Oxidação e redução
Summary
TLDRIn this educational video, the instructor explains key concepts of oxidation and reduction (redox) reactions, focusing on how electron transfer alters the oxidation number (NOX) of elements. The video covers essential topics like oxidizing and reducing agents, the periodic table's influence on these reactions, and the role of free radicals in oxidative processes. Special attention is given to the concept of auto-redox reactions and the importance of antioxidants in combating free radical damage. The session is geared toward helping students understand these fundamental concepts and perform well in chemistry exams.
Takeaways
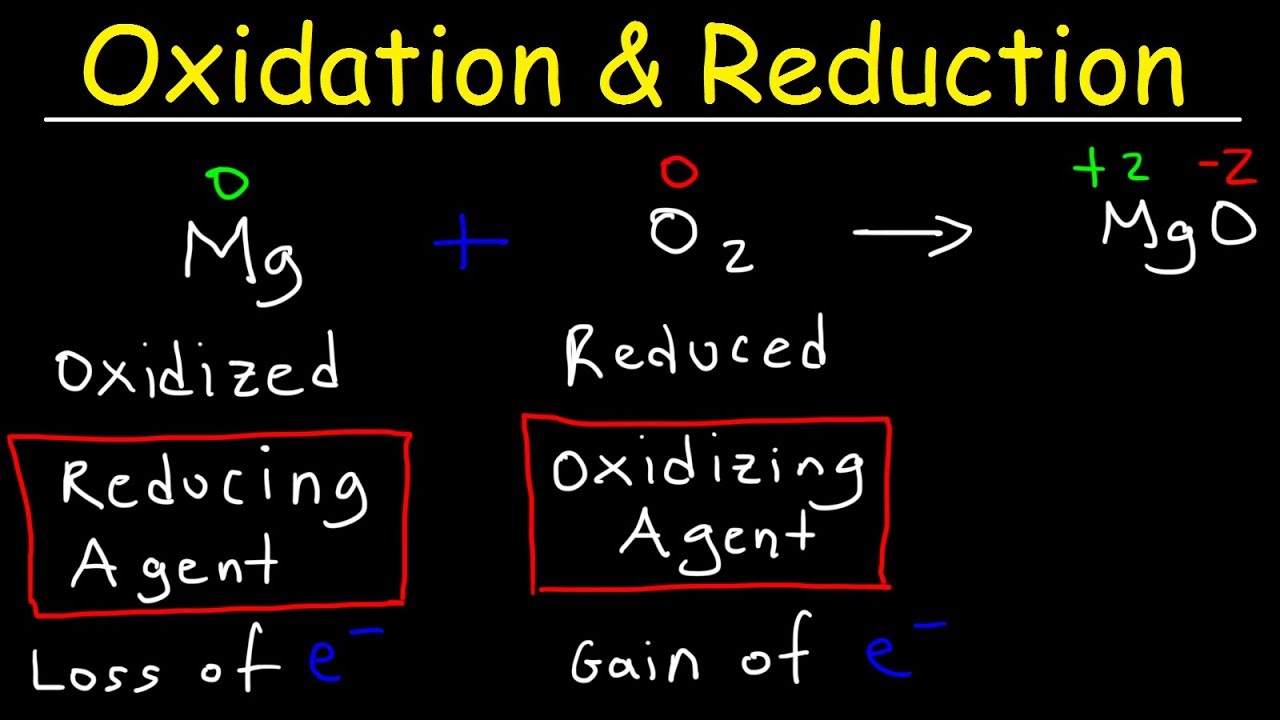
- 😀 **Oxidation** is the loss of electrons, resulting in an increase in oxidation number (Nox) and a more positive charge.
- 😀 **Reduction** is the gain of electrons, leading to a decrease in oxidation number (Nox) and a more negative charge.
- 😀 An **oxidizing agent** causes oxidation by accepting electrons and gets reduced in the process.
- 😀 A **reducing agent** causes reduction by donating electrons and gets oxidized in the process.
- 😀 To remember oxidation and reduction: **OIL RIG** - Oxidation Is Loss, Reduction Is Gain.
- 😀 Free radicals are highly reactive species with unpaired electrons and can damage cells. They seek electrons to stabilize themselves.
- 😀 **Antioxidants**, like vitamin C, neutralize free radicals by donating electrons, thus preventing oxidative damage.
- 😀 In a **disproportionation** (auto-redox) reaction, the same substance is both oxidized and reduced, like hydrogen peroxide.
- 😀 **Metals** tend to lose electrons and are thus **reducing agents**, while **non-metals** tend to gain electrons and act as **oxidizing agents**.
- 😀 The periodic table can help predict oxidation and reduction behavior: metals usually oxidize and are reducing agents, while non-metals reduce and are oxidizing agents.
Q & A
What is oxidation and how does it relate to the loss of electrons?
-Oxidation refers to the process of losing electrons. When an atom loses electrons, it becomes more positive, and its oxidation state (NOX) increases. This is because electrons carry negative charges, so losing them results in a more positively charged ion.
What is reduction, and how does it relate to the gain of electrons?
-Reduction is the process of gaining electrons. When an atom gains electrons, it becomes more negative, and its oxidation state (NOX) decreases. This is because the addition of negatively charged electrons makes the atom more negative.
How can you differentiate between an oxidizing agent and a reducing agent?
-An oxidizing agent causes oxidation by accepting electrons, and as a result, it undergoes reduction. A reducing agent causes reduction by donating electrons, and as a result, it undergoes oxidation.
