Lorentz Transformation | Full Theory And Derivation | Subscribe | Like | Share
Summary
TLDRThe video discusses the concepts of reference frames and Lorentz transformation in physics. It explains how motion and observations vary between different frames, distinguishing between non-accelerated and accelerated frames. The discussion emphasizes the consistency of the speed of light in all inertial frames and introduces equations that describe these transformations. The video also covers practical examples, such as how light travel time changes across frames, and includes mathematical derivations to illustrate these points. The content ultimately highlights the significance of Lorentz transformation in ensuring the invariance of physical laws, essential for understanding Einstein's theory of relativity.
Takeaways
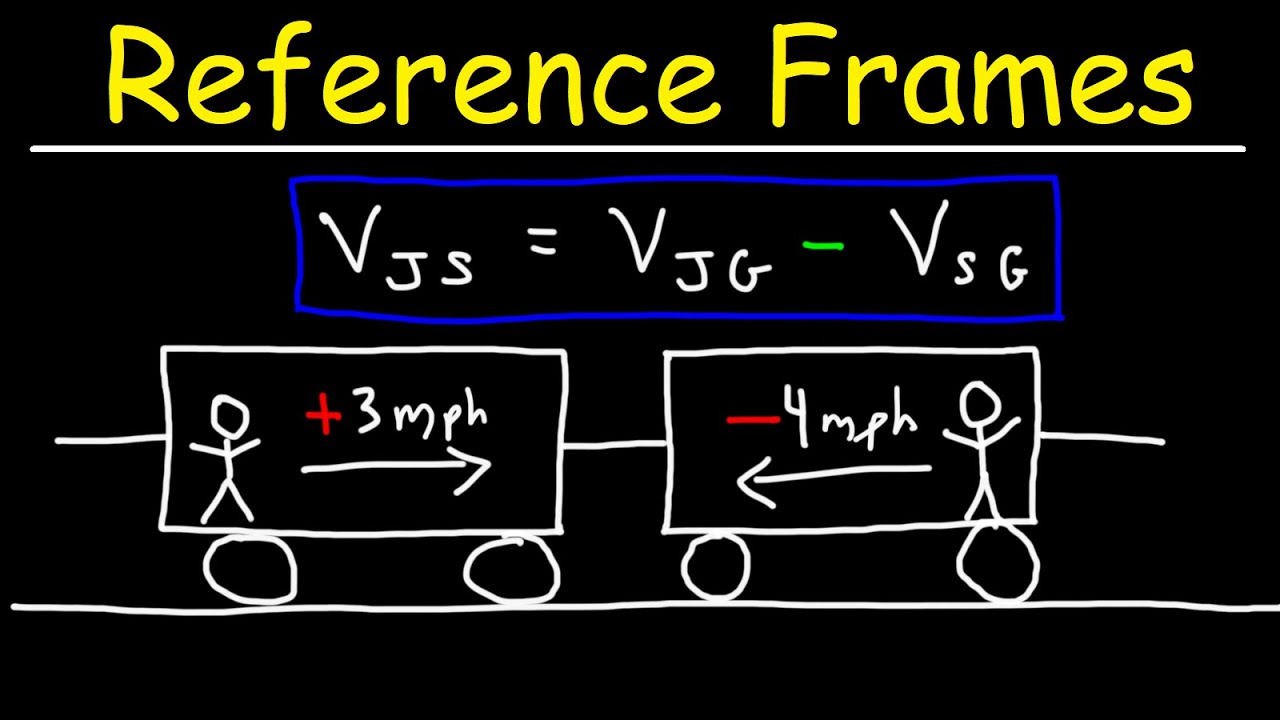
- 😀 A reference frame is a coordinate system used to measure the position and motion of objects.
- 😀 A virtual reference frame refers to an observational perspective where the frame is moving relative to other systems.
- 😀 If no external forces are applied, particles in a system exhibit uniform motion or remain stationary.
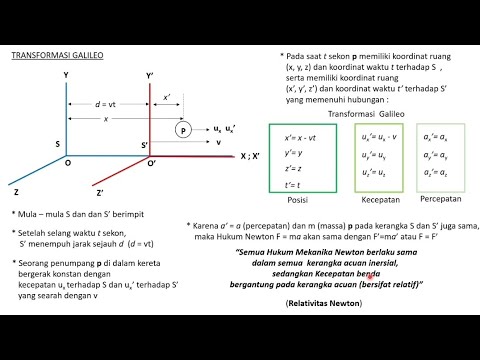
- 😀 The Lorentz transformation equations convert position and time from one reference frame to another, especially for high-velocity systems.
- 😀 The Lorentz factor (gamma) accounts for the effects of relativistic speeds on time and space.
- 😀 Special relativity ensures the laws of physics remain invariant across different inertial reference frames.
- 😀 The Lorentz transformation helps describe how objects behave at velocities close to the speed of light.
- 😀 A key Lorentz transformation equation is x' = γ(x - vt), where x and t are the position and time in the original frame.
- 😀 The Lorentz factor γ = 1 / √(1 - v²/c²) corrects for relativistic effects as the velocity approaches the speed of light.
- 😀 Using Lorentz transformation, time and space can be calculated from different reference frames, especially when dealing with light-speed motion.
Q & A
What is the main topic discussed in the script?
-The main topic of the script is loan transmission and the concept of reference frames in physics, particularly in the context of external forces and particle motion.
What does the term 'reference frame' mean in the context of the script?
-'Reference frame' refers to a perspective or coordinate system from which the position and motion of objects are observed. It is essential for understanding the behavior of particles or objects in different systems.
What is the significance of acceleration in relation to reference frames?
-Acceleration plays a crucial role in distinguishing between different types of reference frames. In non-accelerating frames, the motion of particles remains predictable, while in accelerated frames, forces such as velocity changes come into play.
What does it mean when the script mentions a 'virtual frame of reference'?
-A 'virtual frame of reference' refers to an imagined or hypothetical frame in which the motion of particles can be observed under ideal conditions, especially when external forces are absent.
How does the script explain the role of external forces in a system?
-The script explains that if no external force is applied to a system, the motion of particles within the system can be described using non-accelerated reference frames, meaning the particles' velocity remains constant.
What is the relationship between velocity and reference frames in the script?
-The script states that in non-accelerated reference frames, velocity remains constant. This concept is key in understanding how objects behave when observed from different frames of reference.
What role does the 'Lorentz transformation' play in the context of the script?
-The Lorentz transformation is used to convert the position and time coordinates of events between different inertial frames of reference, particularly when considering objects moving at high velocities close to the speed of light.
What is the importance of 'time dilation' in the context of light travel as mentioned in the script?
-Time dilation refers to the phenomenon where time is perceived differently depending on the velocity of the observer relative to the object in motion. The script mentions how light will take a different time to reach a destination depending on the observer’s reference frame.
How does the script approach the idea of transformation equations?
-The script discusses transformation equations as mathematical tools used to shift between different reference frames, allowing one to calculate the position and time of events from different perspectives in physics.
What conclusion does the script reach regarding invariance in reference frames?
-The script concludes that certain physical laws, such as those involving velocity and acceleration, remain invariant (unchanged) when moving between different reference frames, meaning the equations governing these processes hold true across different frames of reference.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード5.0 / 5 (0 votes)