible to corrosion, scratches, or other forms of damage, which is a major advantage over traditional metals.
What are the temperature-related properties of metallic glass?
-Metallic glasses are strong at room temperature, but they soften significantly when heated to a few hundred degrees Celsius. This allows them to be molded into different shapes. Upon cooling, they regain their strength, making them highly versatile in manufacturing processes.
Why aren't metallic glasses used in large-scale applications like bridges or cars yet?
-While metallic glasses have impressive properties, they are not yet widely used in large-scale applications due to their high production costs, which are mainly due to the use of expensive metals. Additionally, their brittleness under high stress makes them unsuitable for load-bearing applications like bridges or cars, though advancements in material toughness may change this in the future.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード関連動画をさらに表示
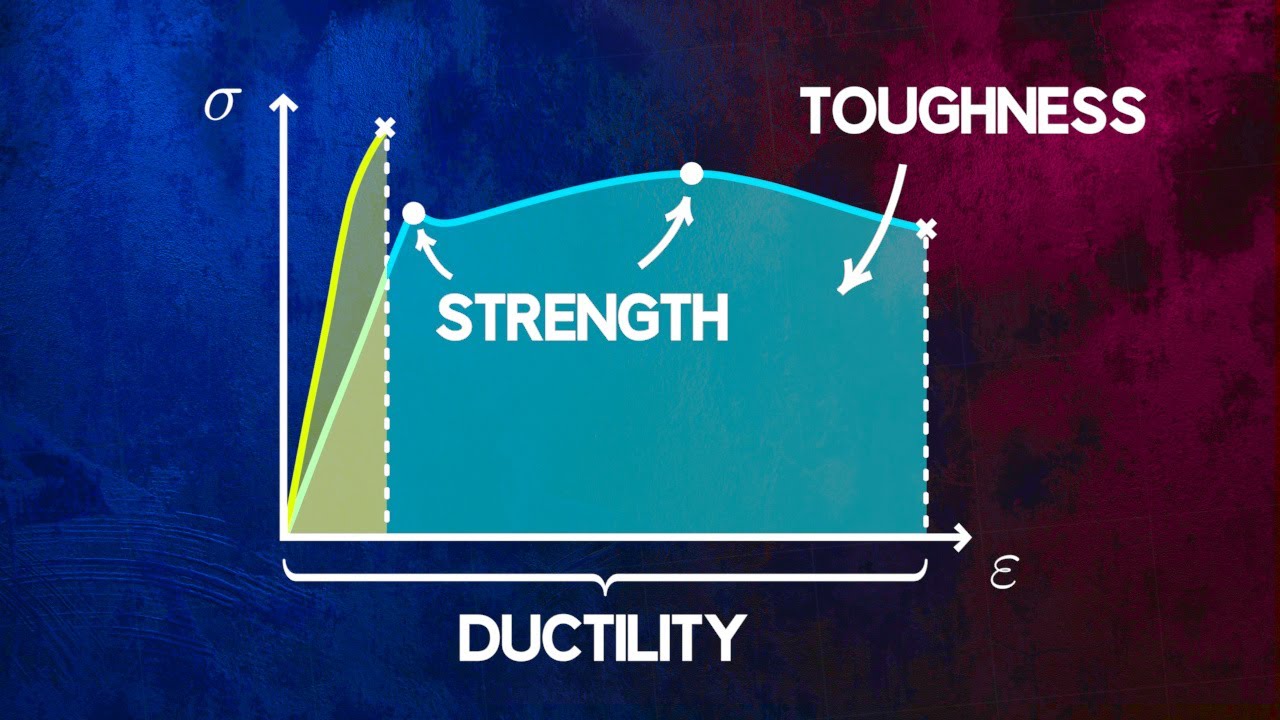
Understanding Material Strength, Ductility and Toughness

Teknologi Material dalam Arsitektur
How Recycling Works

GCSE Chemistry - Metallic Bonding #20

10 Toxic Kitchen Items You Should Declutter Immediately (what to do instead, part 2)

Why is it so hard to recycle plastic? - People Fixing the World, BBC World Service
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