What happens when a substance undergoes oxidation in terms of its electron behavior?
-When a substance undergoes oxidation, it loses electrons. This loss of electrons causes the substance to become more positive because it is losing negatively charged particles.
What is a radical free species, and why are they important in chemical reactions?
-A radical free species is an atom or molecule that has an unpaired electron. This unpaired electron makes the species highly reactive as it seeks to pair up with another electron. Radicals are crucial in many chemical processes, including oxidative damage in biological systems.
Why are antioxidants important for our health in relation to radical free species?
-Antioxidants are important because they neutralize free radicals by donating electrons to them, preventing the radicals from damaging cells. By doing so, antioxidants help to reduce oxidative stress and protect the body from various diseases.
What is the relationship between the periodic table and oxidation/reduction?
-In the periodic table, metals tend to lose electrons and undergo oxidation, making them reducing agents. Nonmetals, on the other hand, tend to gain electrons and undergo reduction, making them oxidizing agents. This relationship is due to the general trends in electron affinity and ionization energy across the table.
What does the term 'auto-redox' or 'disproportionation' refer to?
-Auto-redox or disproportionation occurs when the same substance undergoes both oxidation and reduction simultaneously. An example is hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), where the oxygen atoms in the molecule change their oxidation states during the reaction.
How can you identify a radical free species by examining the number of valence electrons?
-To identify a radical free species, sum the valence electrons of the atoms in the molecule. If the total number of electrons is odd, there is at least one unpaired electron, indicating a radical free species.
How does a metal behave in oxidation and reduction reactions?
-Metals typically undergo oxidation by losing electrons and becoming positively charged. Because they lose electrons, they are considered reducing agents, meaning they can cause other substances to undergo reduction by donating electrons.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード関連動画をさらに表示

[MASTER KIMIA SPM] KIMIA KSSM TING 5 : KESEIMBANGAN REDOKS

Número de Oxidação e Oxirredução - Brasil Escola

REAKSI REDOKS - SIMPLE KONSEP - KIMIA (Kursus Online Rp8.000 per BULAN : cek deskripsi)

Reaksi Redoks | Reduksi Oksidasi | Disproporsionasi | Kimia SMA

Reaksi Oksidasi dan Reduksi - Redoks- kimia kelas 10
Oxidation and Reduction Reactions - Basic Introduction
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
